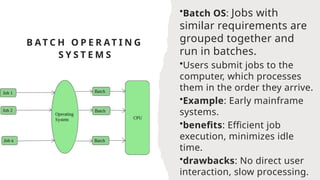
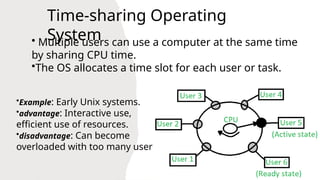
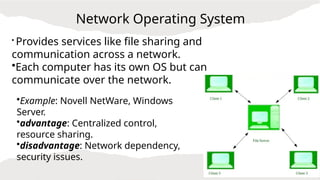
An operating system serves as the interface between software and hardware, managing resources and operations on a computer. There are various types of operating systems including batch, multi-programming, multi-tasking, time-sharing, distributed, network, and real-time systems, each with distinct benefits and drawbacks. Examples include Windows and Linux, with functionalities ranging from job scheduling to multi-user capabilities.