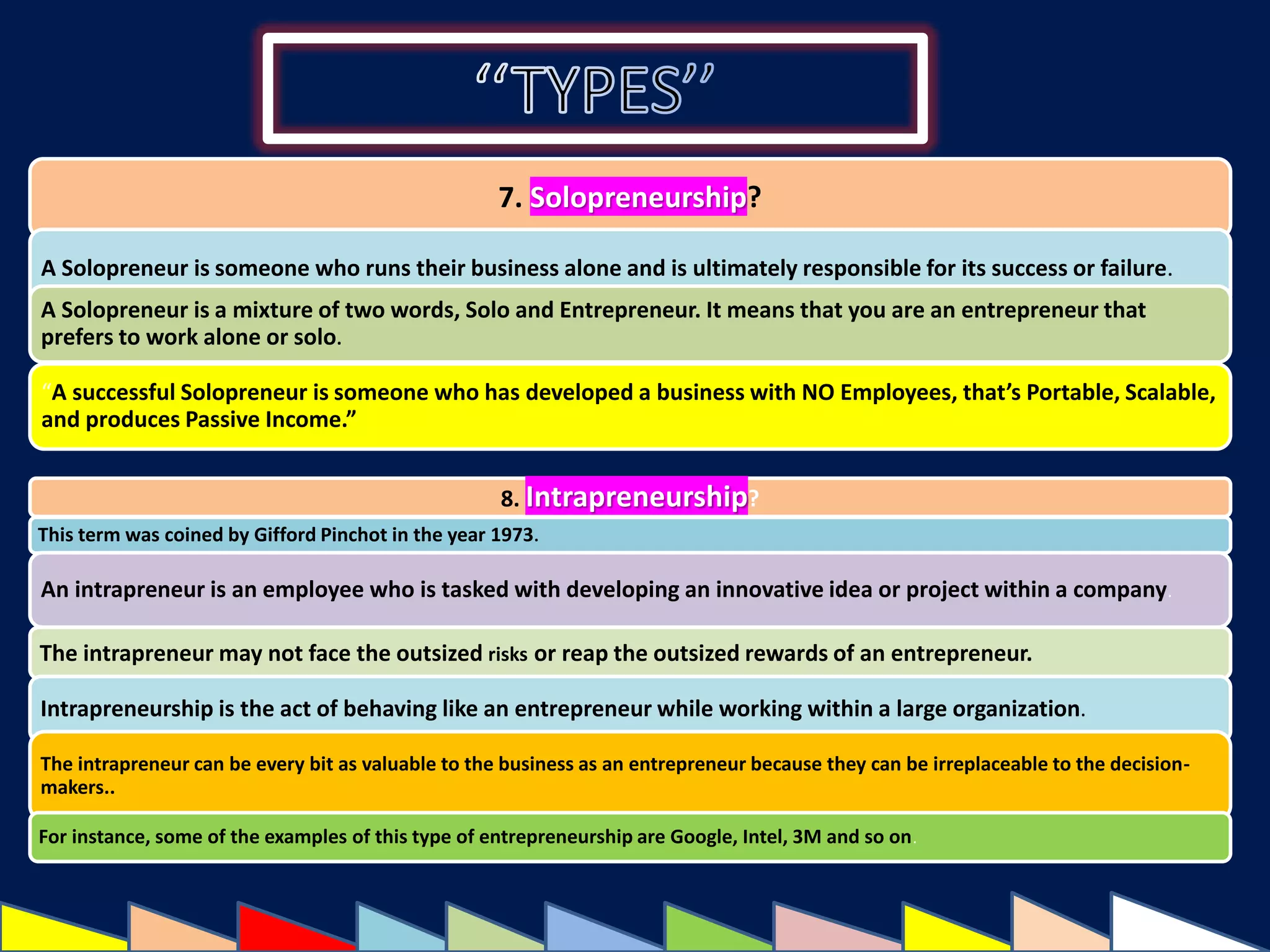
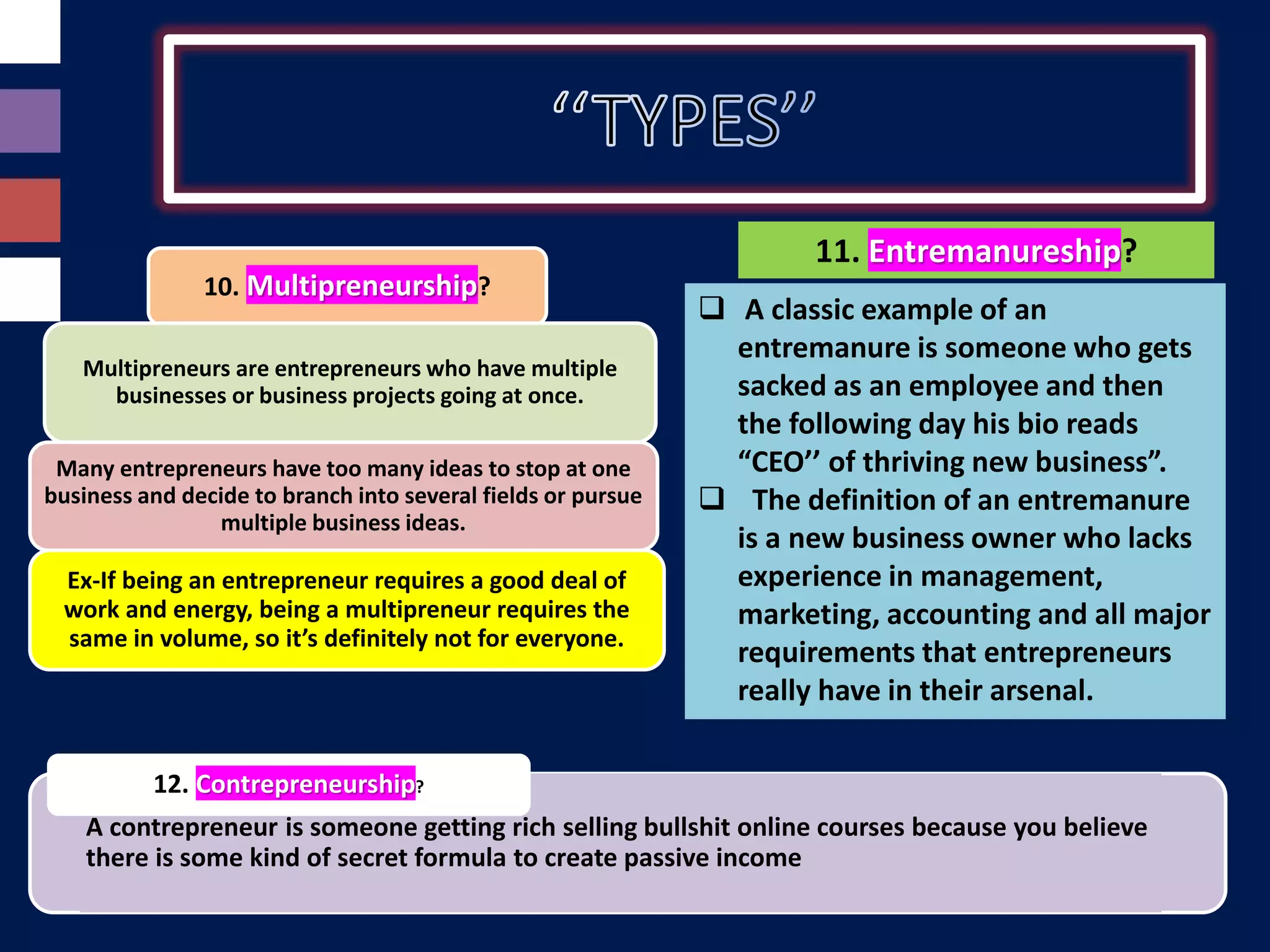
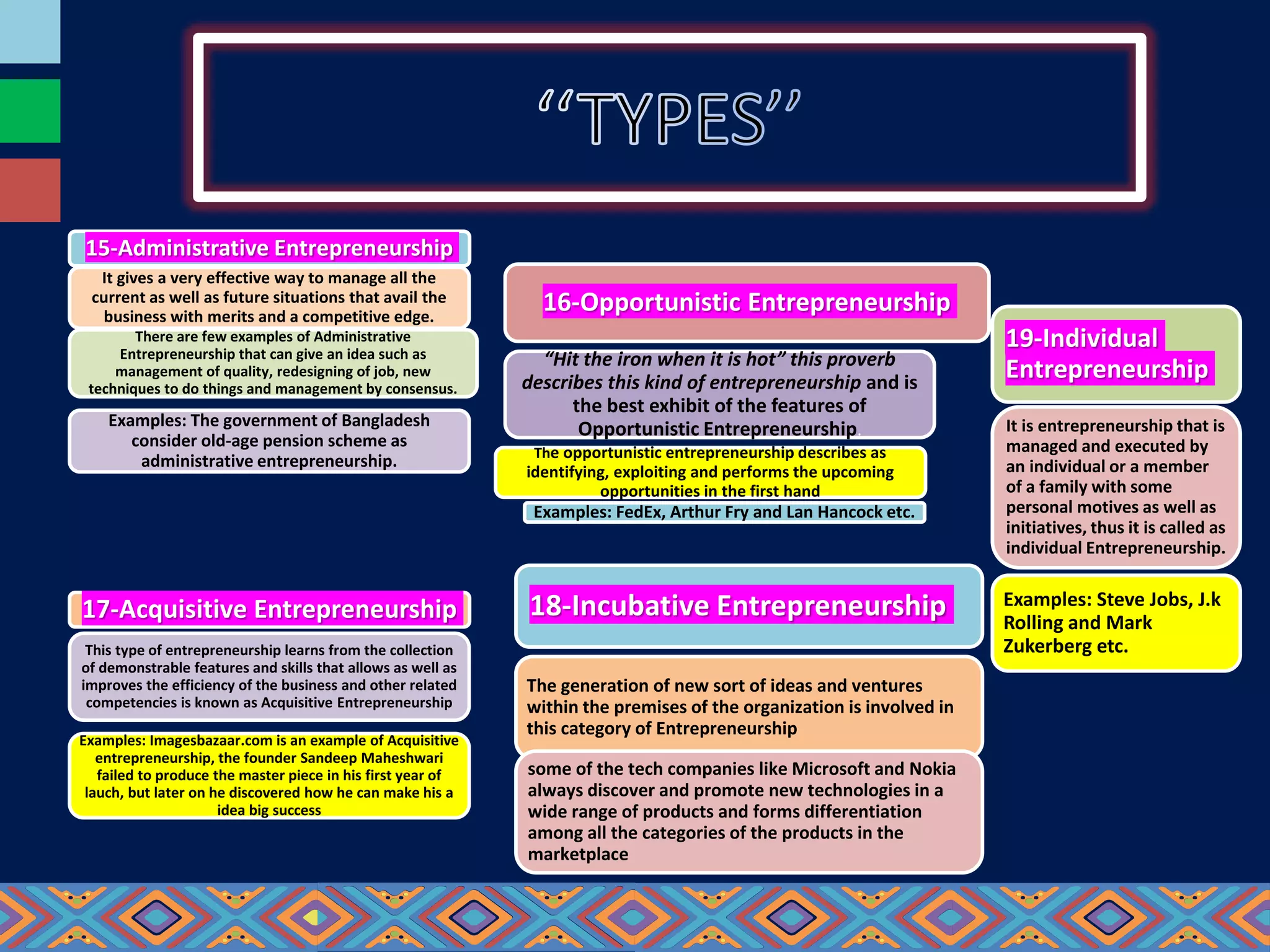
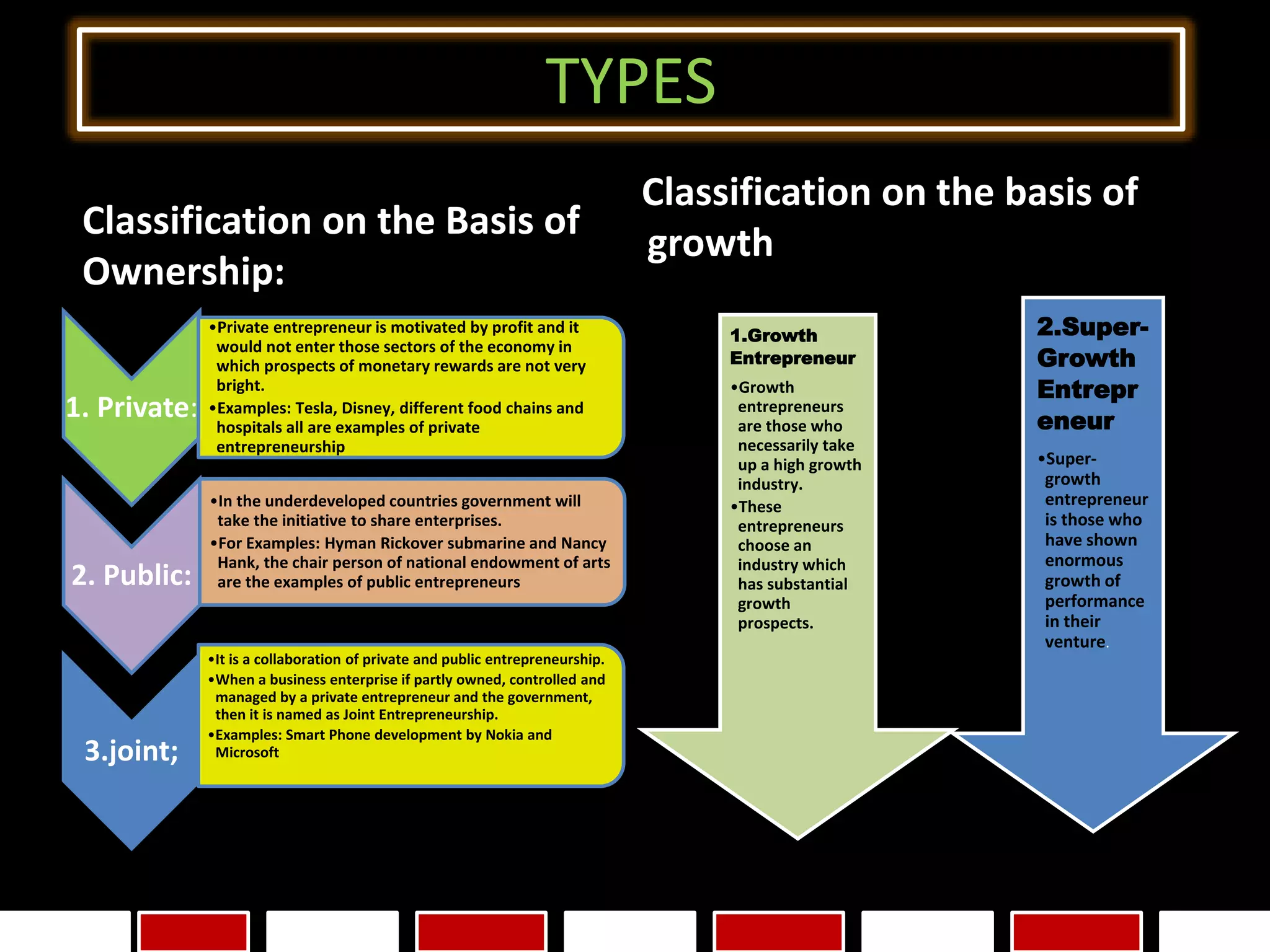
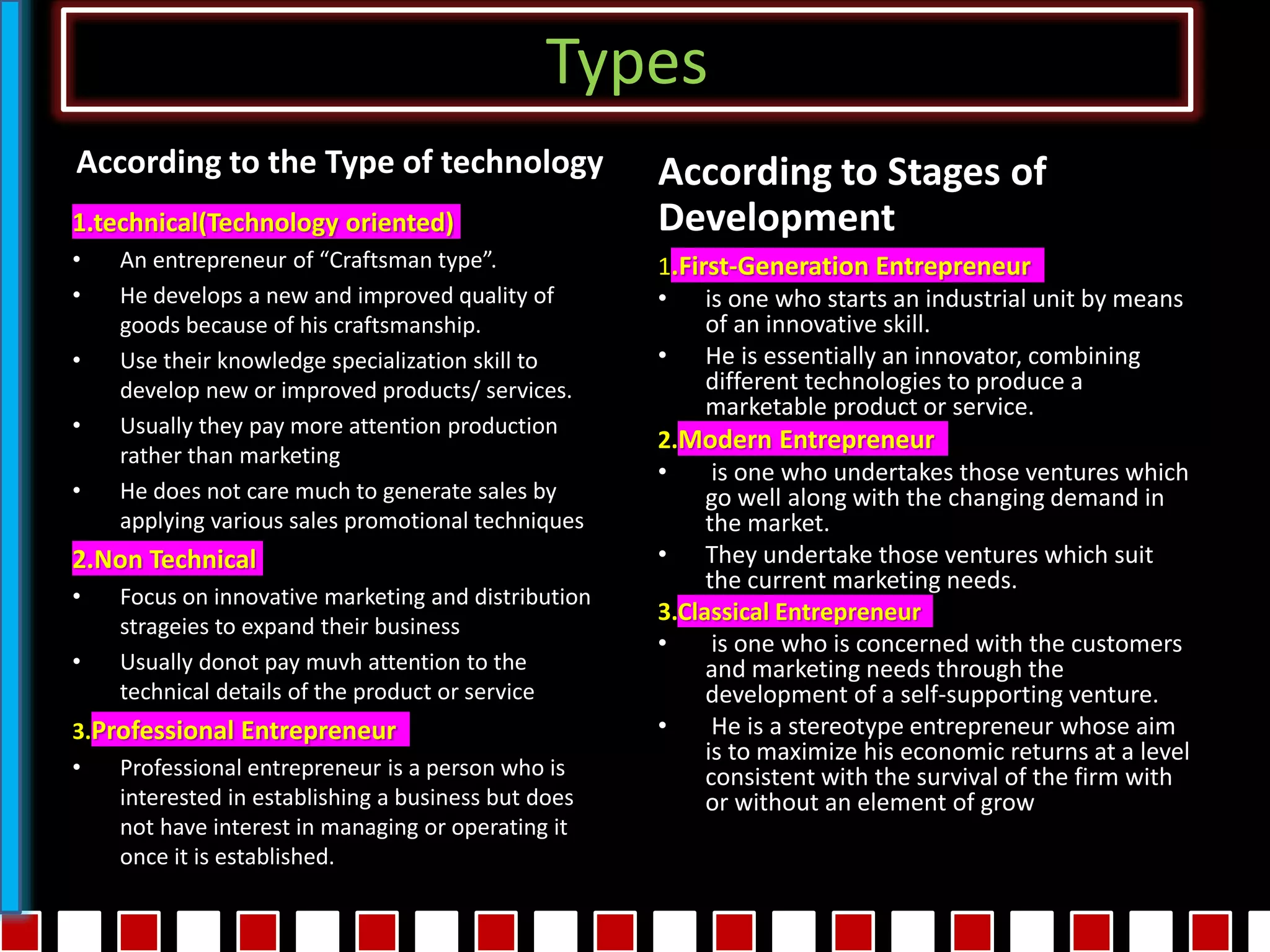
This document provides an exhaustive list of different types of entrepreneurship categorized in various ways. Some of the key types discussed include: online entrepreneurship, wantrepreneurship, social entrepreneurship, webpreneurship, influencer entrepreneurship, solopreneurship, intrapreneurship, multipreneurship, entremanureship, contrepreneurship, dadpreneurship, mompreneurship, opportunistic entrepreneurship, acquisitive entrepreneurship, incubative entrepreneurship, mass entrepreneurship, cultural entrepreneurship, international entrepreneurship, ecopreneurship, transpreneurship, e-entrepreneurship, domestic entrepreneurship, state entrepreneurship, innovative entrepreneurship, imitative