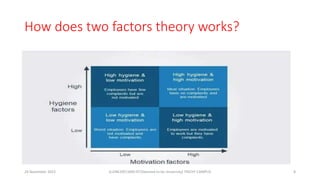
This document discusses Herzberg's two-factor theory of motivation. The theory states that there are two sets of factors that influence job satisfaction and dissatisfaction: motivators and hygiene factors. Motivators such as achievement, recognition, the work itself, and growth opportunities can provide job satisfaction, while hygiene factors relating to company policies, supervision, salary, and working conditions prevent dissatisfaction if adequately maintained but do not directly motivate. The document outlines the objectives, introduction, factors, and application of Herzberg's two-factor theory of motivation.