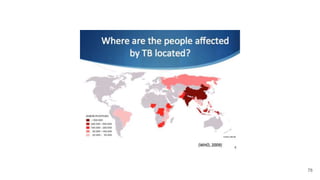
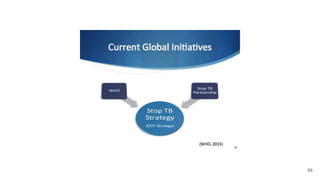
Tuberculosis (TB) is a deadly infectious disease affecting one-third of the world's population, with approximately 9.6 million cases and 1.5 million deaths reported in 2014. High-risk groups include economically disadvantaged individuals, immunocompromised persons, and those with inadequate access to healthcare. The WHO and UN have established strategies to drastically reduce TB incidence and mortality rates by 2030, emphasizing the need for ethical considerations in care and resource allocation.






















![References
Commission on Social Determinants of Health. Closing the gap in a generation: health equity through action on the social determinants of health.
Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 2008. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2008/9789241563703_ eng.pdf Accessed October 20, 2016
FRICK, M.W., 2015. Ethical Considerations in TB. San Antonio, TX: Heartland National TB Center.
HORSBURGH, R.C., Sep 29, 2016, 2016-last update, Epidemiology of tuberculosis [Homepage of UpToDate], [Online]. Available:
www.uptodate.com.
Lönnroth K, Jaramillo E, Williams B, Dye C, Raviglione M. Tuberculosis: the role of risk factors and social determinants. In: Blas E, Sivasankara
Kurup A, eds. Equity, social determinants and public health programmes. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 2010: pp 219–241.
SMITH, C.B., BATTIN, M.P., JACOBSON, J.A., FRANCIS, L.P., BOTKIN, J.R., ASPLUND, E.P., DOMEK, G.J. and HAWKINS, B., 2004. Are there
Characteristics of Infectious Diseases that Raise Special Ethical Issues? Developing World Bioethics, 4(1), pp. 1-16.
STOP TB PARTNERSHIP, November 4, 2015, 2015-last update, TB language guide: ‘United to End TB: Every Word Counts’ [Homepage
of TB Online, Global Tuberculosis Community Advisory Board], [Online]. Available: http://www.tbonline.info/posts/2015/11/4/tb-language-
guide-united-end-tb-every-word-counts/ Accessed [11/06, 2016].
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tuberculosispublichealthfinal-190418143236/85/Tuberculosis-TB-Public-Health-Presentation-31-320.jpg)
![References
WHO, 2016-last update, Trade, foreign policy, diplomacy and health: Tuberculosis control [Homepage of WHO], [Online]. Available:
http://www.who.int/trade/distance_learning/gpgh/gpgh3/en/index7.html Accessed [11/11, 2016].
WHO, 2016-last update, Tuberculosis (TB): Addressing the needs of vulnerable populations [Homepage of WHO], [Online]. Available:
http://www.who.int/tb/areas-of-work/population-groups/en/ Accessed [11/06, 2016].
WHO, 2016-last update, Tuberculosis (TB): Childhood TB [Homepage of WHO], [Online]. Available: http://www.who.int/tb/areas-of-
work/children/en/ Accessed [11/06, 2016].
WHO, March 22, 2016, 2016-last update, WHO calls on countries and partners to "Unite to End Tuberculosis" [Homepage of WHO],
[Online]. Available: http://who.int/mediacentre/news/statements/2016/tb-day/en/ [11/06, 2016].
WHO, 2014. ETHICAL ISSUES IN TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION, CARE AND CONTROL. WHO’s Department of Knowledge, Ethics, and Research
(KER) and the Global TB Programme (GTB).
WHO, 2011. ETHICAL ISSUES IN TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION, CARE AND CONTROL. WHO.
WHO, 2010. Guidance on ethics of tuberculosis prevention, care and control. Switzerland: WHO.
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tuberculosispublichealthfinal-190418143236/85/Tuberculosis-TB-Public-Health-Presentation-32-320.jpg)



![Not Harvard formatted
•Case study of Hoa, Nguyen Binh et al. "National Survey Of Tuberculosis Prevalence In Viet Nam". Bulletin of the World Health Organization
88.4 (2010): 273-280. Web.
•Dye C. Global epidemiology of tuberculosis. Lancet. 2006;367:938–40.[PubMed]
•9. Diwan VK, Thorson A. Sex, gender, and tuberculosis. Lancet. 1999;353:1000–1. [PubMed]
•REF: World Health Organization. Use of high burden country lists for TB by WHO in the post-2015 era: Summary. Available at:
http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/high_tb_burdencountrylists2016-2020summary.pdf?ua=1 (Accessed on September 13,
2016).
•Global Tuberculosis Report 2014. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2014. Copyright © 2014 World Health Organization. Available at:
http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/137094/1/9789241564809_eng.pdf?ua=1. (Accessed on January 12, 2015).
• Zaman, K. "Tuberculosis: A Global Health Problem". J Health Popul Nutr 28.2 (2010): n. pag. Web
36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tuberculosispublichealthfinal-190418143236/85/Tuberculosis-TB-Public-Health-Presentation-36-320.jpg)



















































![99
• HOA, N.B., SY, D.N., NHUNG, N.V., TIEMERSMA, E.W., BORGDORFF, M.W. and COBELENS, F.G., 2010. National survey
of tuberculosis prevalence in Viet Nam. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 88(4), pp. 273-280.
• HOLLOWAY, K., STAUB, K., RÜHLI, F. and HENNEBERG, M., 2014. Lessons from history of socioeconomic
improvements: a new approach to treating multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis. Journal of Biosocial Science, 46(05), pp.
600-620.
• HORSBURGH, R.C., Sep 29, 2016, 2016-last update, Epidemiology of tuberculosis [Homepage of UpToDate], [Online].
• INTERRANTE, J.D., HADDAD, M.B., KIM, L. and GANDHI, N.R., 2015. Exogenous Reinfection as a Cause of Late
Recurrent Tuberculosis in the United States. Annals of the American Thoracic Society, 12(11), pp. 1619-1626.
• JAMISON, D.T., BREMAN, J.G., MEASHAM, A.R., ALLEYNE, G., CLAESON, M., EVANS, D.B., JHA, P., MILLS, A. and
MUSGROVE, P., 2006. Disease control priorities in developing countries. World Bank Publications.
• LAWN, S.D. and ZUMLA, A.I., 2011. Tuberculosis. Lancet (London, England), 378(9785), pp. 57.
• LIENHARDT12, C., 2001. From exposure to disease: the role of environmental factors in susceptibility to and
development of tuberculosis. Epidemiol Rev, 23(2),.
• LOBATO, M.N., SUN, S.J., MOONAN, P.K., WEIS, S.E., SAIMAN, L., REICHARD, A.A. and FEJA, K., 2008. Underuse of
effective measures to prevent and manage pediatric tuberculosis in the United States. Archives of Pediatrics &
Adolescent Medicine, 162(5), pp. 426-431.
• LÖNNROTH, K., JARAMILLO, E., WILLIAMS, B., DYE, C. and RAVIGLIONE, M., 2010. Tuberculosis: the role of risk factors
and social determinants. Equity, social determinants and public health programmes, 219.
• MANGTANI, P., ABUBAKAR, I., ARITI, C., BEYNON, R., PIMPIN, L., FINE, P.E., RODRIGUES, L.C., SMITH, P.G., LIPMAN, M.,
WHITING, P.F. and STERNE, J.A., 2014. Protection by BCG vaccine against tuberculosis: a systematic review of
randomized controlled trials. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of
America, 58(4), pp. 470-480.
• MARAIS, B.J. and ZUMLA, A., 2013. History of tuberculosis and drug resistance. N Engl J Med, 368(1), pp. 88.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tuberculosispublichealthfinal-190418143236/85/Tuberculosis-TB-Public-Health-Presentation-99-320.jpg)

![101
• SIMON, G.G., 2016. Impacts of neglected tropical disease on incidence and progression of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and
malaria: scientific links. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 42, pp. 54-57.
• SMITH, C.B., BATTIN, M.P., JACOBSON, J.A., FRANCIS, L.P., BOTKIN, J.R., ASPLUND, E.P., DOMEK, G.J. and HAWKINS, B.,
2004. Are there Characteristics of Infectious Diseases that Raise Special Ethical Issues? Developing World Bioethics, 4(1),
pp. 1-16.
• STOP TB PARTNERSHIP, November 4, 2015, 2015-last update, TB language guide: ‘United to End TB: Every Word
Counts’ [Homepage of TB Online, Global Tuberculosis Community Advisory Board], [Online]. Available:
http://www.tbonline.info/posts/2015/11/4/tb-language-guide-united-end-tb-every- word-counts/ [11/06, 2016].
• TRUNZ, B.B., FINE, P. and DYE, C., 2006. Effect of BCG vaccination on childhood tuberculous meningitis and miliary
tuberculosis worldwide: a meta-analysis and assessment of cost-effectiveness. The Lancet, 367(9517), pp. 1173-1180.
• UPLEKAR, M., WEIL, D., LONNROTH, K., JARAMILLO, E., LIENHARDT, C., DIAS, H.M., FALZON, D., FLOYD, K., GARGIONI, G.,
GETAHUN, H., GILPIN, C., GLAZIOU, P., GRZEMSKA, M., MIRZAYEV, F., NAKATANI, H., RAVIGLIONE, M. and WHO'S
GLOBAL TB PROGRAMME, 2015. WHO's new end TB strategy. Lancet (London, England), 385(9979), pp. 1799-1801.
• WHITE, P.J. and ABUBAKAR, I., 2016. Improving control of tuberculosis in low-burden countries: insights from
mathematical modeling. Frontiers in microbiology, 7.
• WHITE, V.L., PALIWALLA, M., STEVES, C.J., JADHAV, D. and MOORE-GILLON, J., 2002. Management of tuberculosis in a
British inner-city population. Journal of public health medicine, 24(1), pp. 49-52.
• WHO, 2016-last update, Global Tuberculosis Report 2016 [Homepage of WHO], [Online]. Available:
http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/2016].
• WHO, 2016-last update, Trade, foreign policy, diplomacy and health: Tuberculosis control [Homepage of WHO],
[Online]. Available: http://www.who.int/trade/distance_learning/gpgh/gpgh3/en/index7.html [11/11, 2016].
• WHO, 2016-last update, Tuberculosis (TB): Addressing the needs of vulnerable populations [Homepage of WHO],
[Online]. Available: http://www.who.int/tb/areas-of-work/population-groups/en/ [11/06, 2016].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tuberculosispublichealthfinal-190418143236/85/Tuberculosis-TB-Public-Health-Presentation-101-320.jpg)
![102
• WHO, 2016-last update, Tuberculosis (TB): Childhood TB [Homepage of WHO], [Online]. Available:
http://www.who.int/tb/areas-of-work/children/en/ [11/06, 2016].
• WHO, March 22, 2016, 2016-last update, WHO calls on countries and partners to "Unite to End Tuberculosis"
[Homepage of WHO], [Online]. Available: http://who.int/mediacentre/news/statements/2016/tb-day/en/ [11/06,
2016].
• WHO, 2015-last update, Use of high burden country lists for TB by WHO in the post-2015 era [Homepage of World
Health Organisation], [Online]. Available:
http://who.int/tb/publications/global_report/high_tb_burdencountrylists2016-2020summary.pdf?ua=1 [11/13, 2016].
• WHO, 2014-last update, Ethical issues in Tuberculosis prevention, care and control [Homepage of World Health
Organisation], [Online]. Available: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/ethics_in_tb_factsheet_28jan11rev.pdf [11/6,
2016].
• WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION, 2015. The End TB Strategy.Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 2015, . WORLD HEALTH
ORGANIZATION, 2006. Global tuberculosis control: surveillance, planning, financing:
• WHO report 2006.
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION, 2004. BCG vaccine. WHO position paper. Releve epidemiologique
• hebdomadaire, 79(4), pp. 27-38.
• YASIN, Y., BIEHL, K. and EROL, M., 2015. Infection of the Invisible: Impressions of a Tuberculosis Intervention Program
for Migrants in Istanbul. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health, 17(5), pp. 1481-1486.
• ZAMAN, K., 2010. Tuberculosis: a global health problem. Journal of health, population and nutrition, , pp. 111-113.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tuberculosispublichealthfinal-190418143236/85/Tuberculosis-TB-Public-Health-Presentation-102-320.jpg)