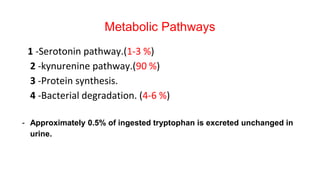
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid obtained through diet that has several important metabolic functions in the body. It can be broken down through four main pathways: 1) the serotonin pathway where tryptophan is converted to serotonin, an important neurotransmitter; 2) the kynurenine pathway which clears excess tryptophan and provides precursors for other important molecules; 3) incorporation into proteins; and 4) bacterial degradation in the gut producing compounds like indole. Dysregulation of these pathways can lead to conditions like carcinoid syndrome or affect circadian rhythms and reproduction.