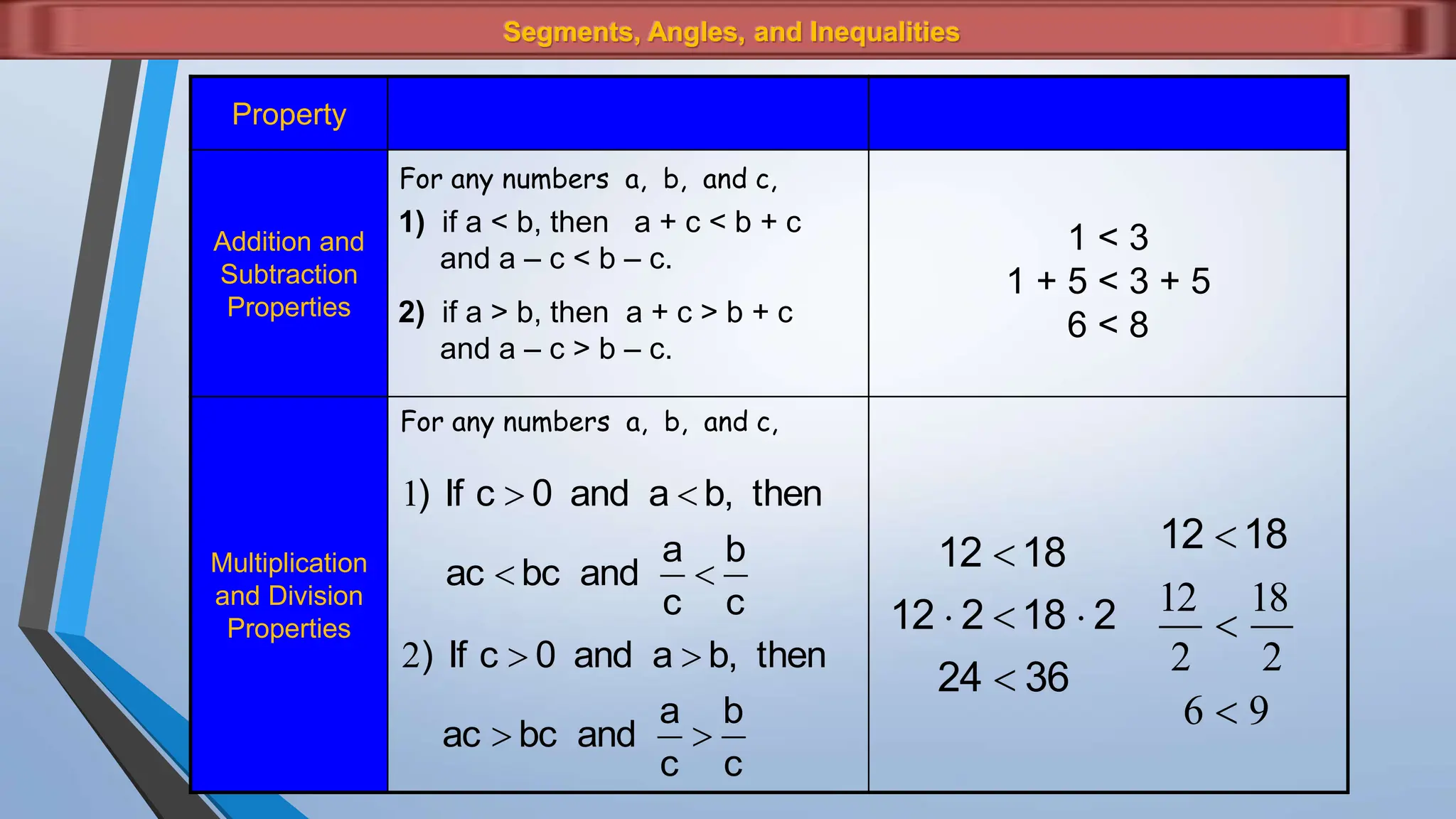
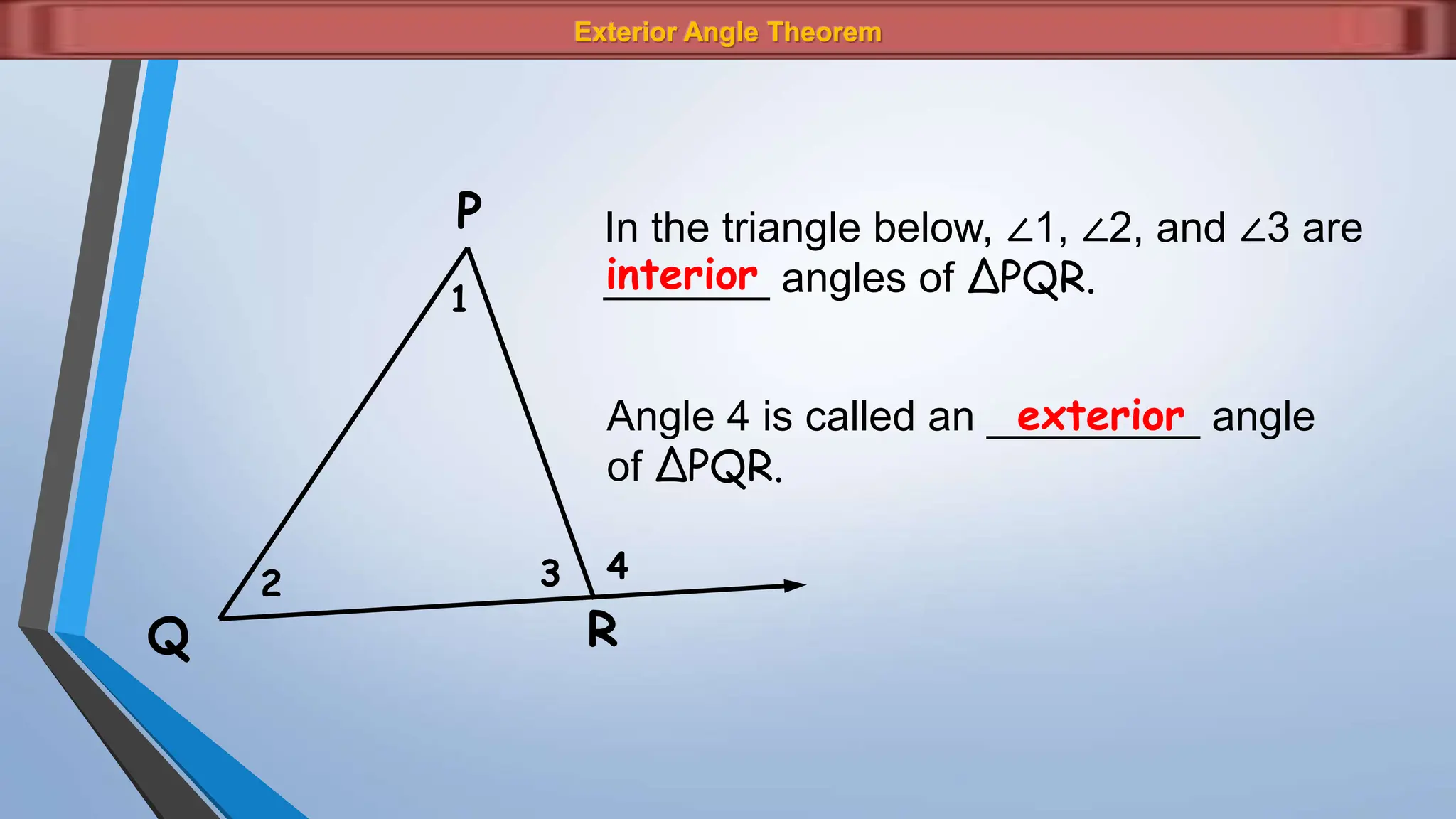
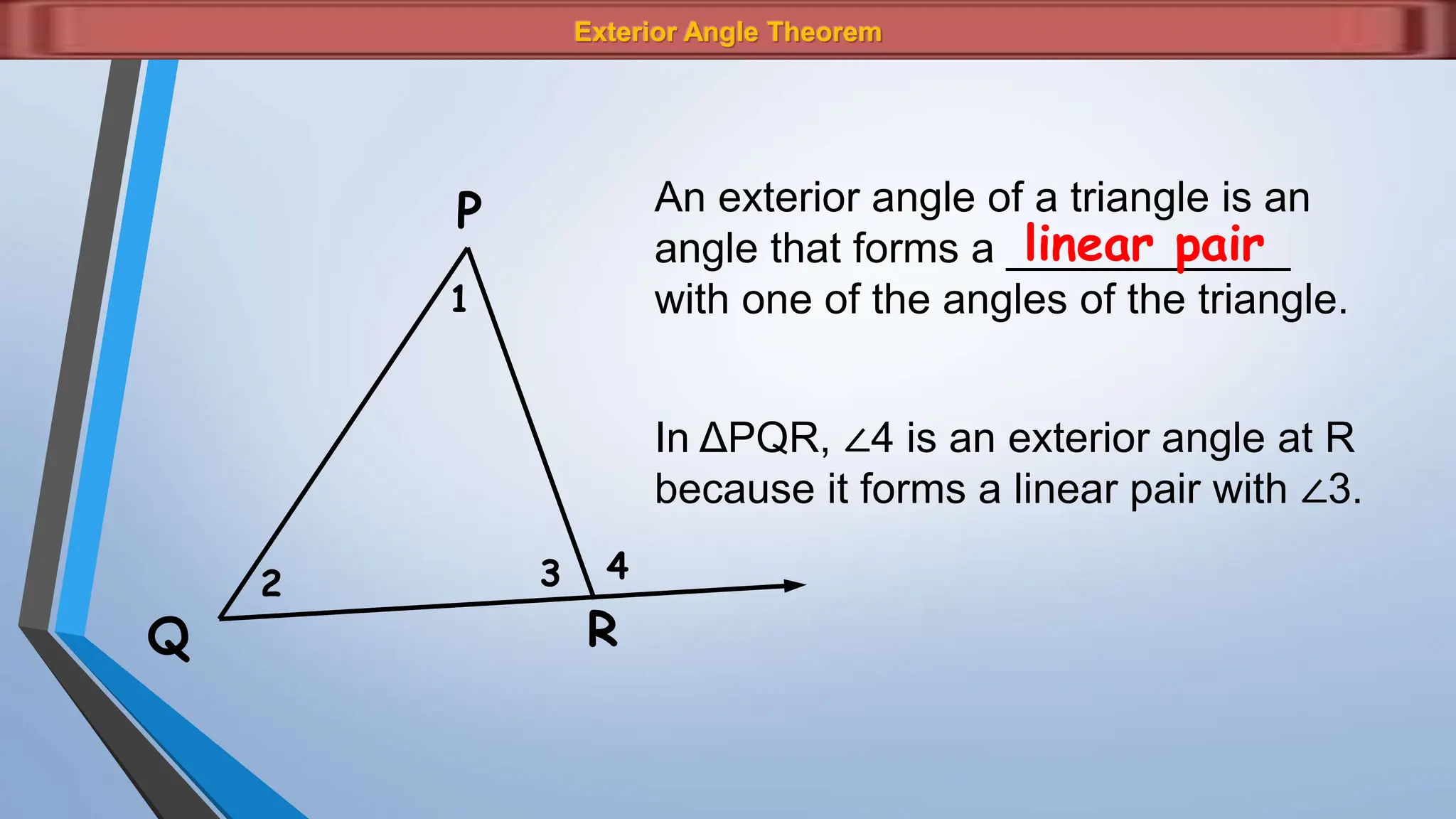
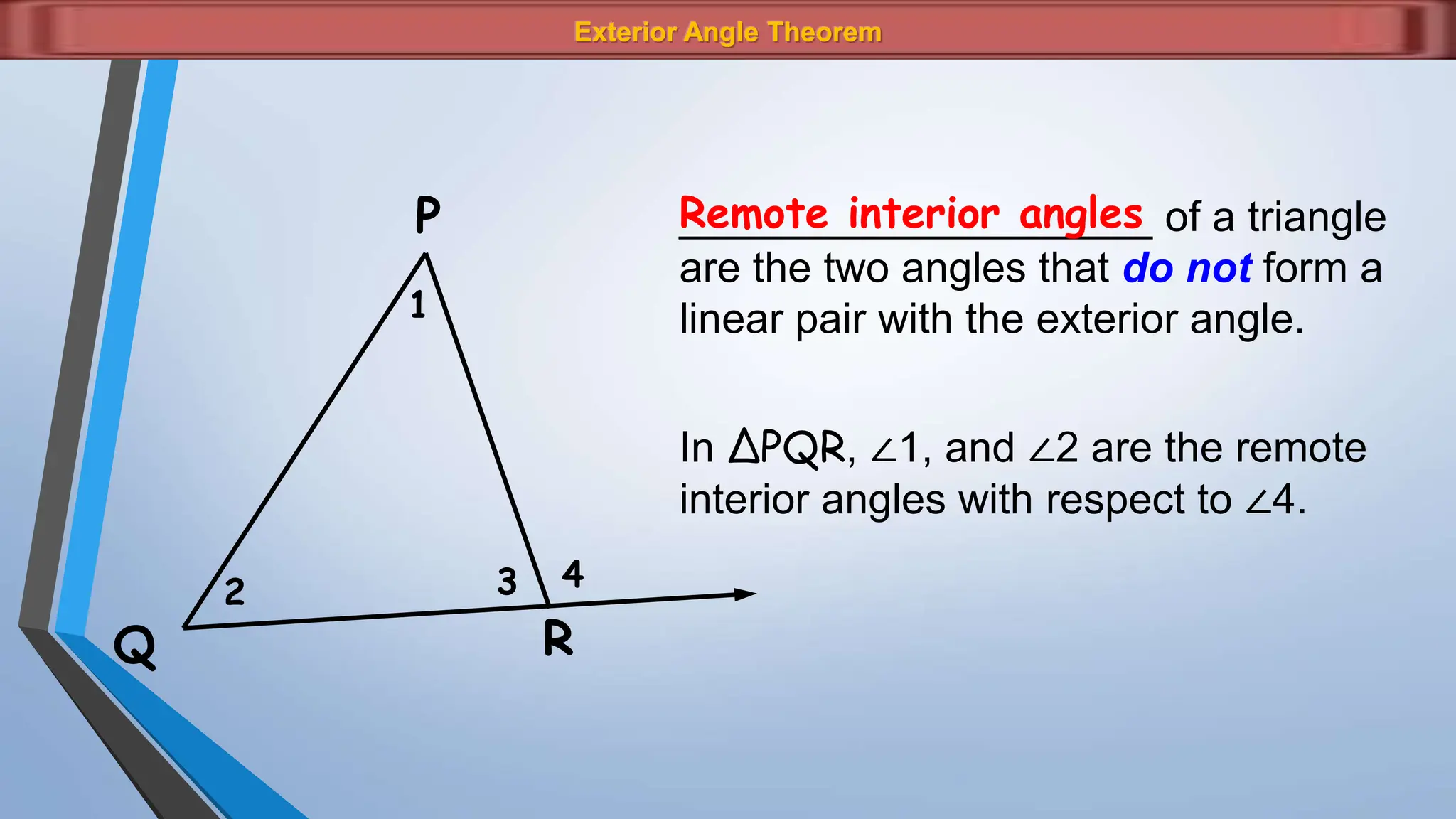
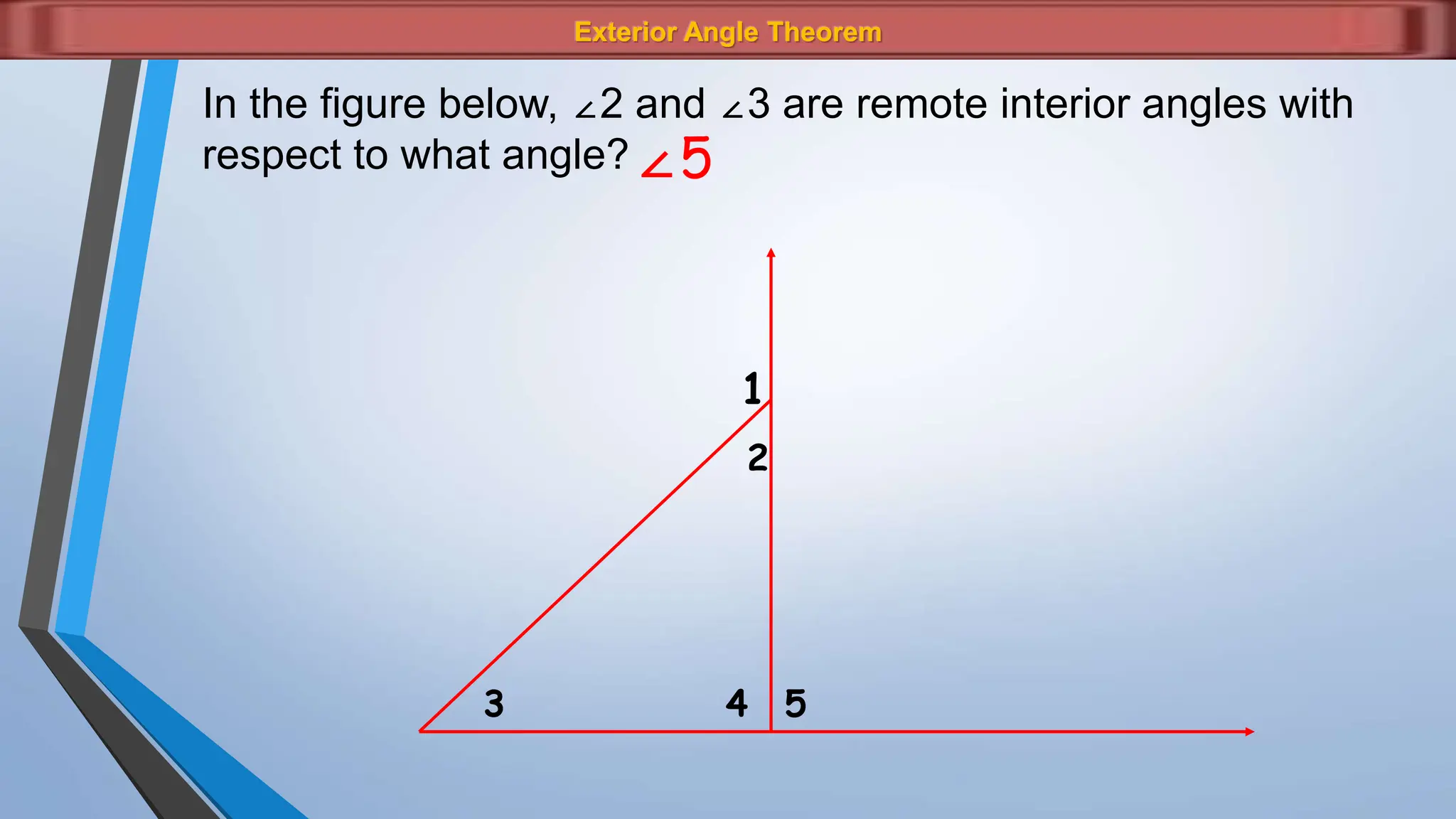
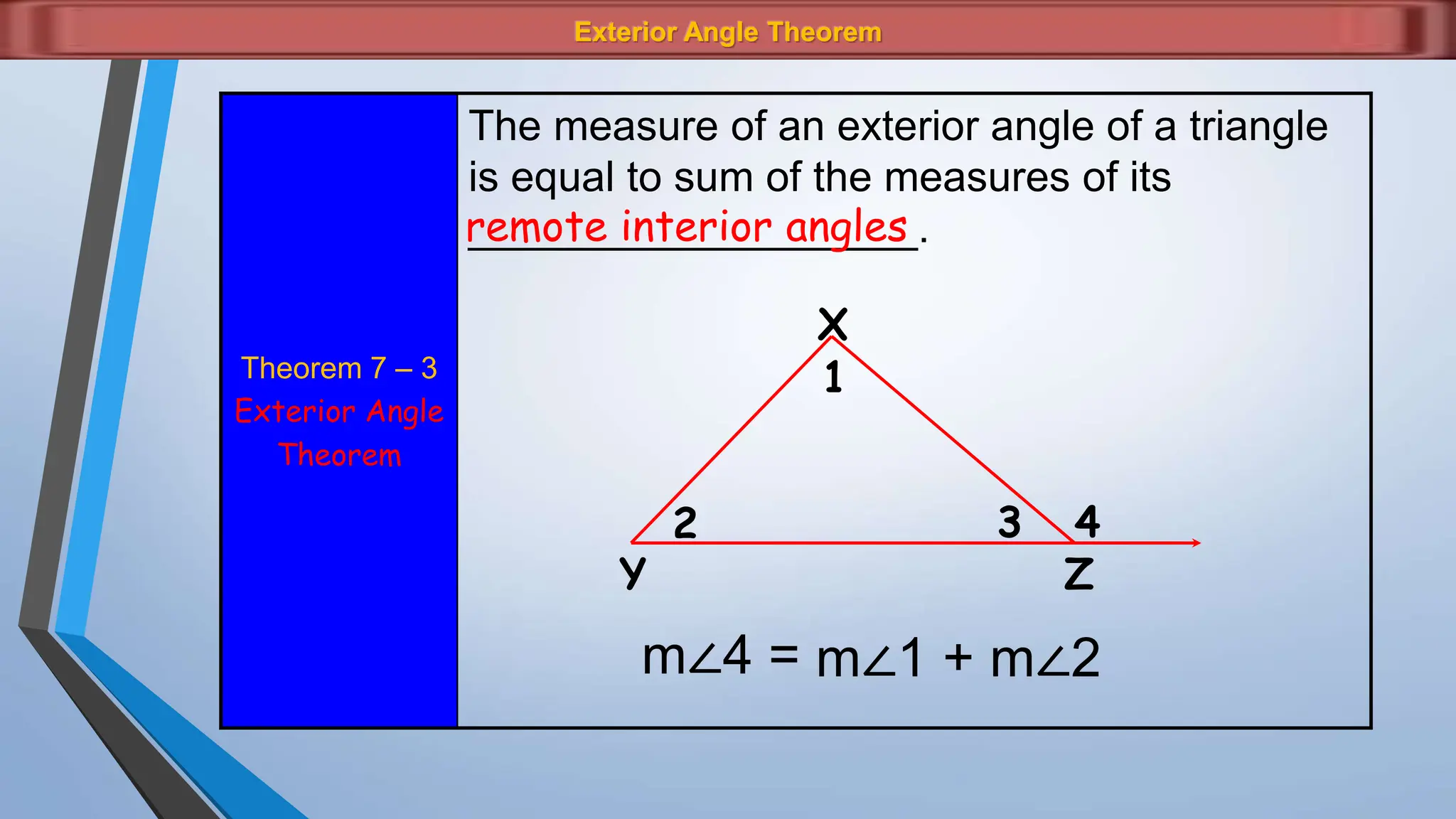
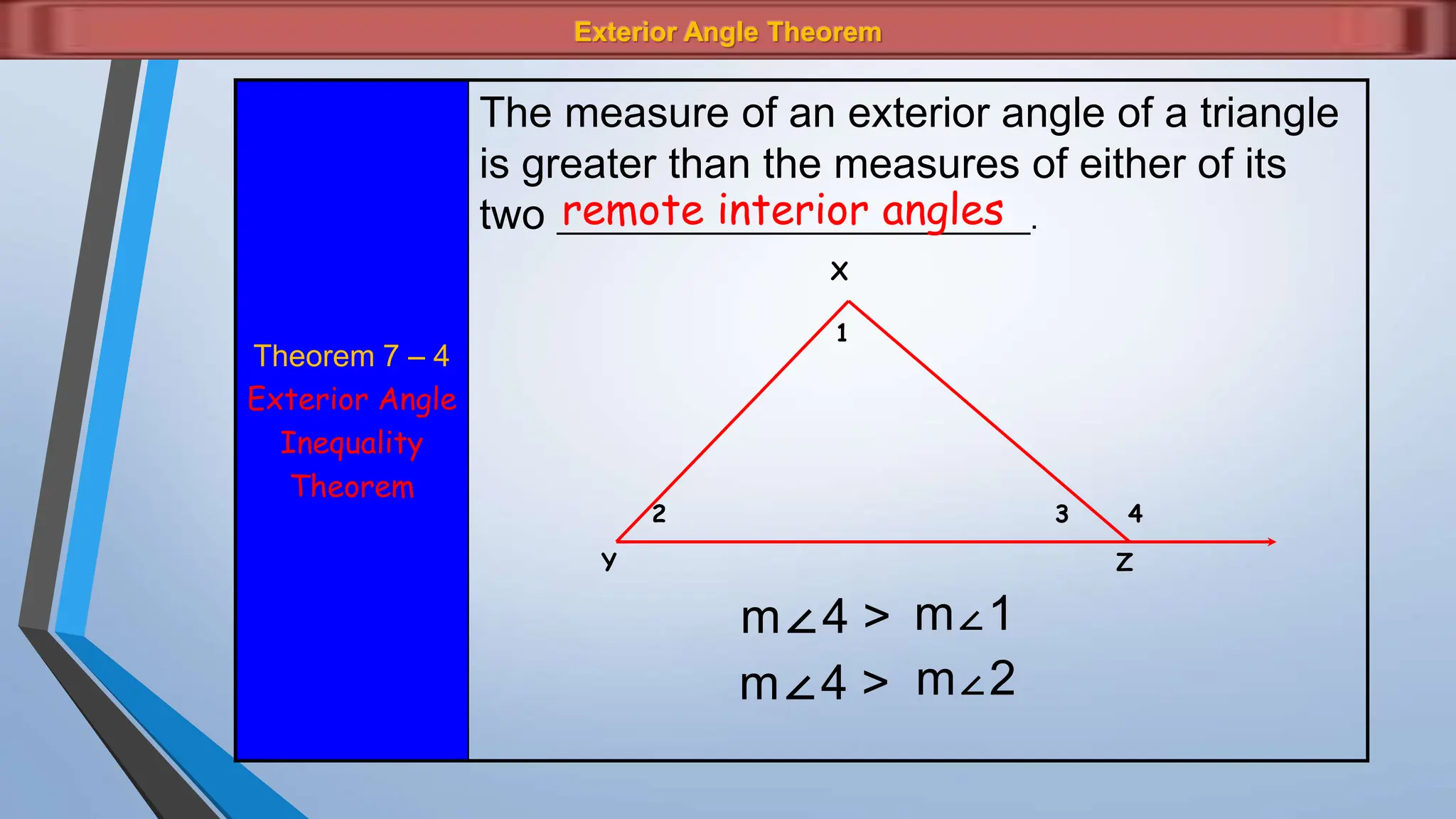
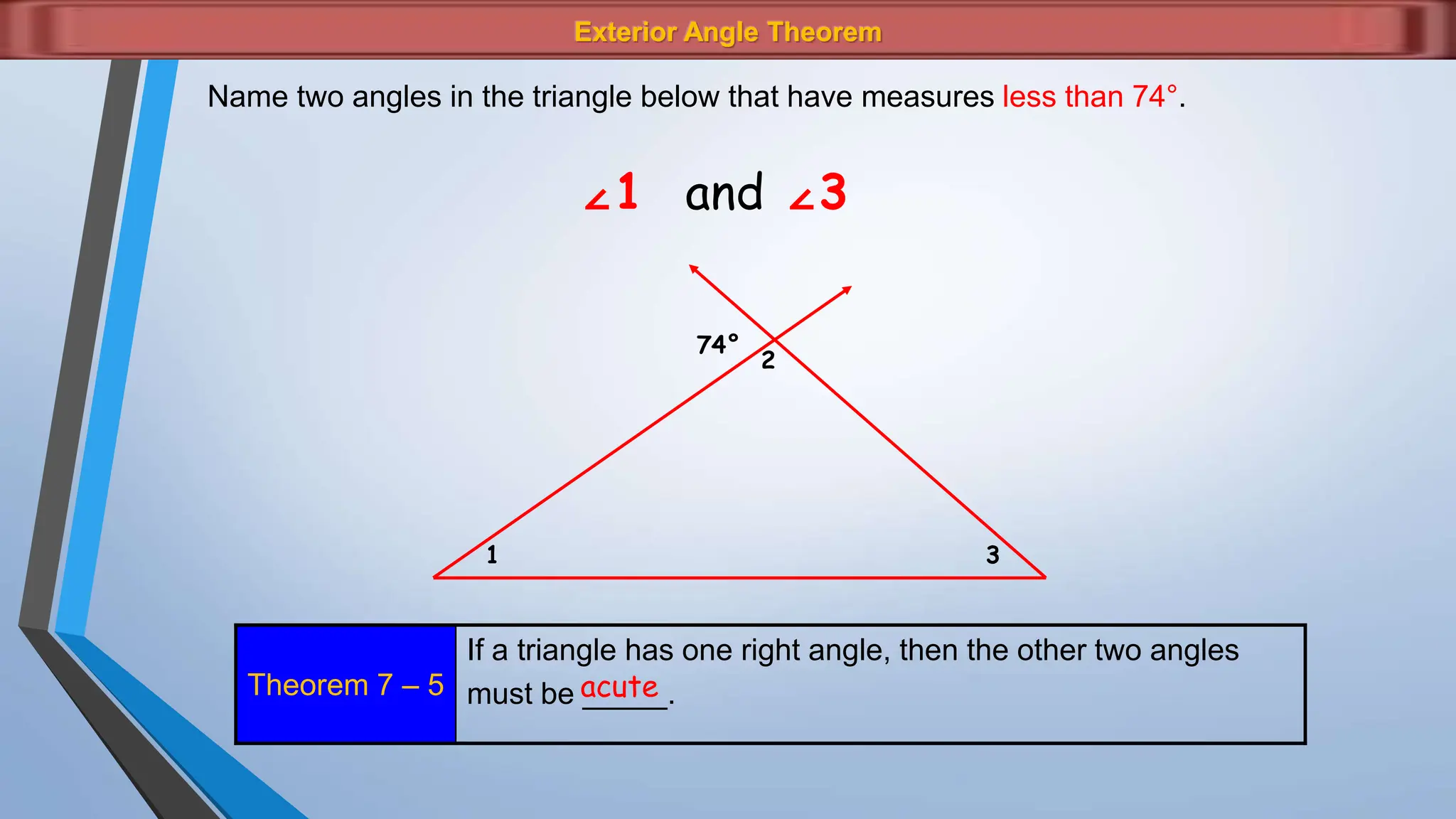
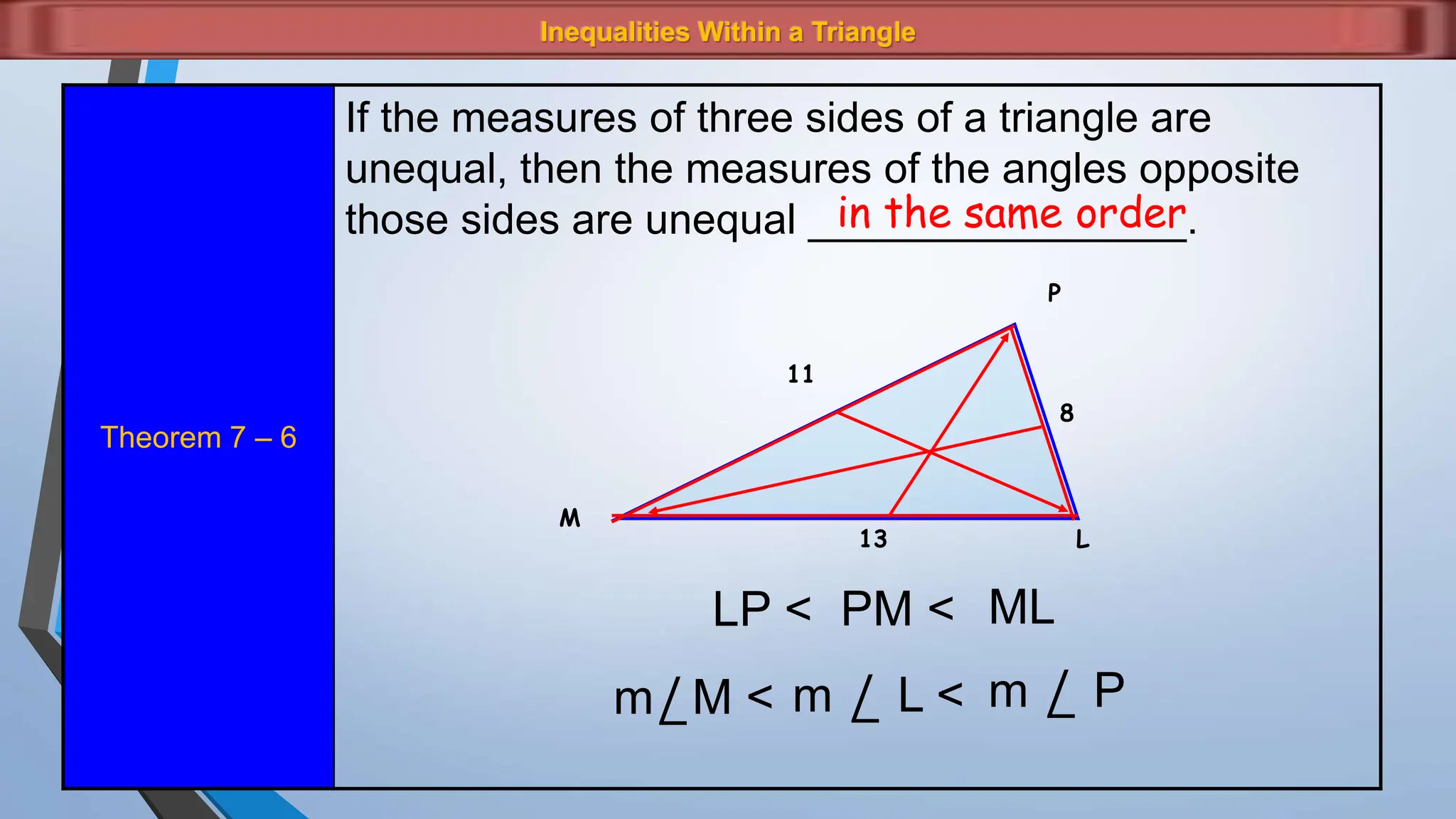
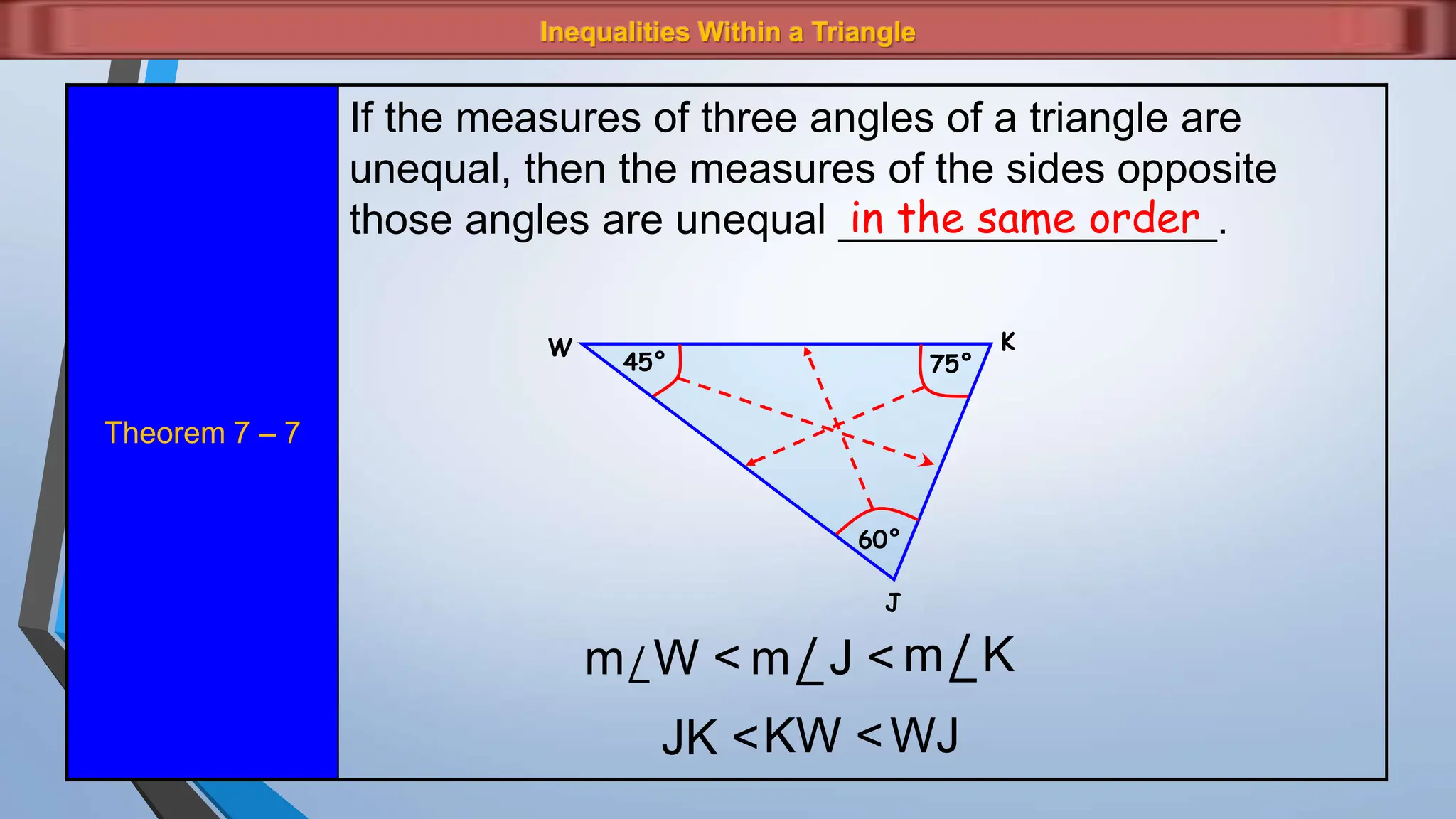
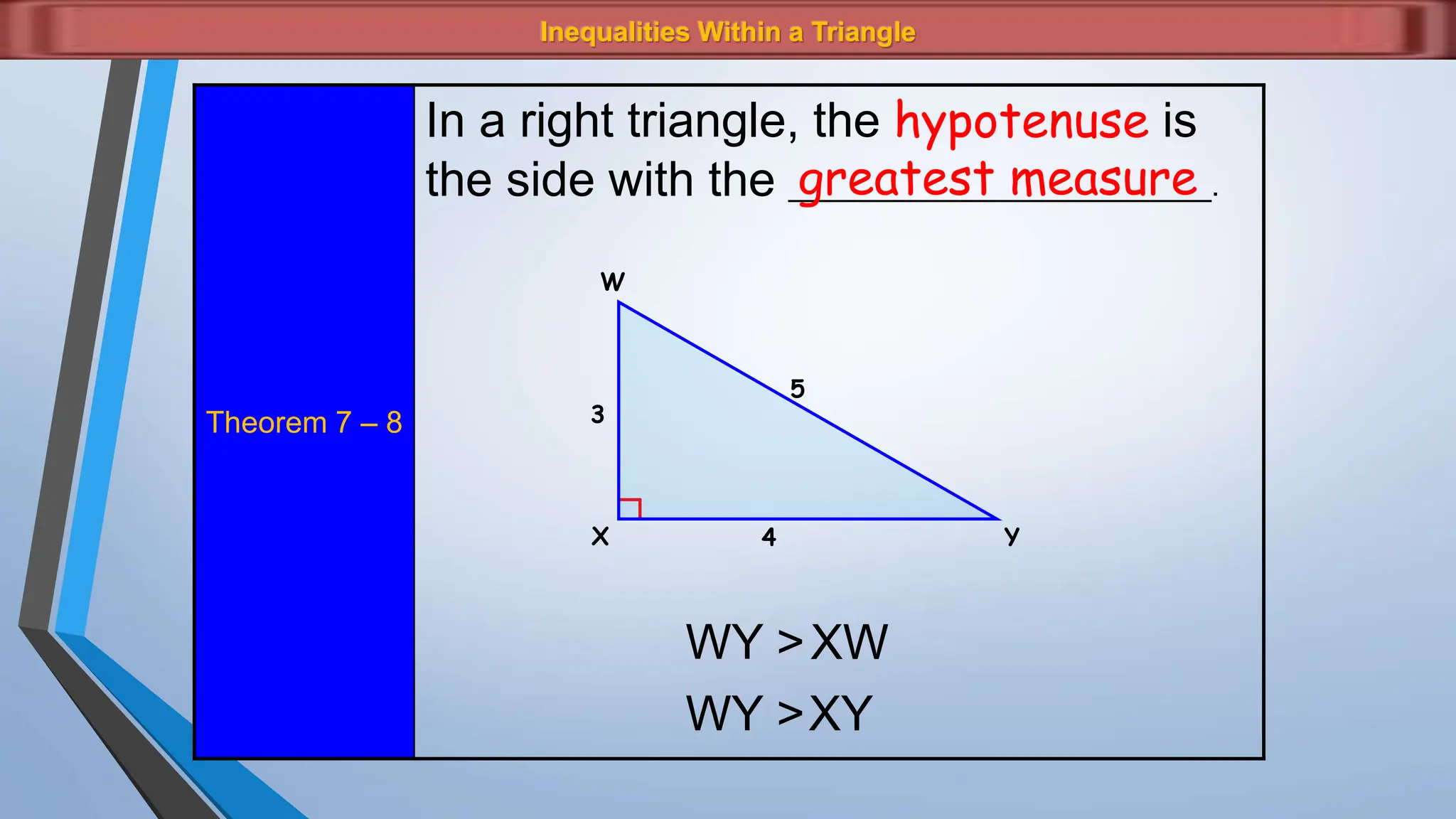
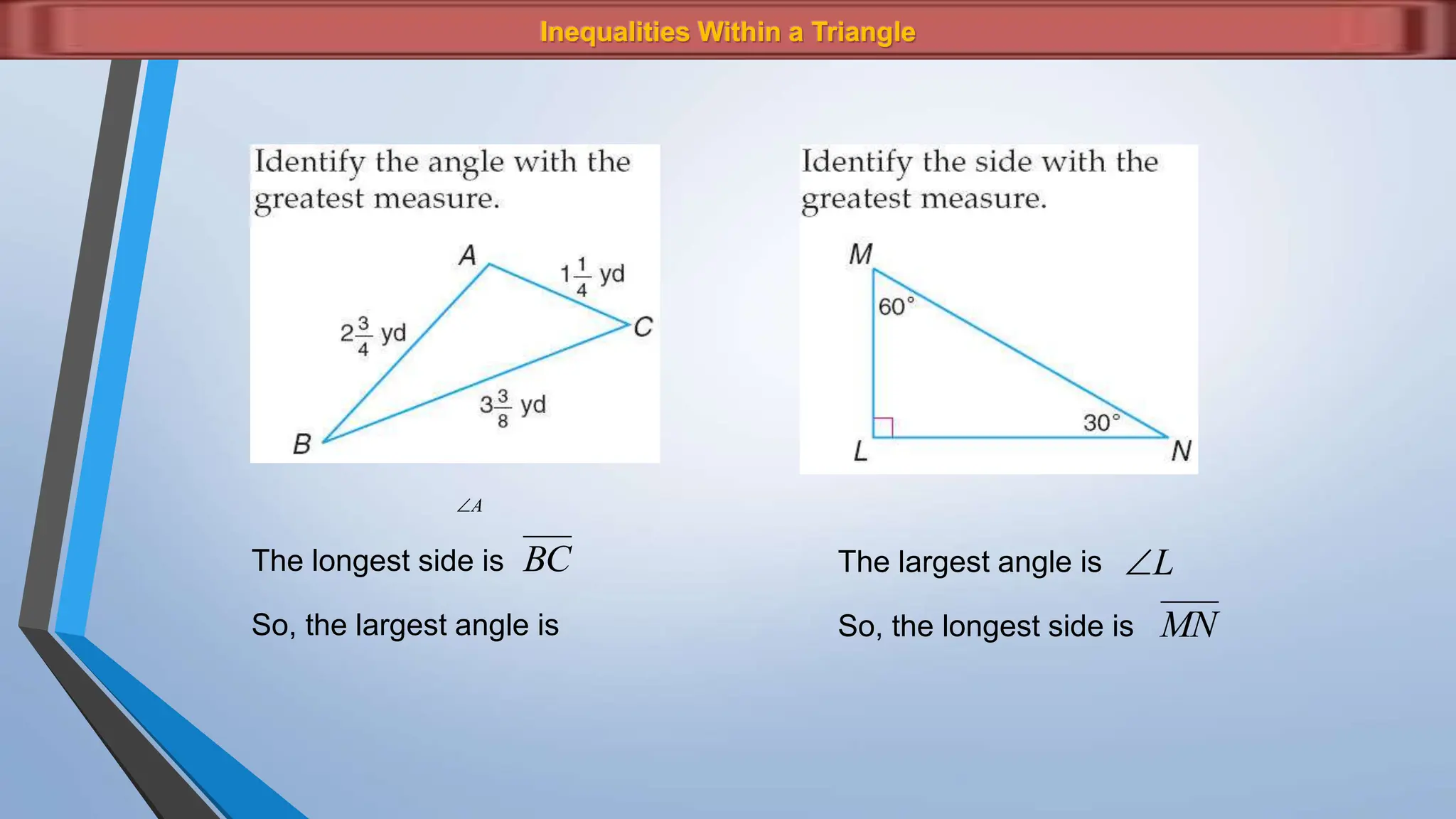
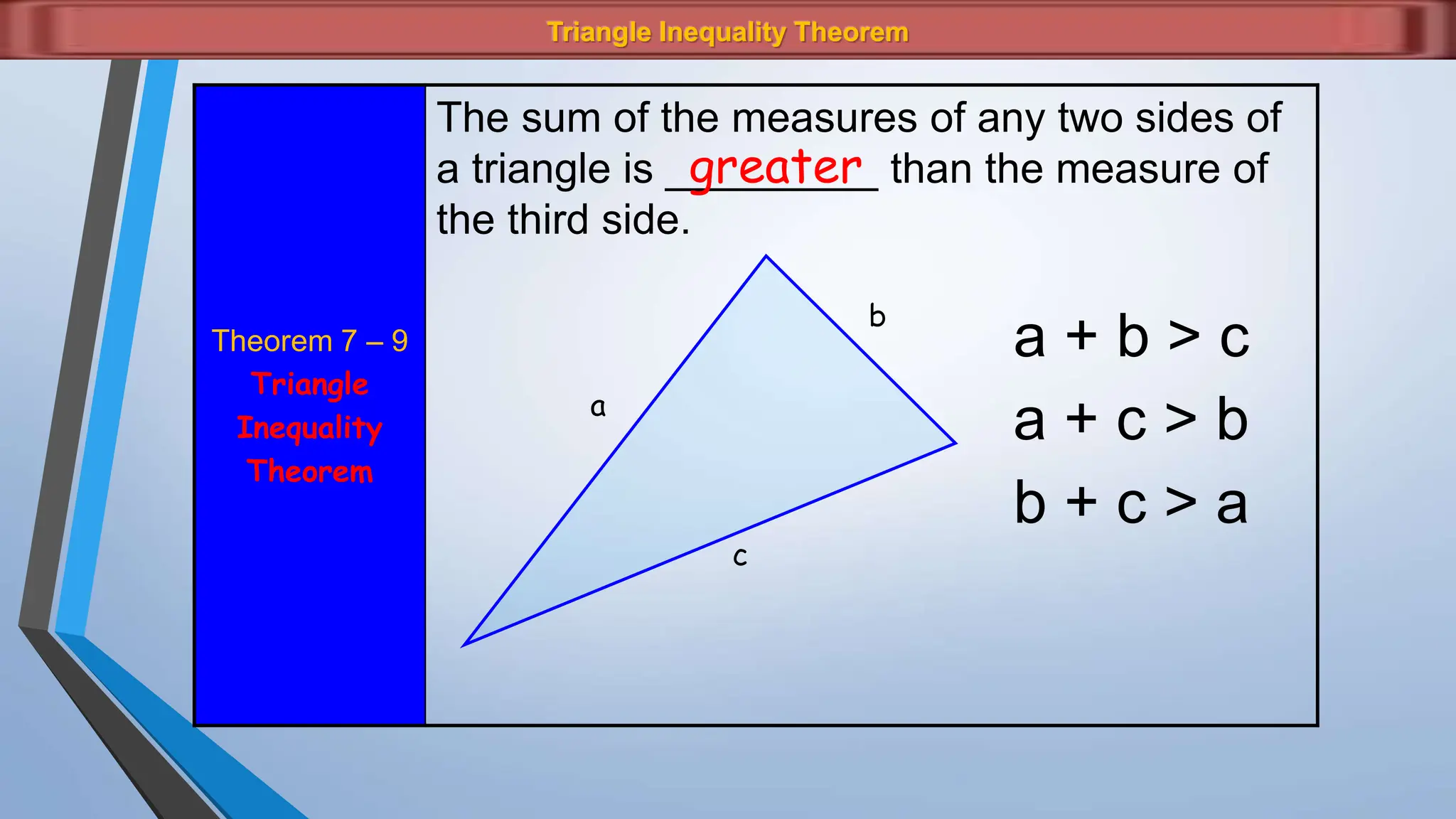
The document discusses various properties and theorems related to angles and segments in triangles, including the triangle inequality theorem, exterior angle theorem, and inequalities within a triangle. Key topics covered include the relationships between angles and sides, as well as methods for establishing the measures of angles and sides based on their properties. Illustrative examples are provided to demonstrate the application of these theorems.