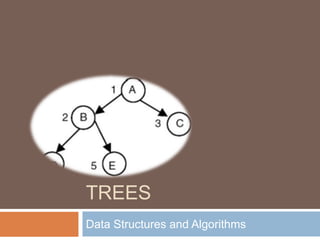
Trees are hierarchical data structures that impose an ordered structure on data. A tree has a root node and may have many child nodes partitioned into subtrees. Binary trees restrict nodes to have at most two children. Binary trees can be represented using arrays or linked lists. Common traversals of binary trees include inorder, preorder, and postorder. Binary search trees organize nodes so that all left descendants are less than the parent and all right descendants are greater. Deletion of nodes in a binary search tree depends on whether the node has zero, one, or two children.