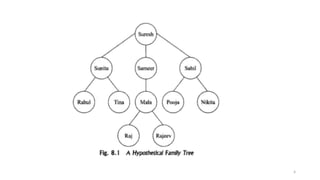
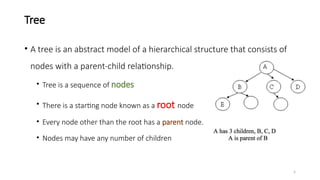
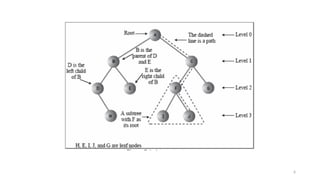
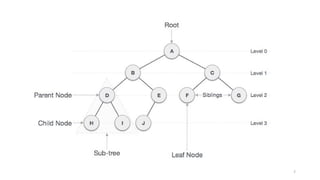
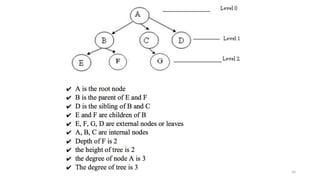
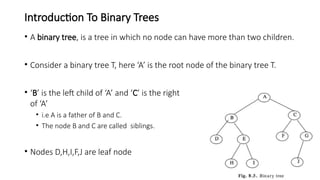
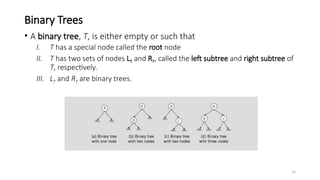
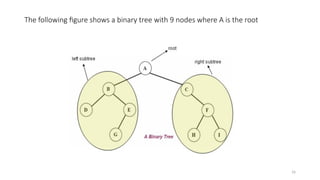
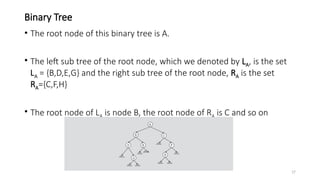
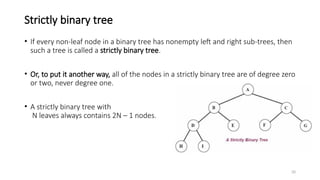
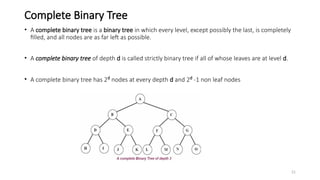
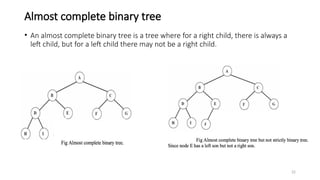
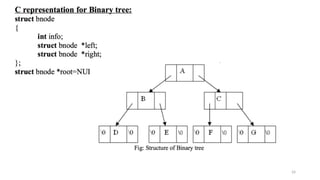
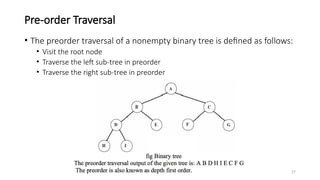
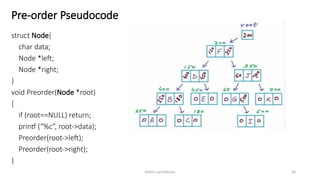
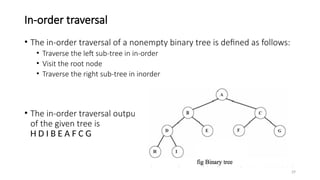
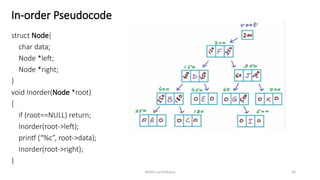
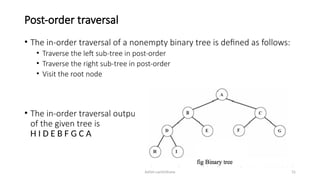
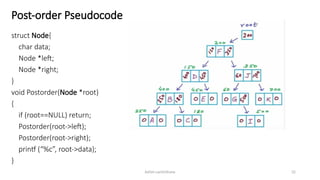
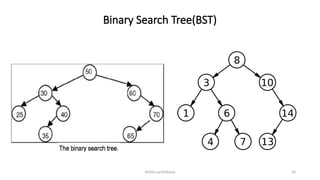
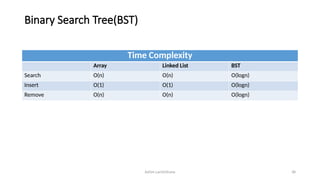
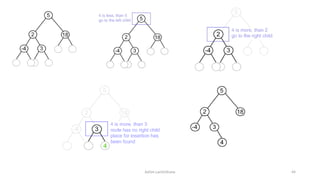
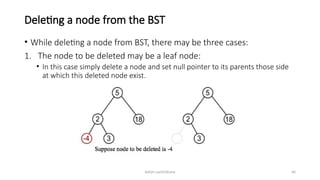
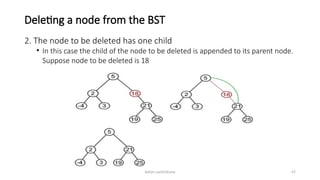
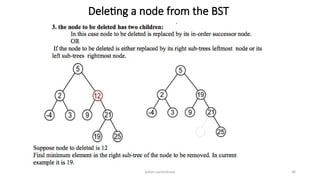
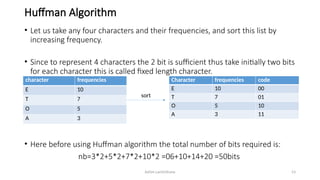
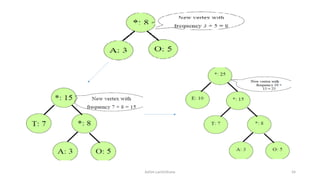
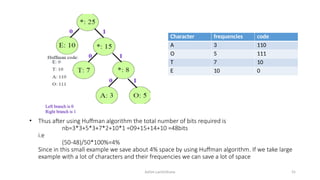
The document introduces tree data structures, focusing on concepts like binary trees and binary search trees (BST), and their key characteristics, definitions, and applications. It covers tree traversal methods, including in-order, pre-order, and post-order traversals, along with algorithms for BST operations like insertion, deletion, and searching. Additionally, it discusses the Huffman algorithm for data compression utilizing binary trees.