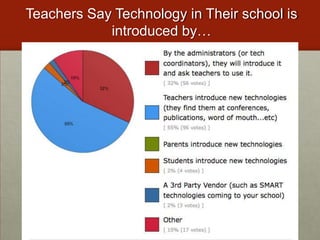
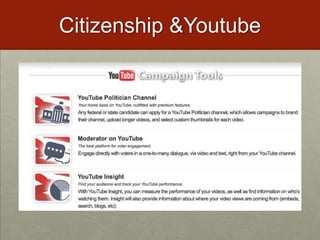
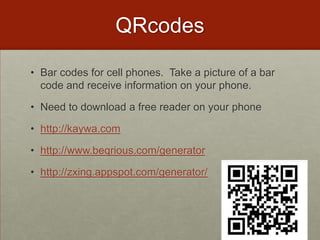
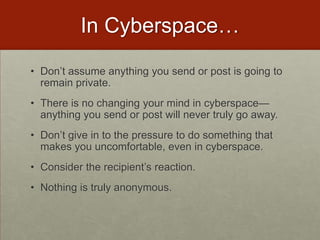
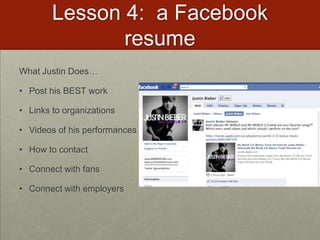
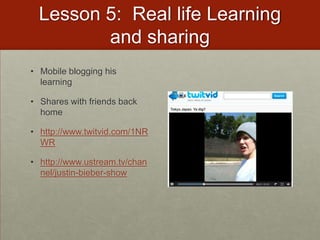
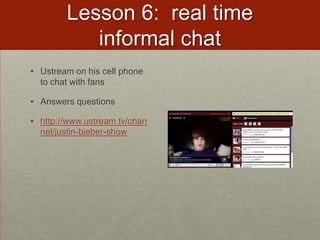
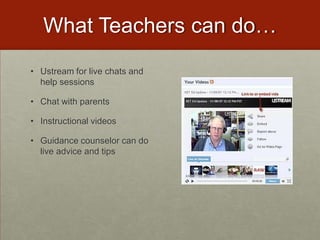
This document discusses various ways that teachers have incorporated students' mobile technologies into classroom learning. It provides examples of teachers who have had students:
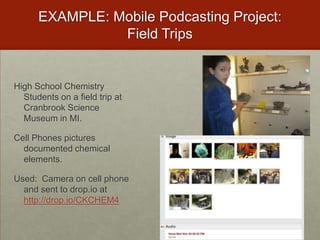
- Take photos on field trips and upload them to document findings.
- Develop avatars to take oral exams on mobile devices to improve engagement.
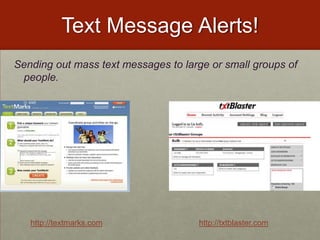
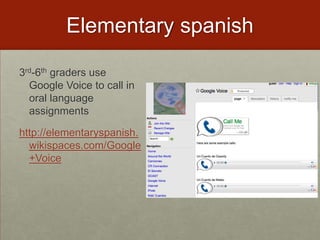
- Use text messaging to participate in class activities like submitting vocabulary words or science facts.
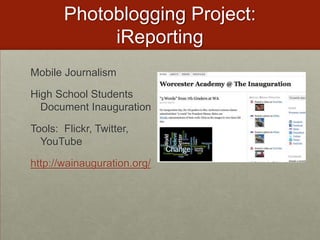
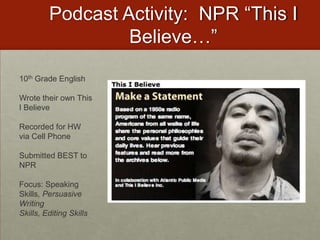
- Create mobile podcasts and videos to document events like presidential inaugurations.
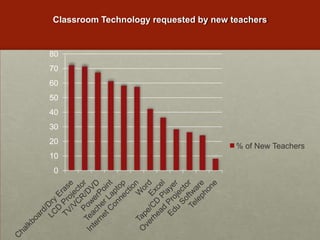
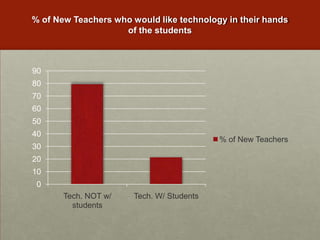
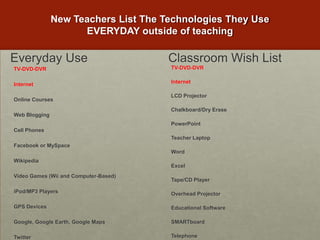
The examples illustrate how teachers have shifted from banning mobile devices to allowing their use to enhance participation and engagement in learning activities.