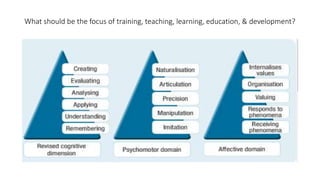
The document provides an outline for a training on teaching methods for TVET trainers. It discusses key terms like training, teaching, learning, and professional development. It also covers learning theories including behavioral, cognitive, social, and constructivist approaches. A variety of training methods are presented such as lectures, role plays, and group discussions. The importance of selecting appropriate training methods and materials based on learning objectives, styles, and other criteria is emphasized. Effective session planning is also discussed, including defining objectives, content, methods, and evaluation.