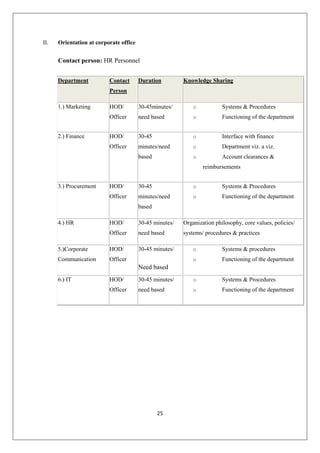
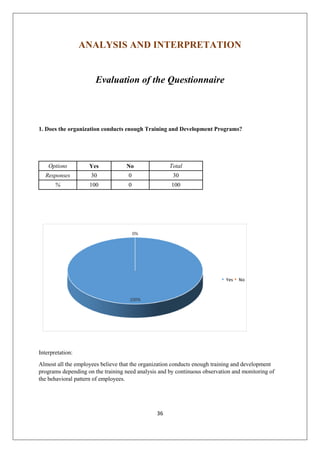
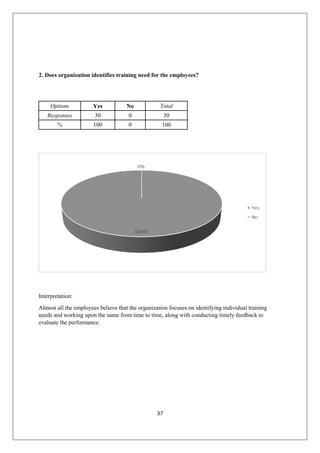
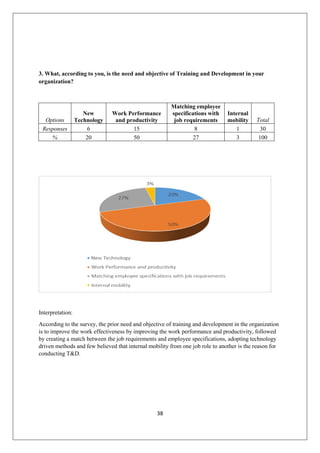
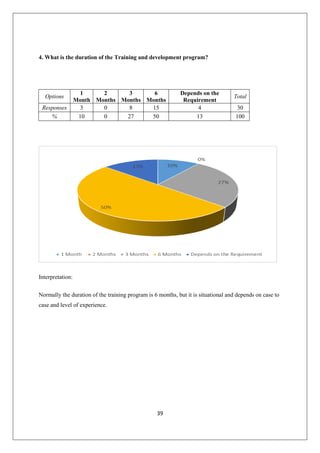
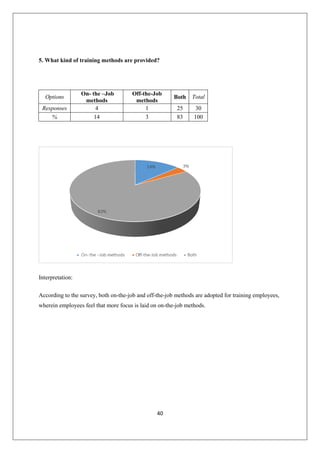
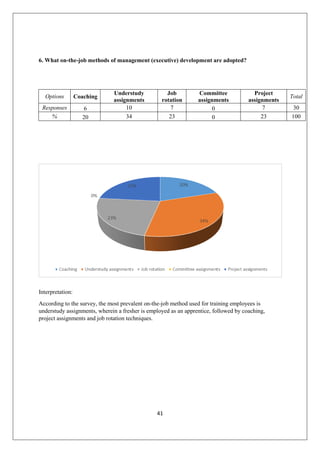
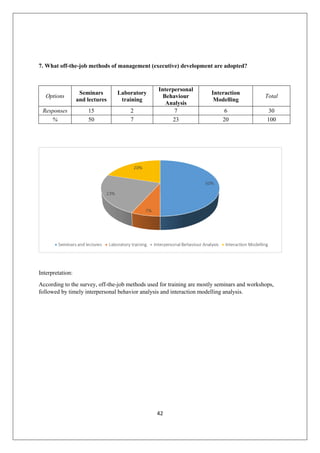
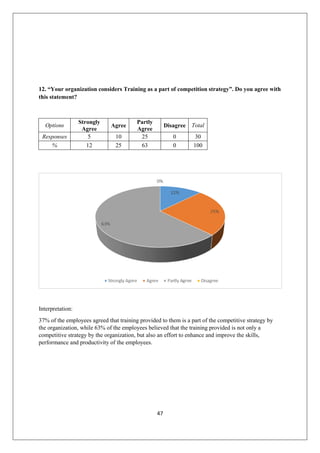
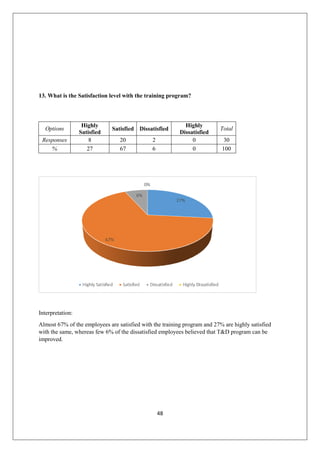
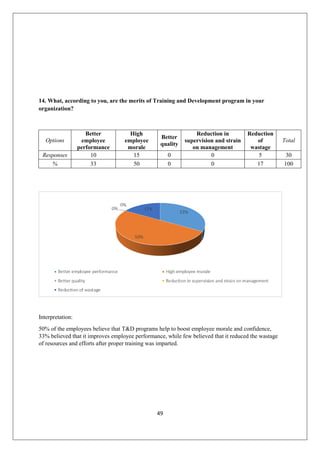
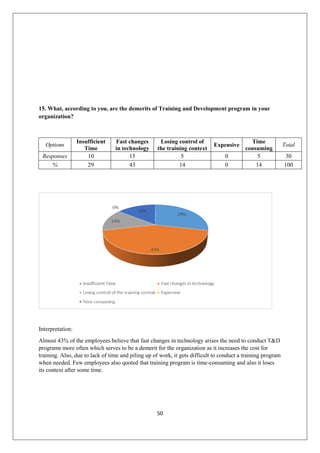
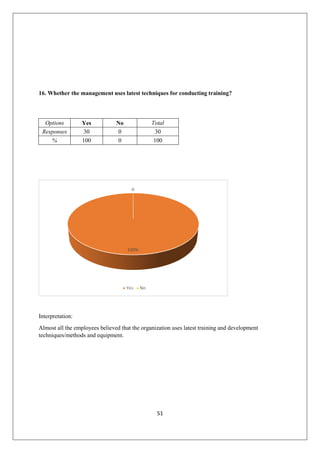
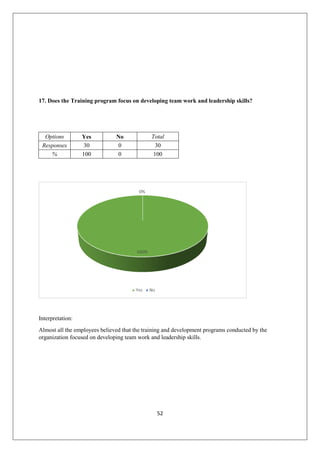
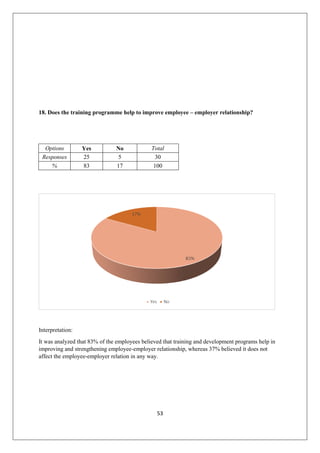
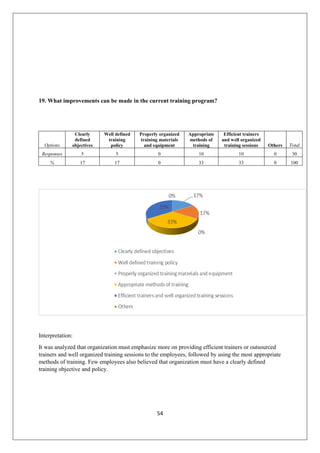
The document provides an in-depth overview of training and development at Jindal Saw Ltd, emphasizing its role in enhancing employee performance and organizational effectiveness. It includes detailed chapters on the organization's history, training objectives, research methodology, data analysis, findings, and recommendations, illustrating the importance of a skilled workforce in achieving business goals. The company, part of the O.P. Jindal Group, operates in various sectors, including large diameter pipes and seamless tubes, and focuses on employee welfare and innovative practices to maintain its market leadership.