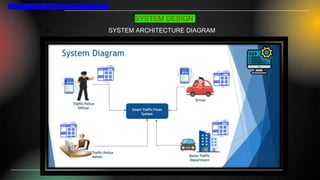
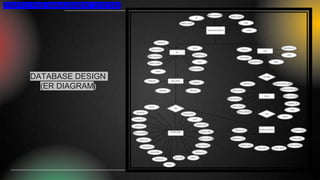
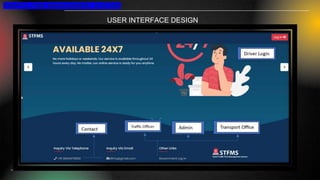
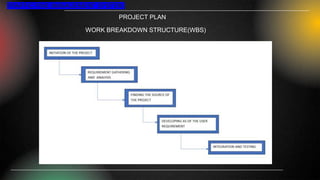
The smart traffic fine management system project aims to modernize traffic violation management by automating fine issuance and payment processes, utilizing technologies like PHP, MySQL, and JavaScript for enhanced efficiency and transparency. It addresses gaps found in traditional methods, including inefficiencies and data privacy concerns, while providing real-time processing and robust administrative tools for monitoring. The development faced challenges in team coordination and data management but prioritized user-centric design and risk management for reliable deployment.