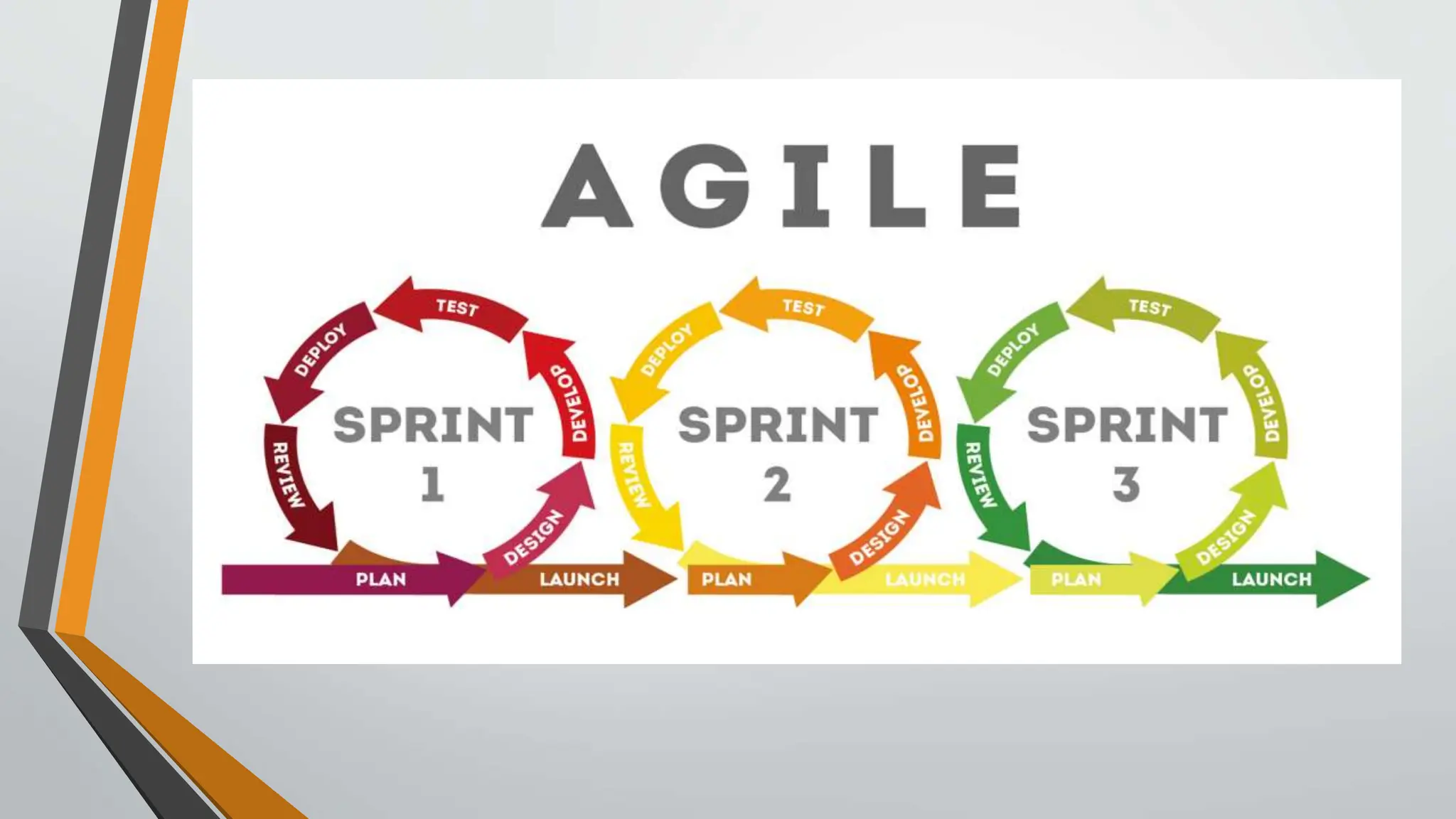
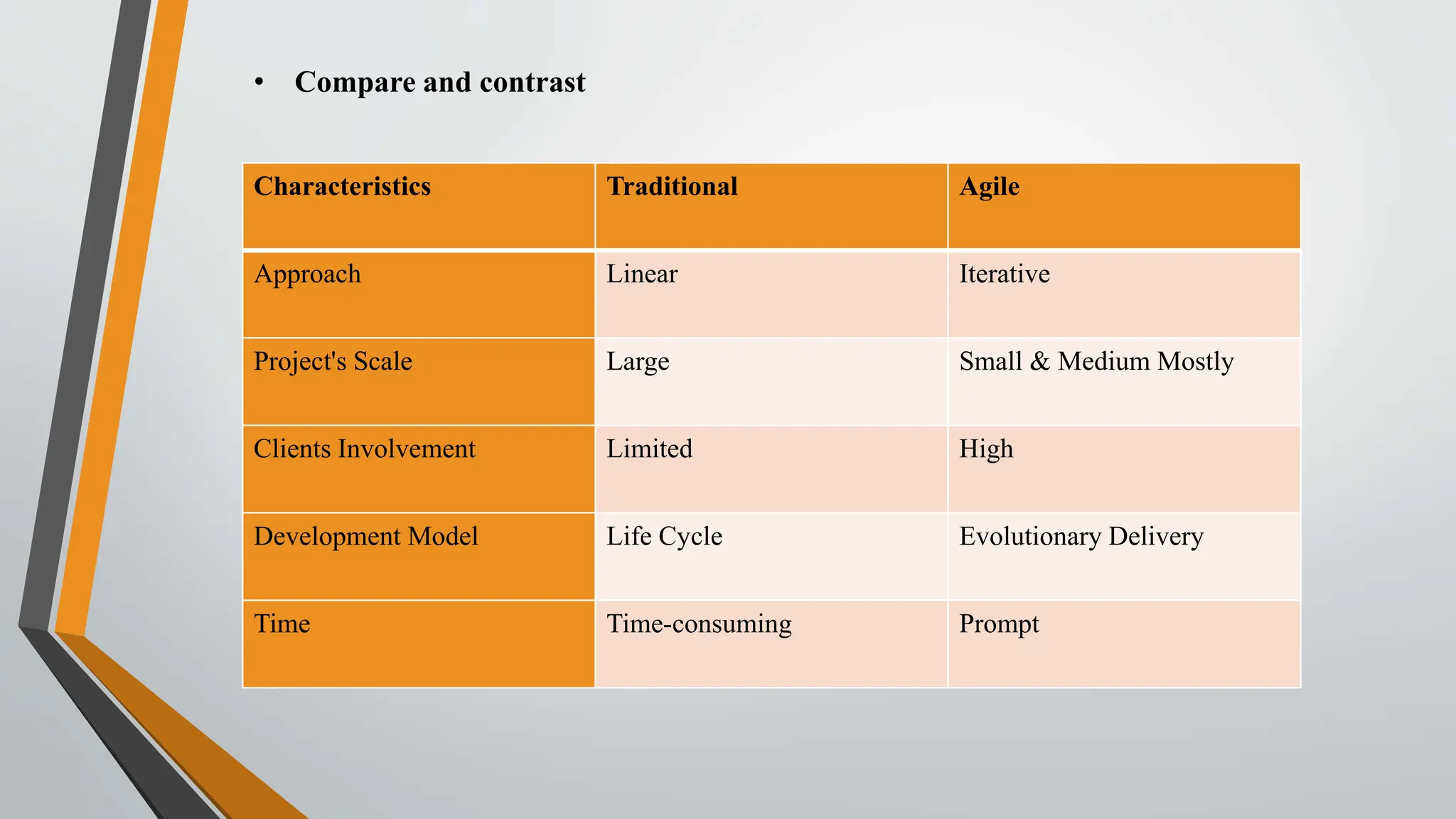
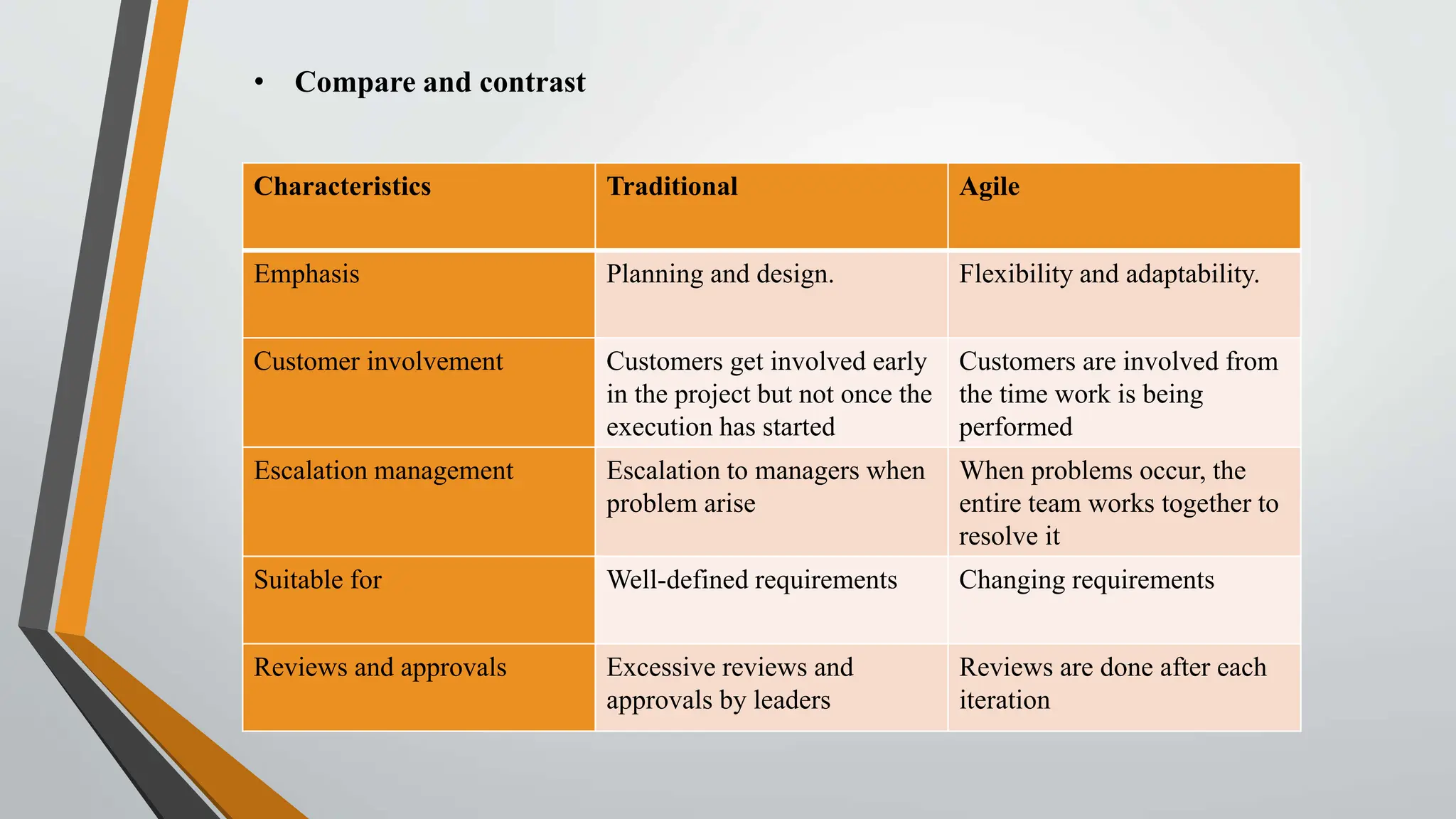
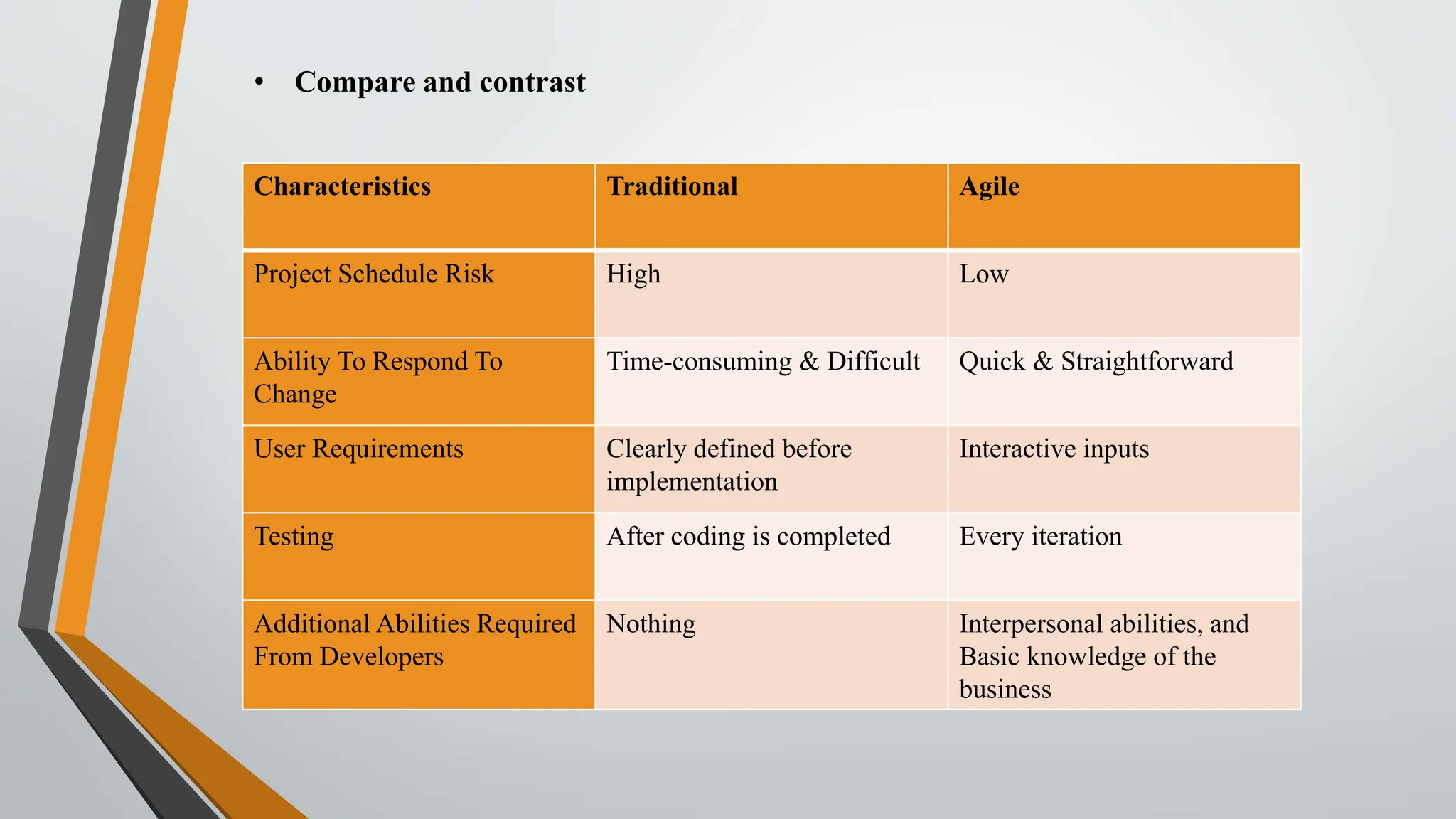
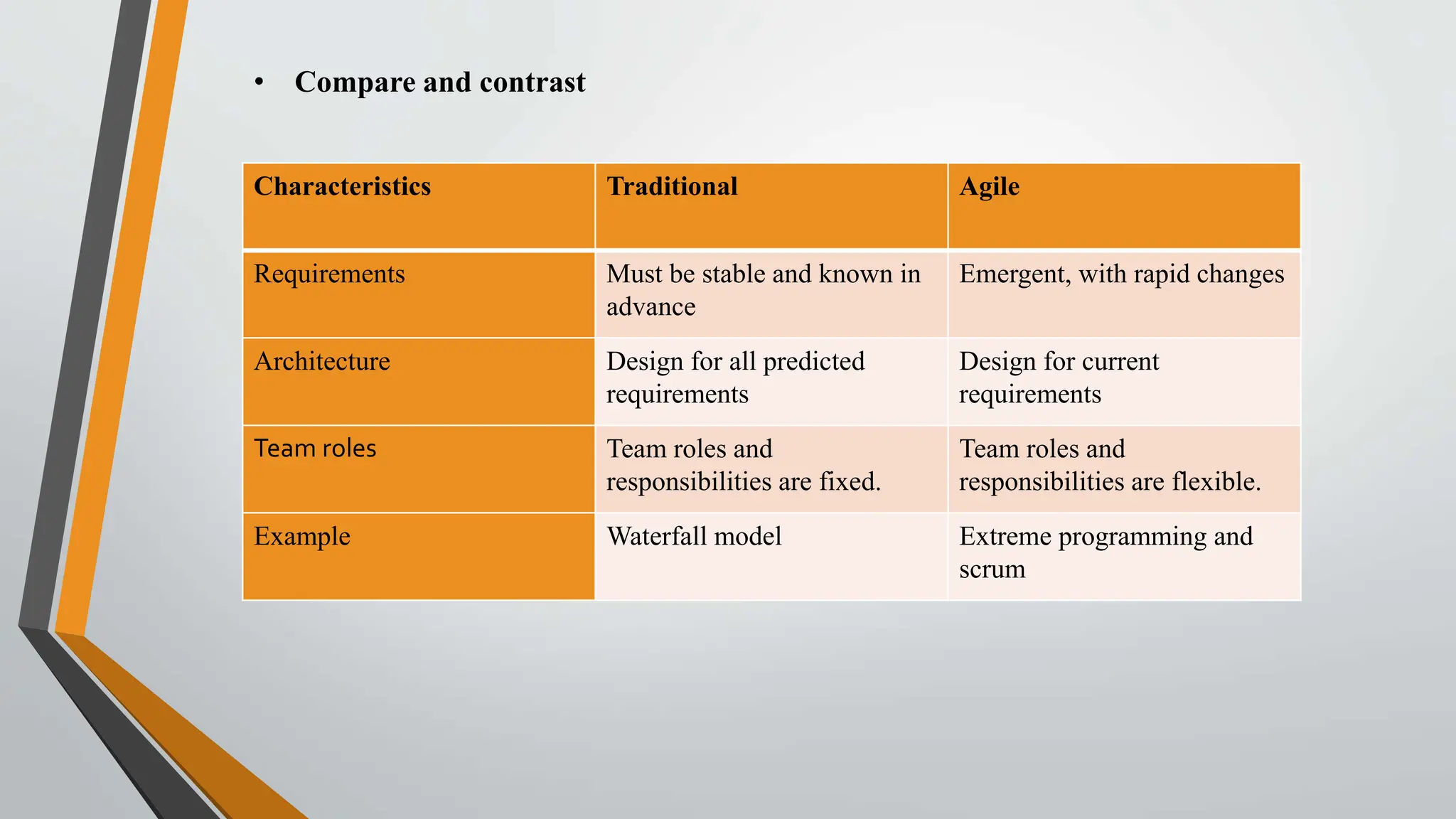
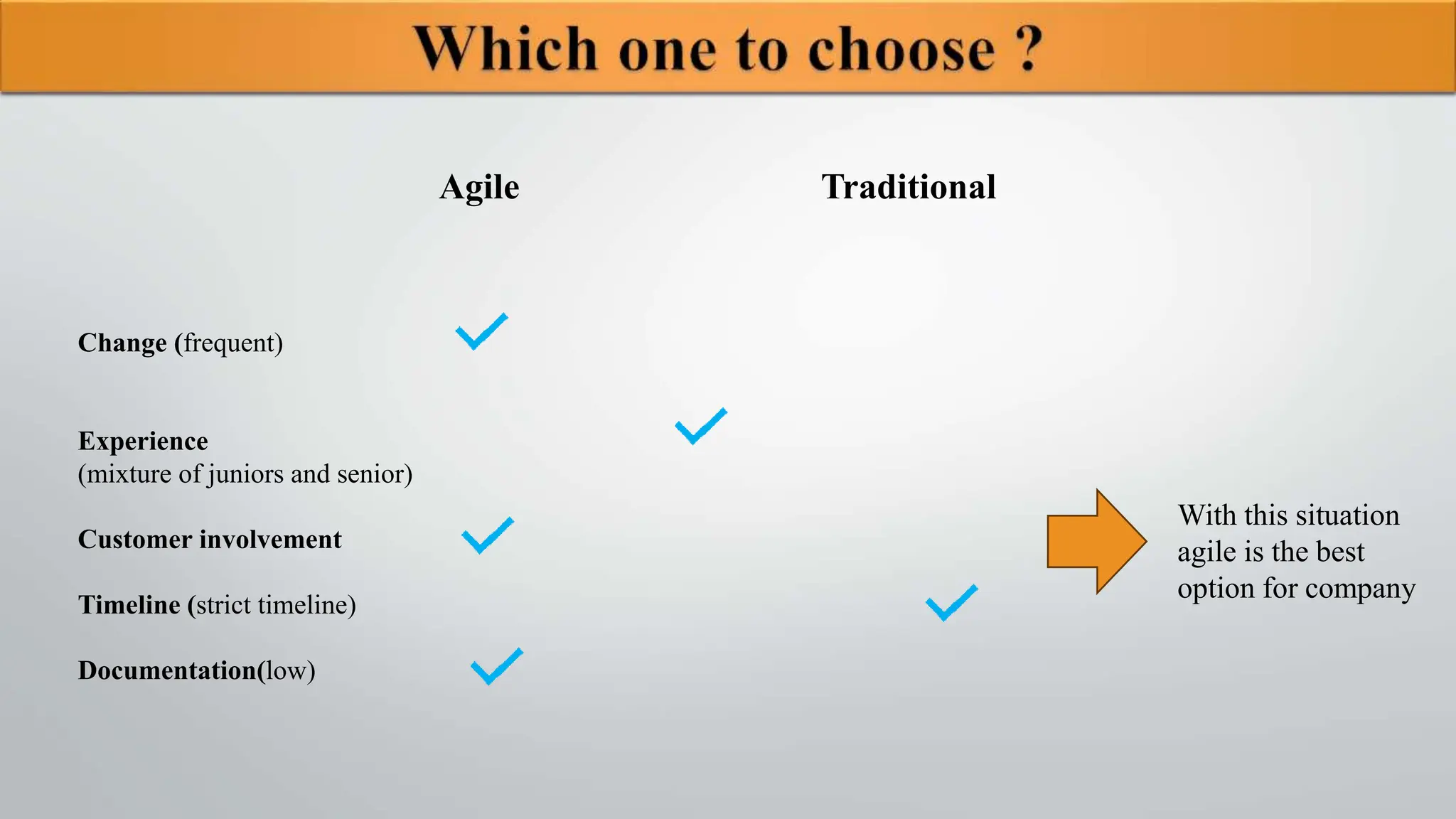
The document compares traditional project management and agile project management methodologies. Traditional project management follows a linear, predictive approach with extensive planning and limited customer involvement, while agile focuses on customer feedback, flexibility, and iterative processes. Agile methods demonstrate higher productivity, better quality, and lower costs compared to traditional methods, but face challenges such as poor resource planning and limited documentation.