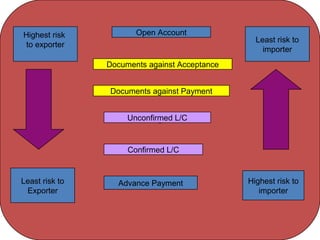
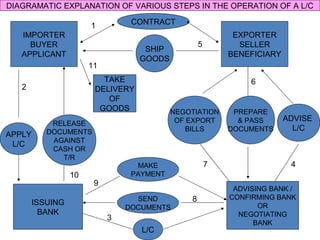
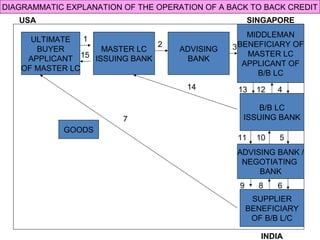
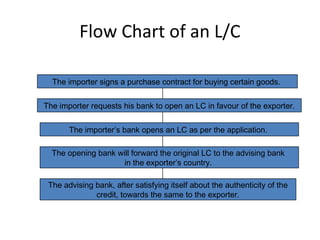
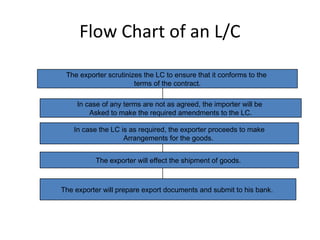
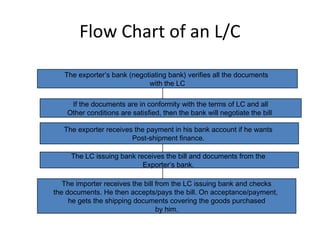
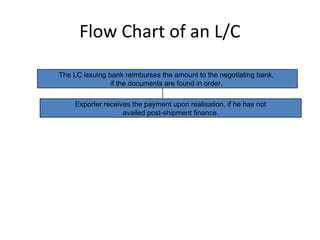
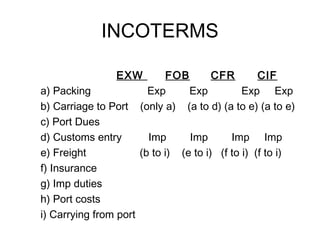
This document discusses various terms and concepts related to trade finance. It begins by defining key trade finance instruments like letters of credit, and explains the roles of parties involved like applicant, issuing bank, beneficiary, etc. It then discusses types of payments and credits in international trade like open account, documents against payment, and confirmed letters of credit. The rest of the document covers topics like pre-shipment and post-shipment finance, types of credits, documents used, risks involved, and regulatory requirements for trade finance. Diagrams are provided to illustrate the process and flow of letters of credit and back-to-back credits.