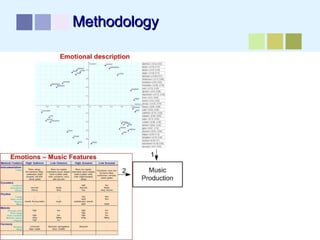
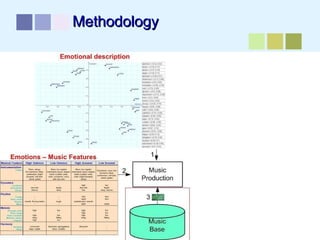
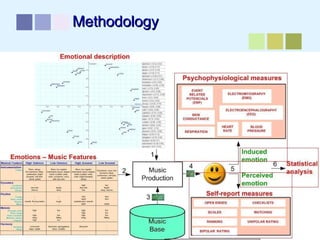
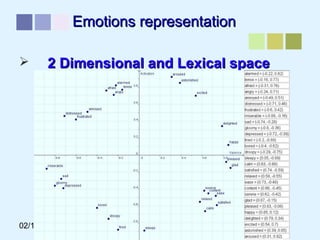
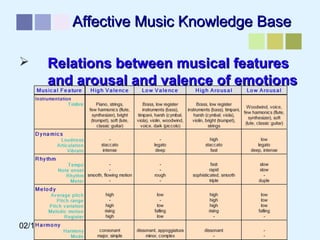
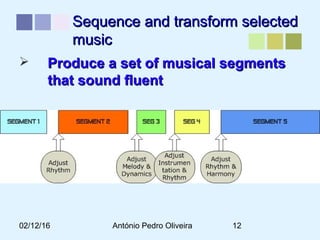
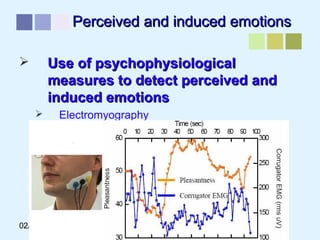
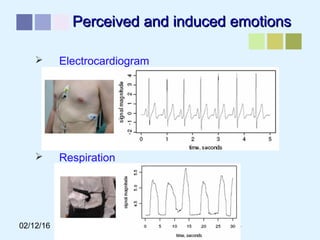
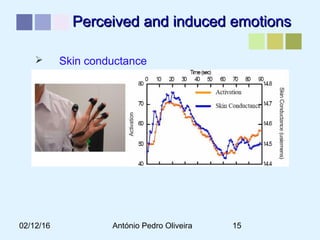
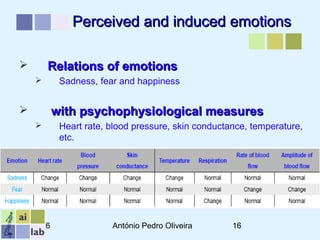
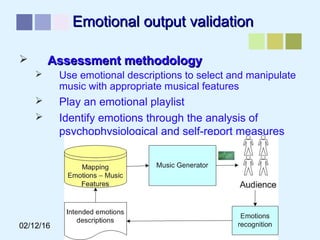
This document outlines a methodology for developing an affective-psychophysiological model of music production. The methodology involves representing emotions in dimensional space, creating an affective music knowledge base linking musical features to emotional arousal and valence, and manipulating music segments to produce emotional outputs. The emotional outputs will be validated using psychophysiological measures and self-reports to assess the perceived and induced emotions. The goal is to design a computational model of music production grounded in affective and psychophysiological foundations that can reliably express and induce emotions through music.