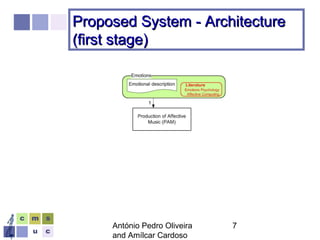
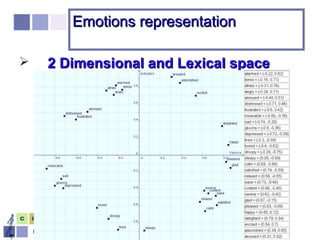
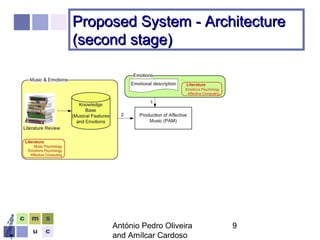
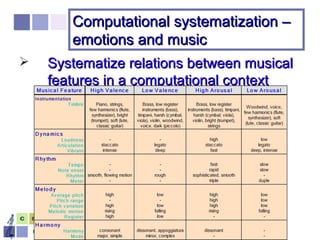
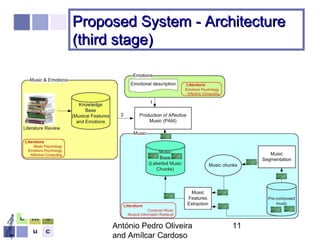
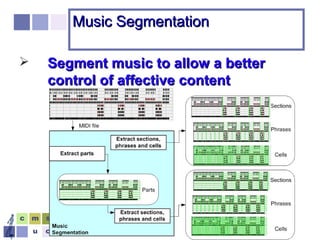
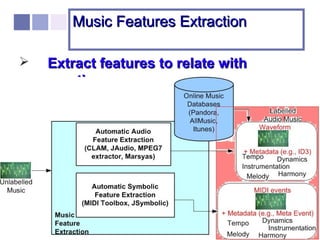
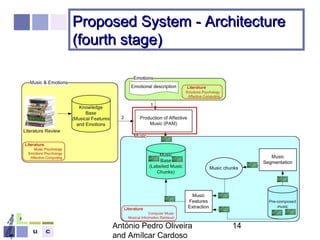
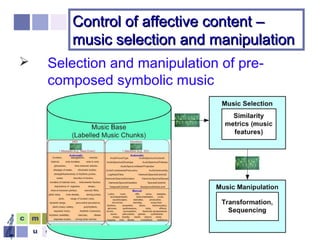
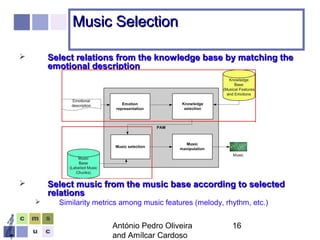
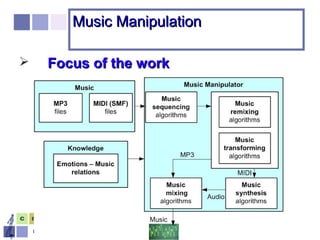
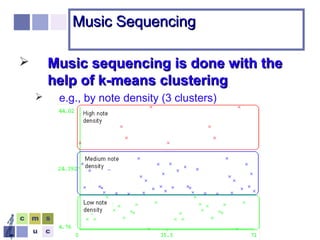
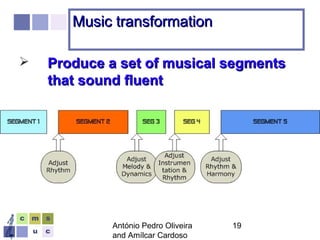
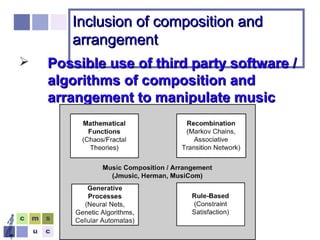
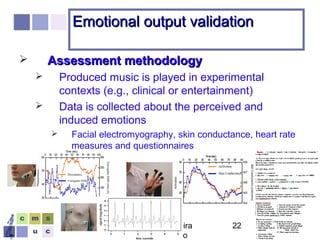
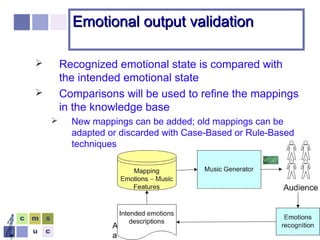
The document proposes a computer system to control affective content in music production. The system would have four main stages: 1) represent emotions in a two-dimensional or lexical space, 2) systematize relationships between music features and emotions, 3) segment and extract features from music, and 4) select and manipulate pre-composed music to match intended emotional descriptions. The emotional output of the manipulated music would be validated through experiments collecting physiological and subjective feedback to refine the system's mappings between music features and emotions.