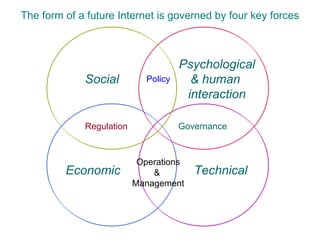
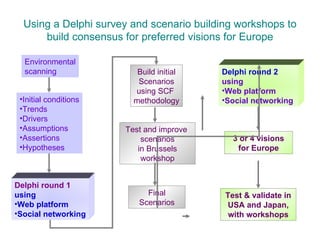
The document discusses key areas and forces that will shape the future of the Internet, based on a study conducted by the Oxford Internet Institute. It explores technological, social, economic, and regulatory trends and how they will interrelate. The goals of the study were to define possible future scenarios for the Internet and assess their socioeconomic impacts. The researchers used a Delphi survey technique and scenario building workshops to develop consensus visions for Europe's future Internet.