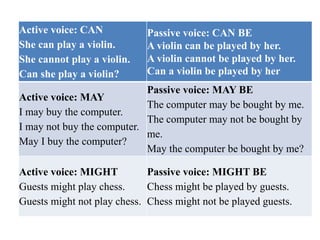
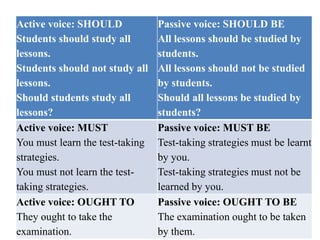
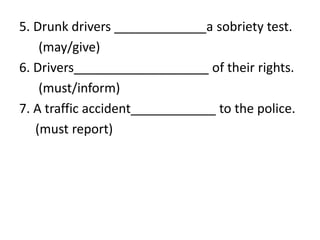
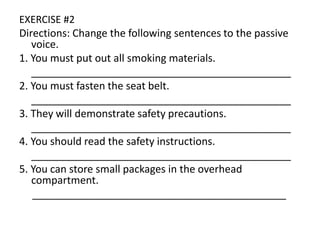
This document discusses the use of modal verbs in the passive voice. It provides examples of active and passive voice constructions using common modal verbs like can, may, must, should, etc. followed by exercises for readers to practice changing sentences between active and passive voice using modal verbs. Key points covered include:
- The basic structure of modal + be + past participle for passive voice
- Examples of active and passive constructions for various modal verbs
- Exercises transforming sentences between active and passive voice with modals