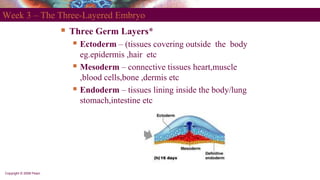
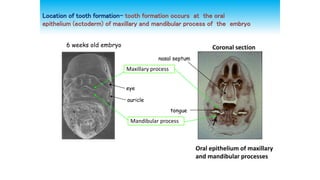
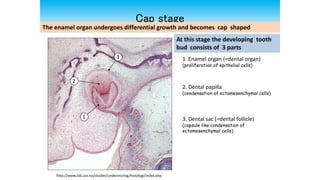
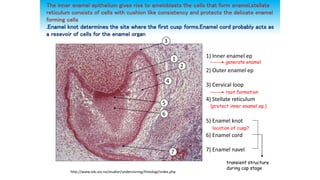
This document discusses tooth development from the early embryonic stages through formation of the tooth bud and germ. It describes how the three germ layers give rise to the tissues of the body, including the ectoderm forming the oral epithelium where teeth develop. Tooth formation begins with thickening of the oral epithelium into dental lamina, from which 10 tooth buds arise. The buds develop through bud, cap and bell stages as the enamel organ, dental papilla and follicle form. Different layers of the enamel organ and transient structures like the enamel knot are involved in shaping the developing tooth and determining cusp locations.