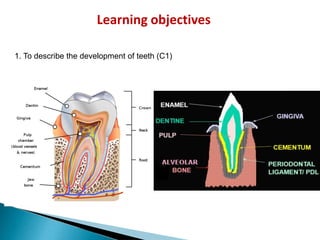
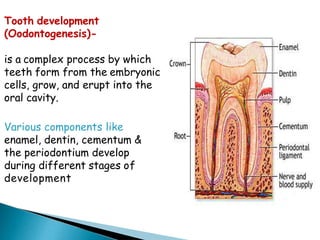
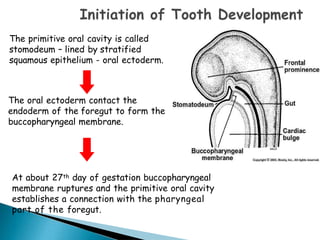
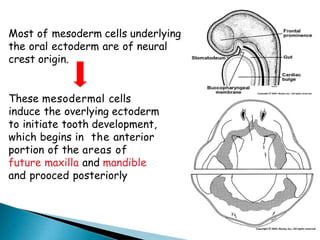
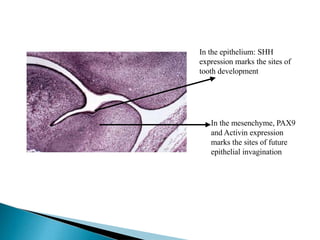
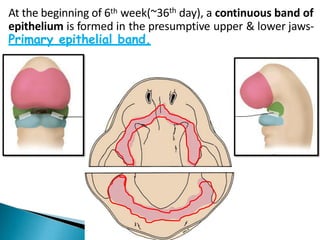
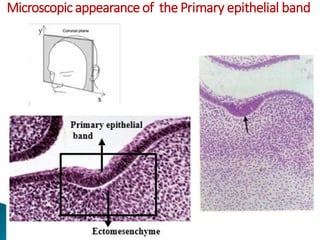
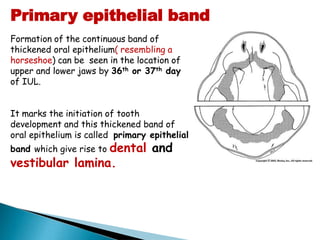
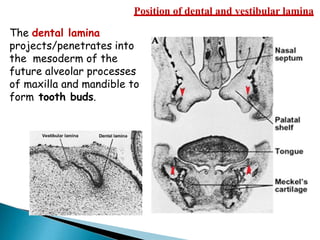
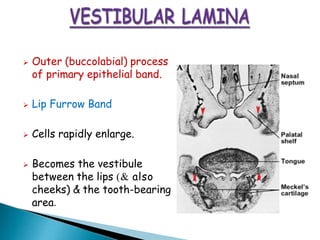
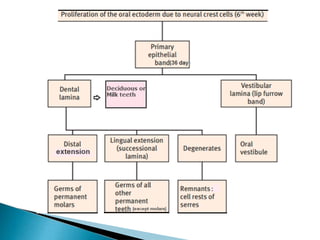
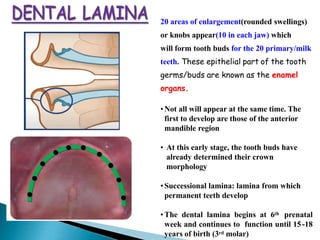
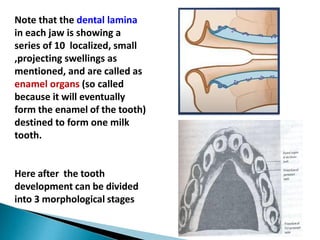
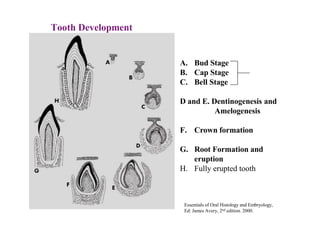
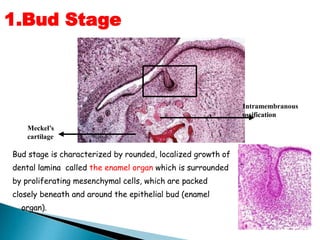
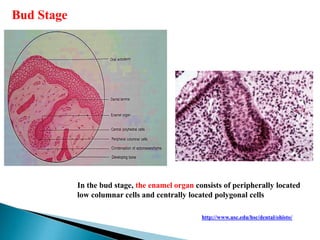
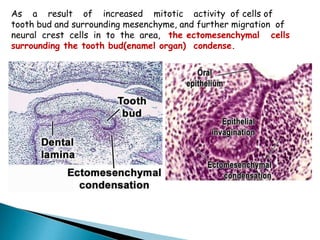
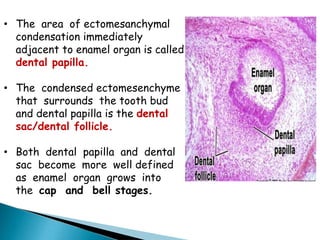
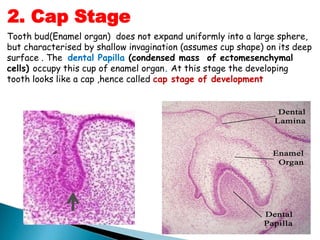
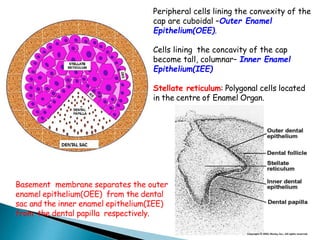
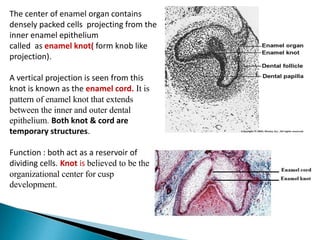
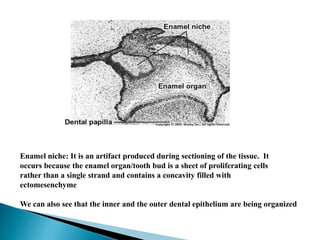
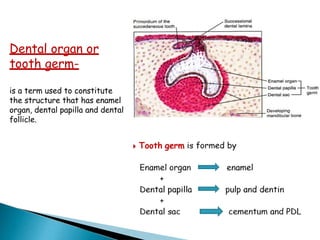
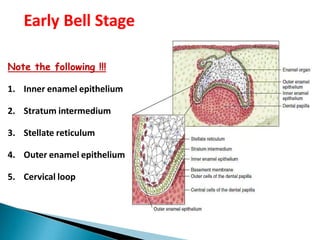
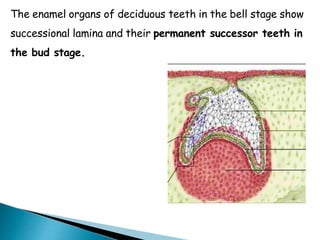
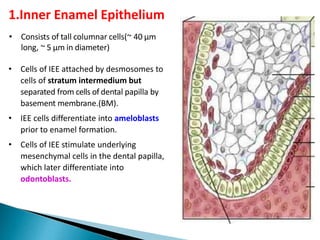
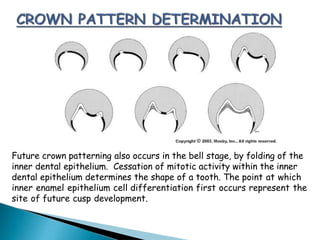
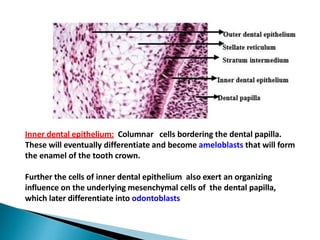
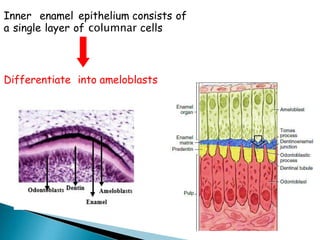
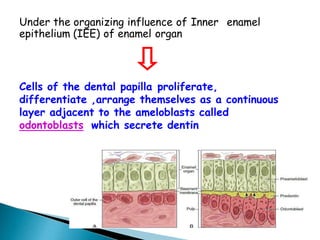
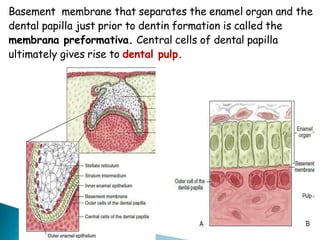
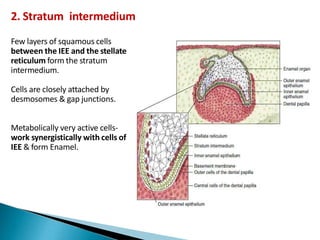
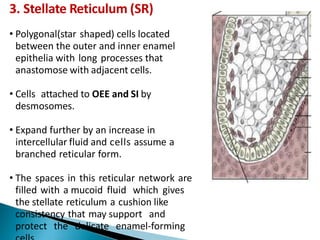
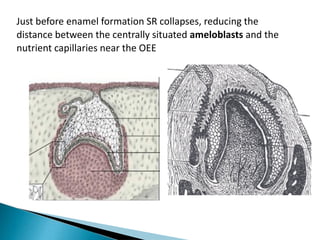
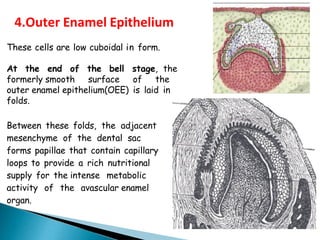
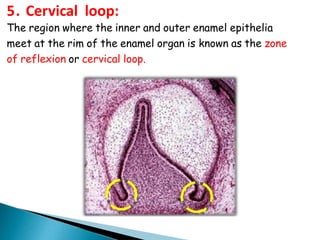
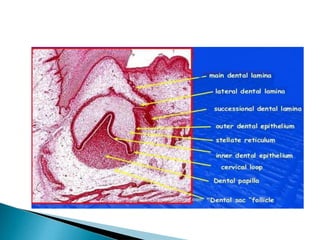
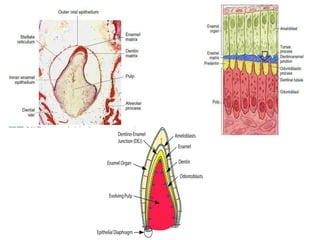
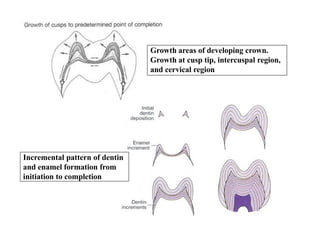
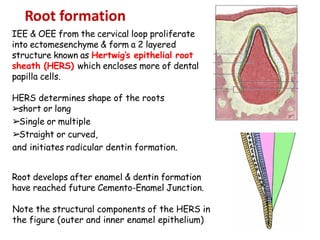
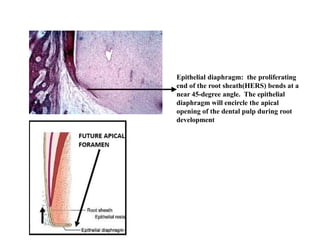
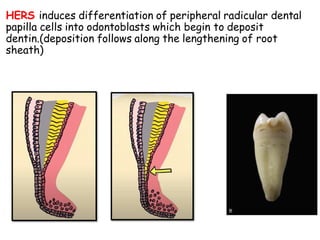
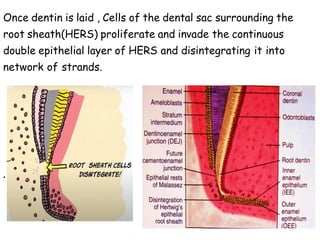
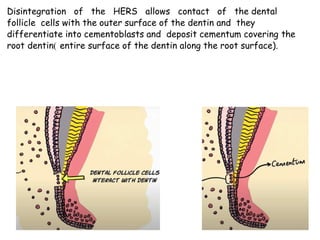
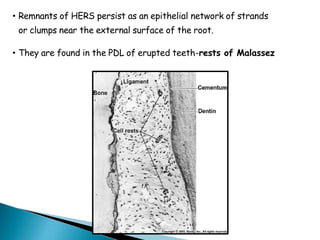
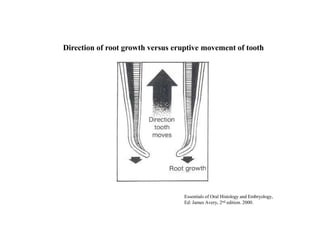
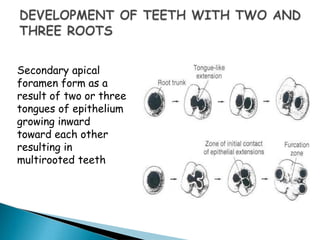
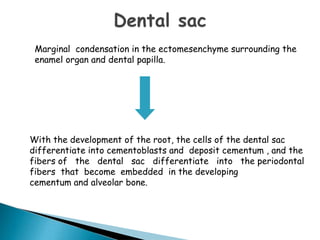
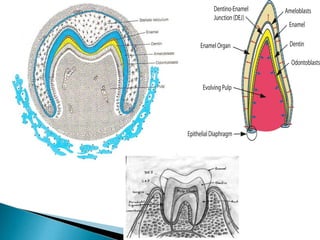
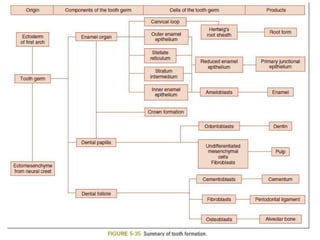
The development of teeth (odontogenesis) is a complex process where teeth form from embryonic cells and grow and erupt into the oral cavity. It begins around the 6th week of gestation with the formation of the primary epithelial band in the upper and lower jaws, from which the dental lamina develops and projects into the underlying mesenchyme to form tooth buds. These buds develop through the bud, cap, and bell stages to form the crown and root structures. Various cell types differentiate and interact to form enamel, dentin, cementum, and the periodontium. Root formation occurs after crown formation is complete, guided by Hertwig's epithelial root sheath which determines the root shape. Teeth continue developing and