Embed presentation
Download to read offline


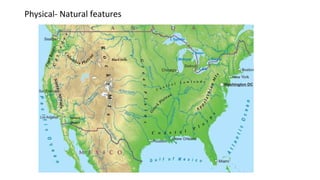

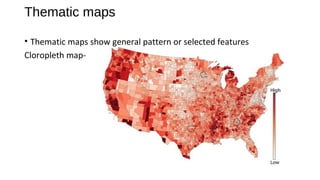
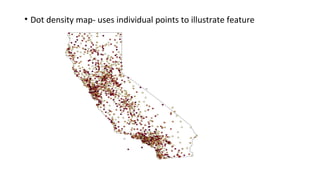


Maps and globes are tools used by geographers to represent Earth. Maps are 2D representations that show location and distances but inevitably distort the 3D globe when flattened. While lacking detail, globes maintain accuracy but are bulky. There are two main types of maps - reference maps like political and physical maps that show selected environmental details, and thematic maps that illustrate patterns or features through methods like color schemes or dot densities.






