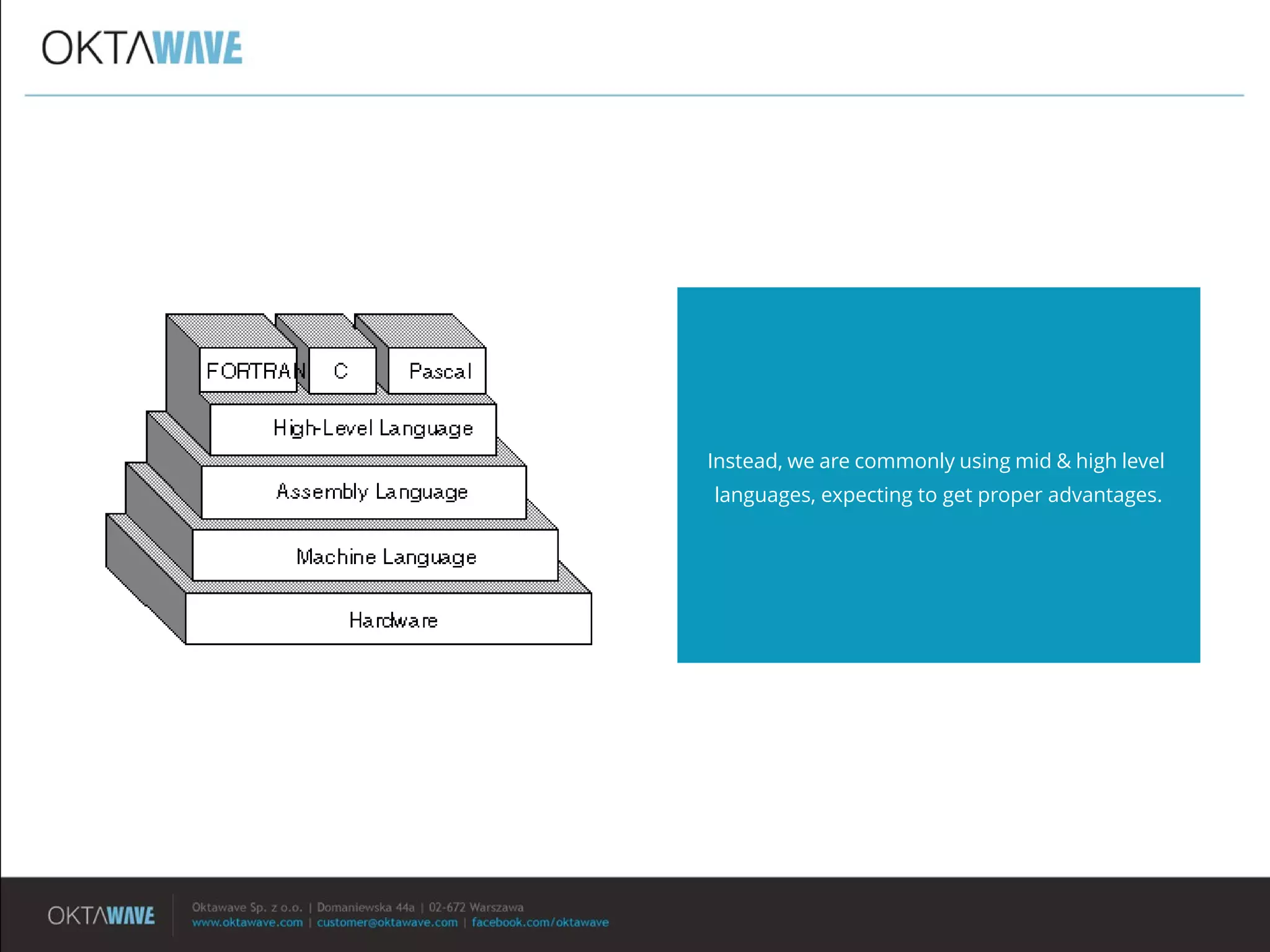
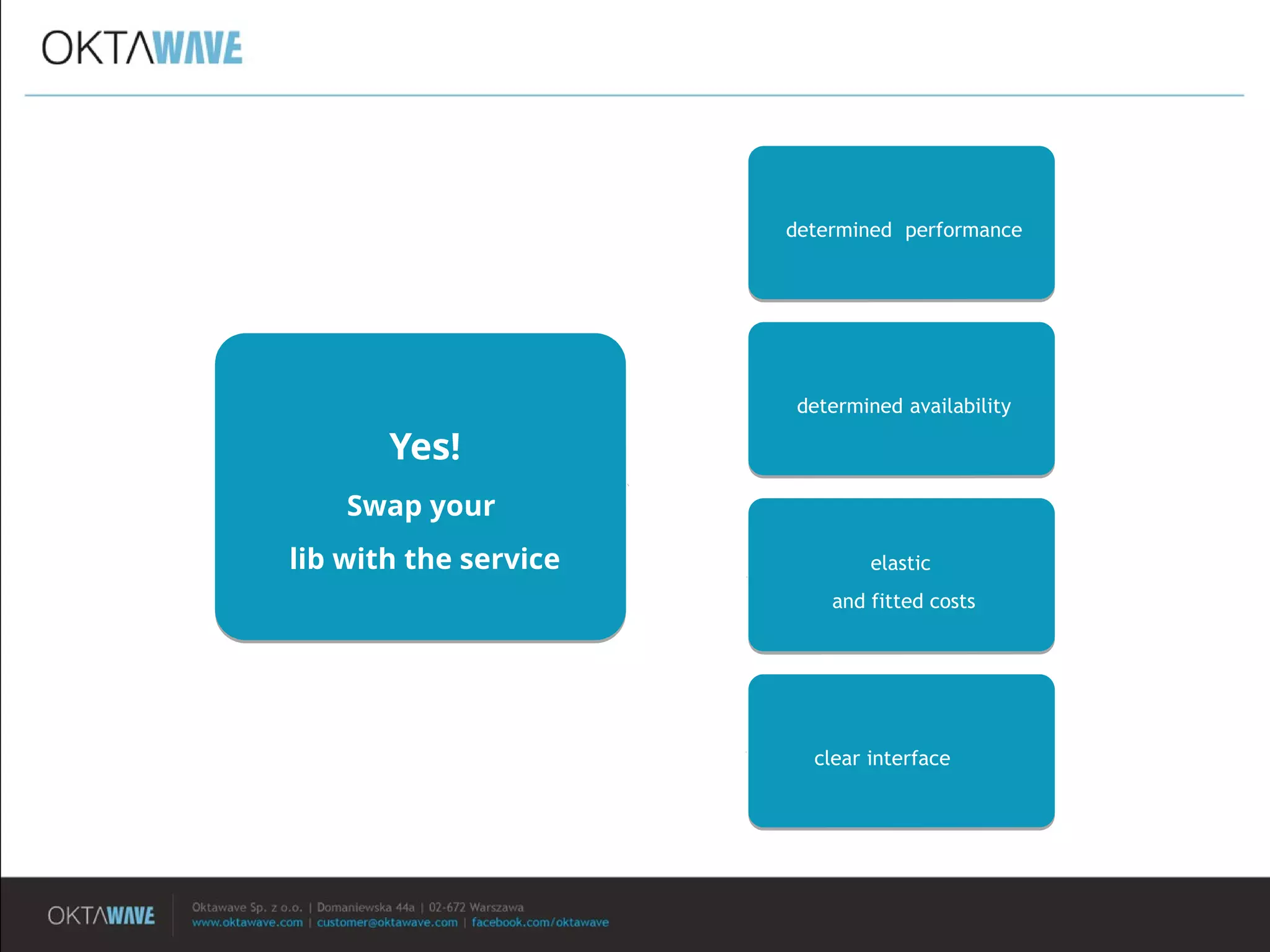
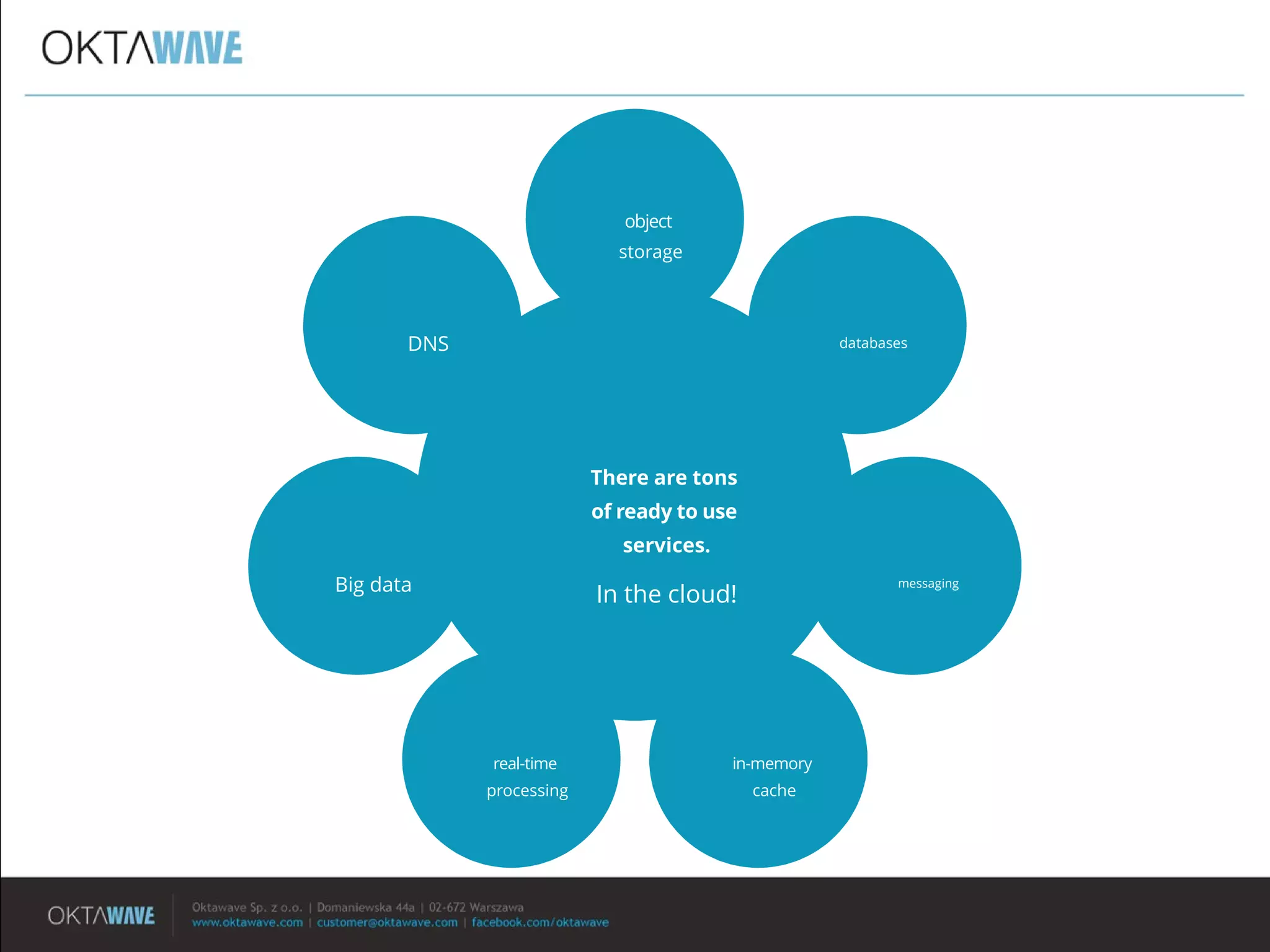
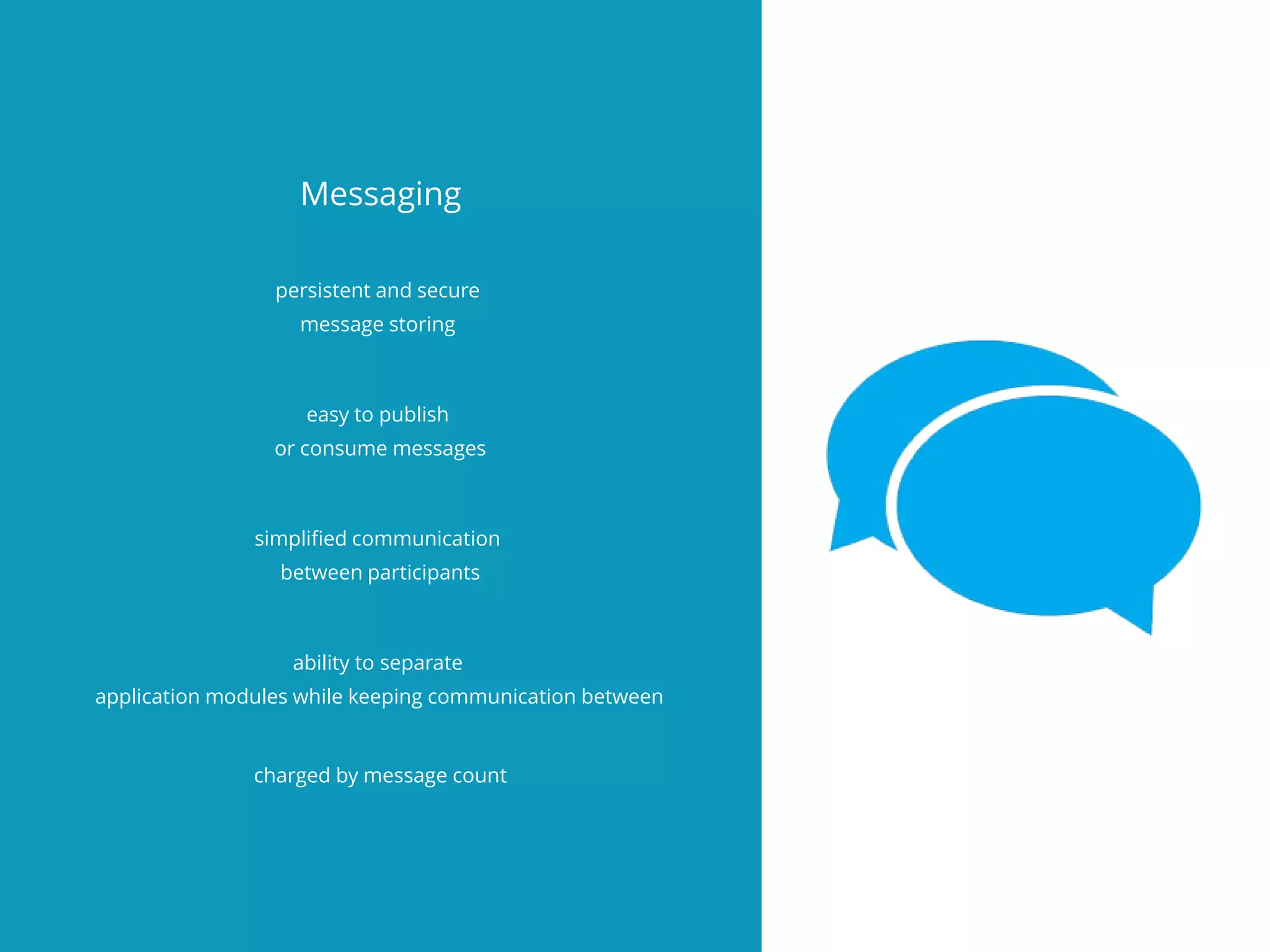
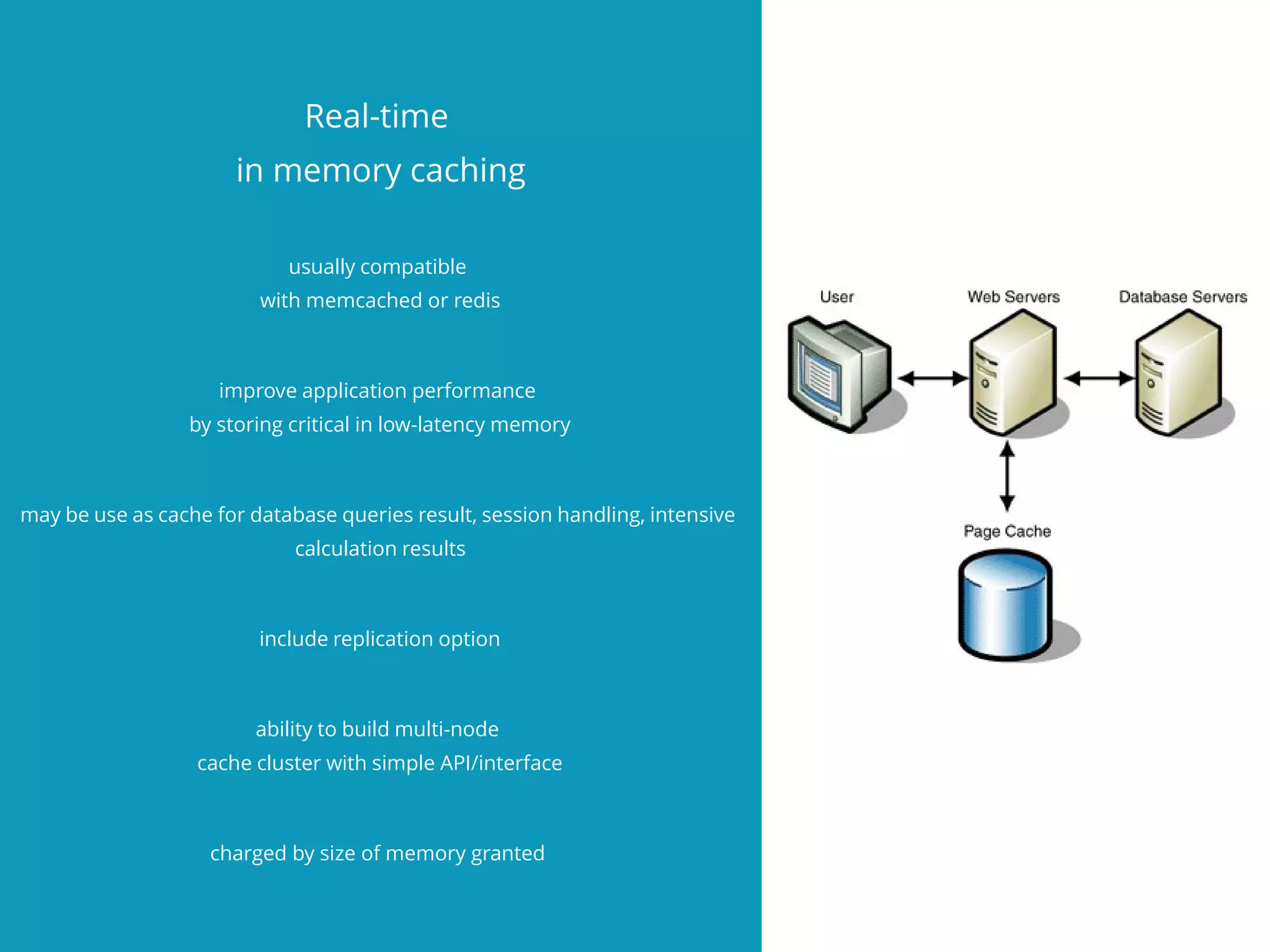
The document discusses the disadvantages of monolithic applications and advocates for a modular approach in cloud computing to enhance high availability. It highlights the benefits of using ready-made cloud services for functions such as storage, databases, and real-time processing, which can improve performance and scalability. The document encourages developers to exchange their libraries for cloud services to better manage application complexity and costs.