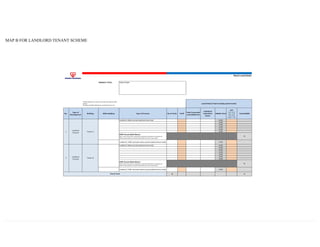
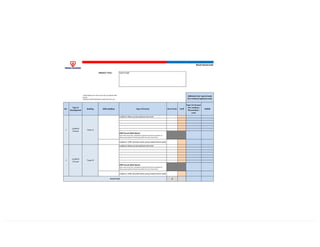
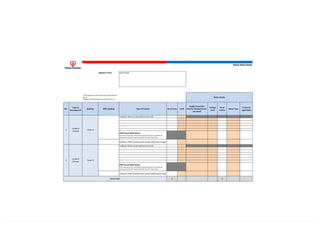
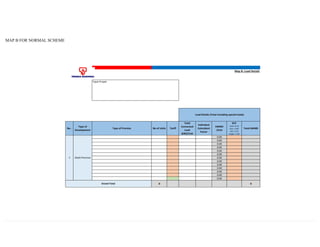
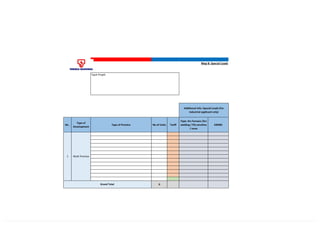
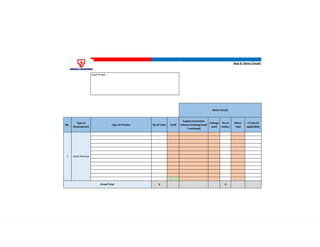
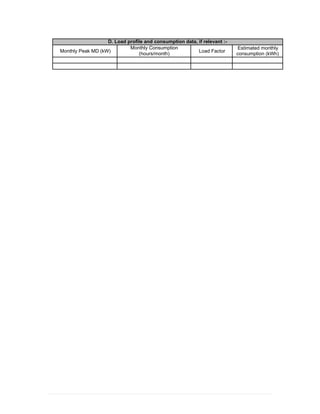
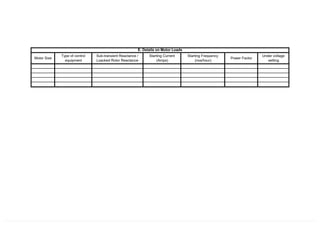
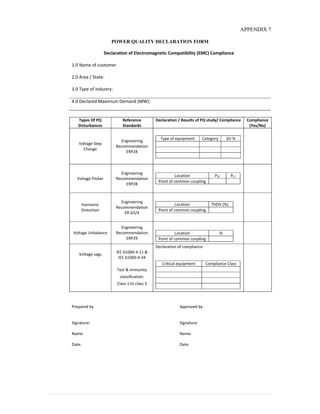
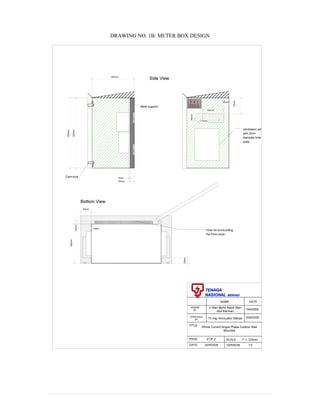
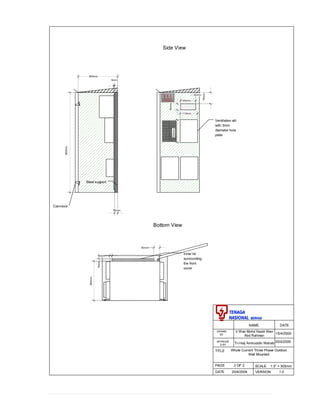
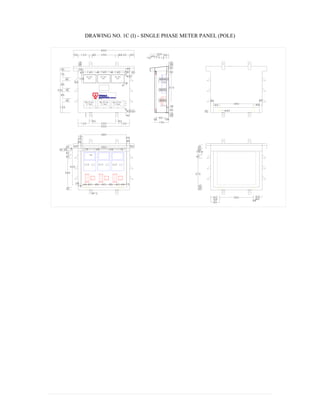
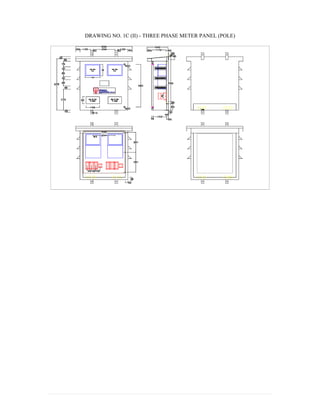
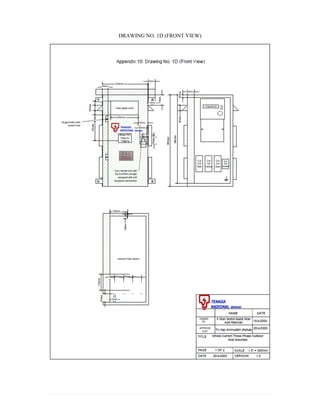
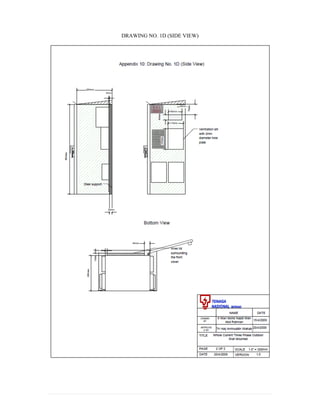
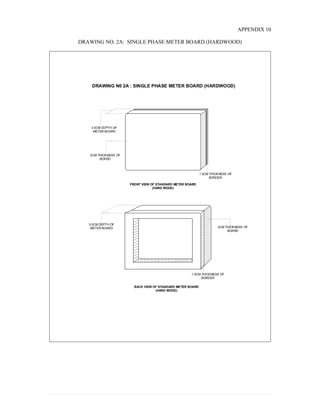
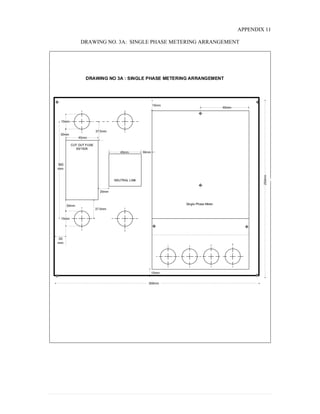
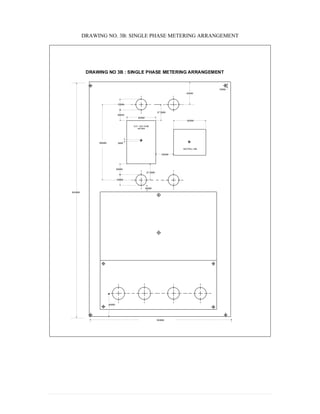
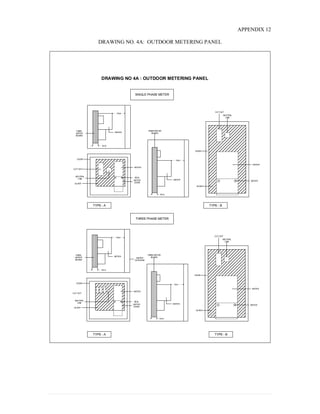
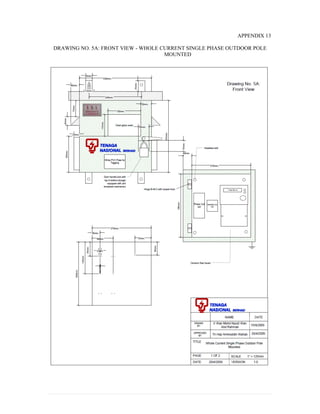
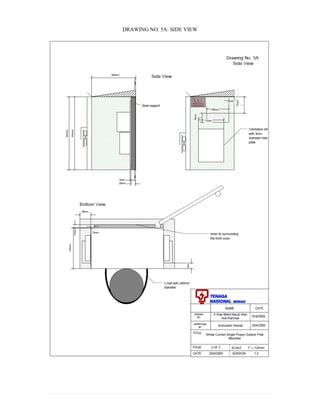
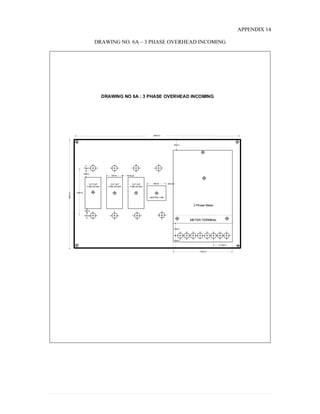
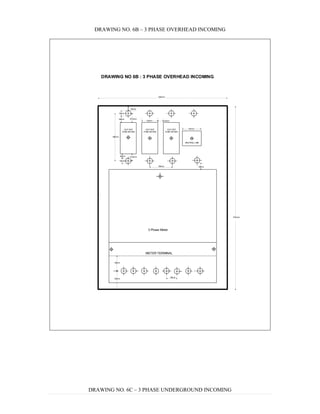
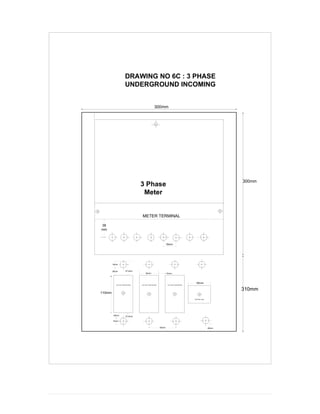
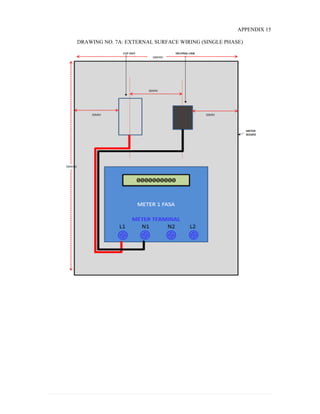
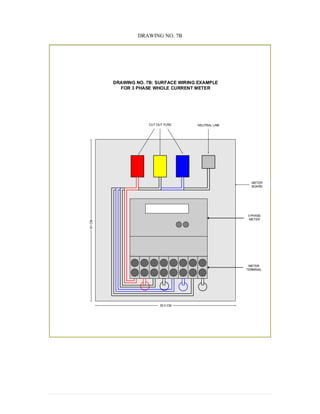
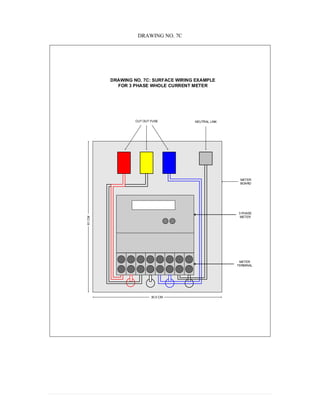
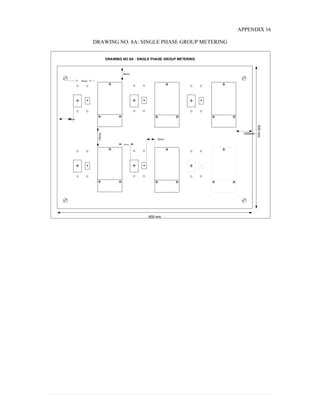
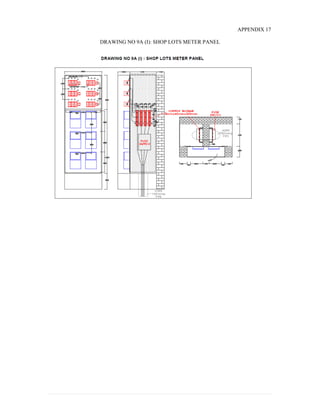
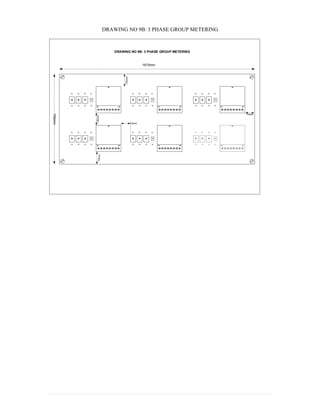
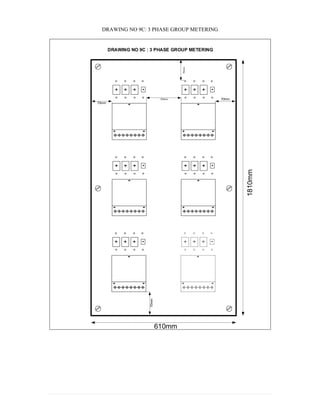
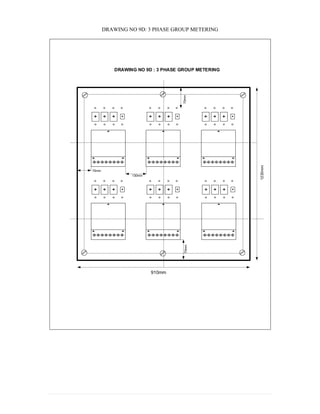
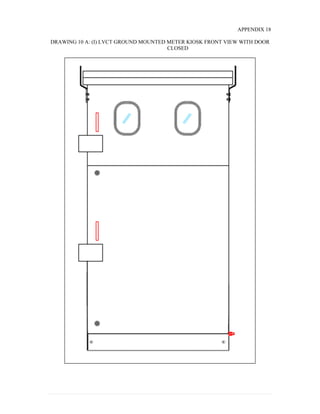
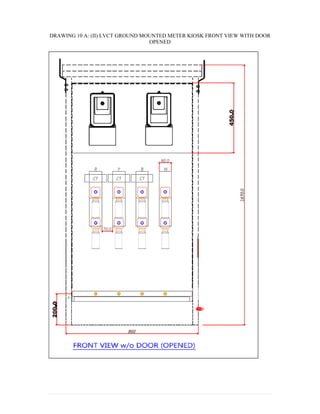
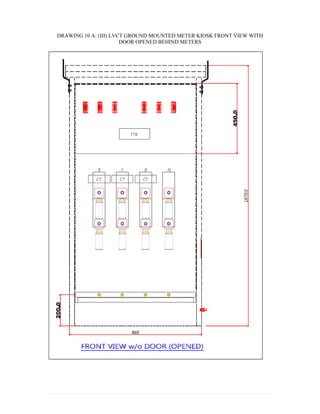
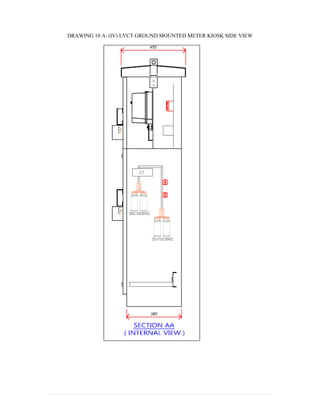
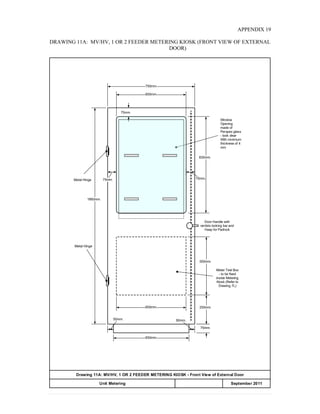
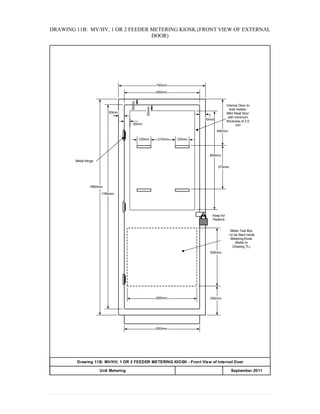
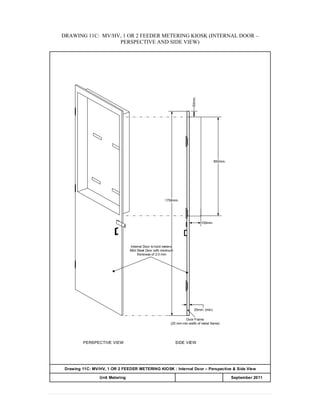
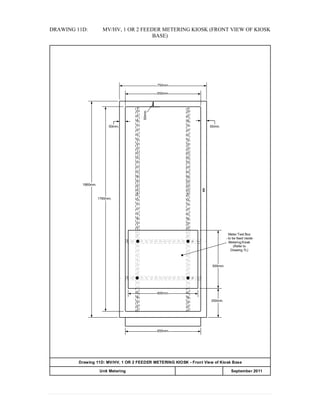
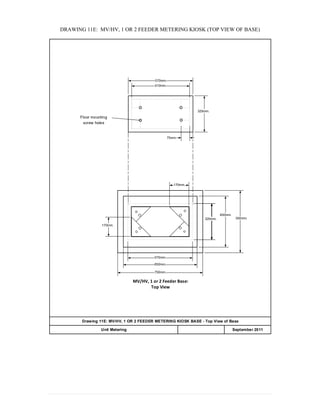
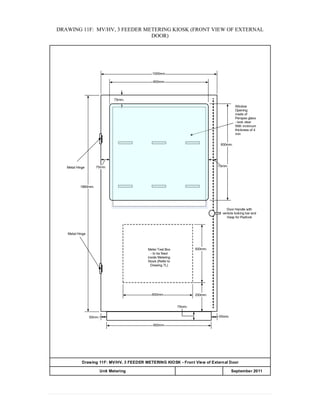
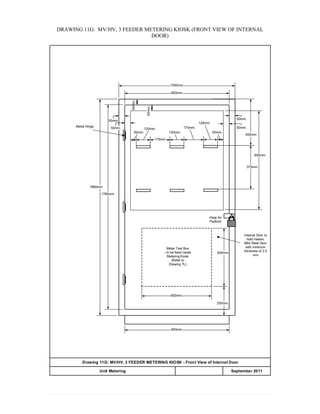
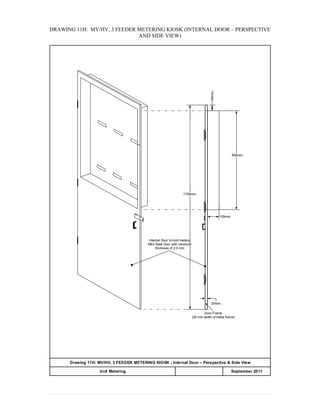
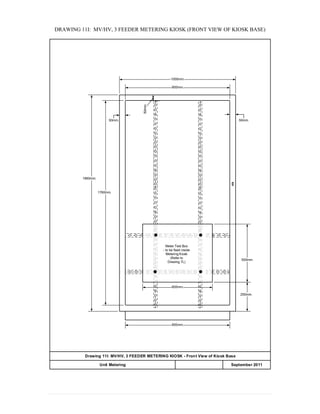
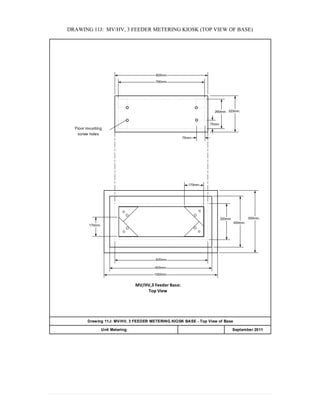
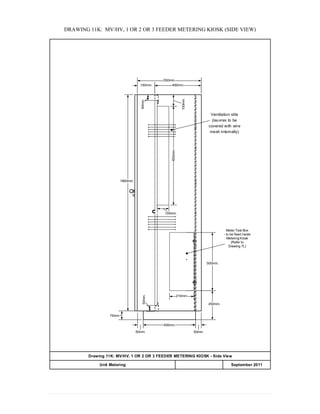
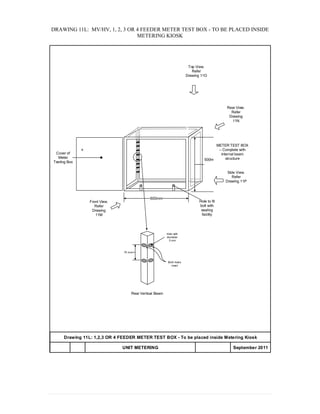
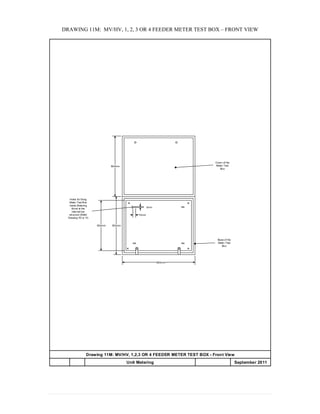
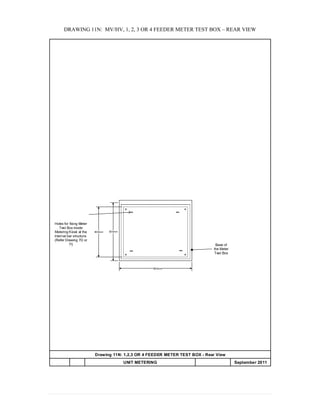
This document provides information on TNB's electricity system and supply application processes. It discusses TNB's divisions, electrical system including voltages and frequencies, types of supplies such as load-based applications (under or over 100A), standby supplies, temporary supplies, and multi-tenanted premises. The document outlines the application process for loads under and over 100A, as well as for streetlights. It also discusses planning, design, demand estimation and connection guidelines.