1) The patient experienced a transient loss of consciousness while exercising on a bike. She had no warning symptoms, tongue biting, or confusion after. Witnesses reported spasming but no seizure activity.
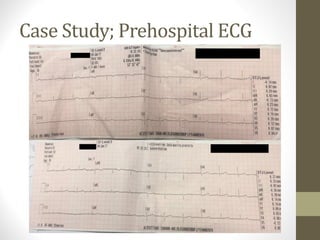
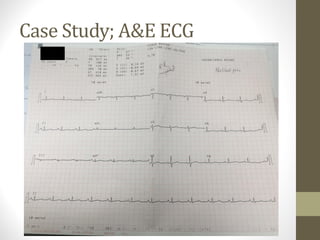
2) Initial assessment found no abnormalities on exam, ECG, or bloodwork. Prehospital and hospital ECGs were normal.
3) The syncope is believed to be non-cardiac and vasovagal in nature, likely precipitated by dehydration and eating disorder contributing factors. The patient was discharged with reassurance and advice.