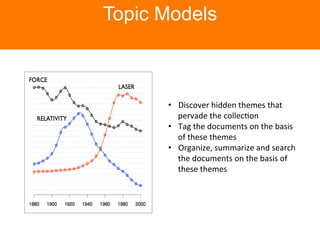
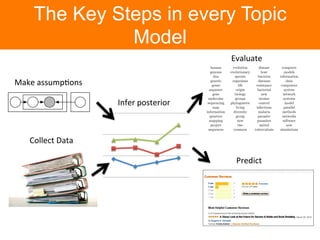
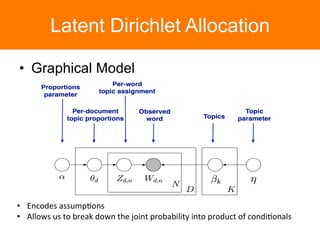
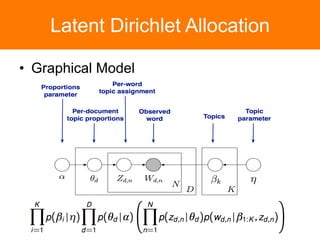
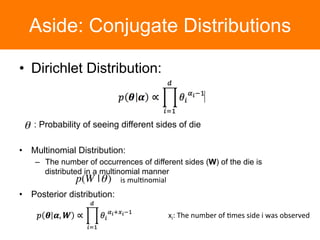
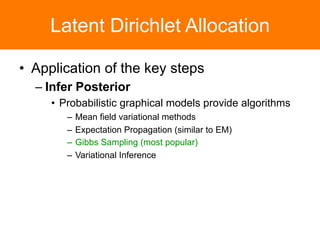
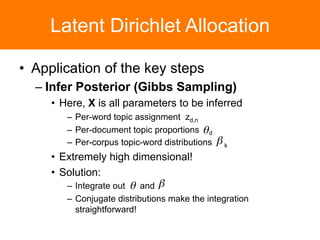
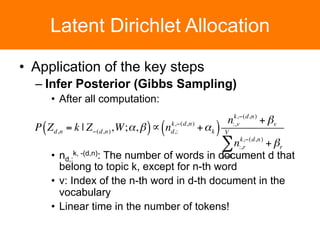
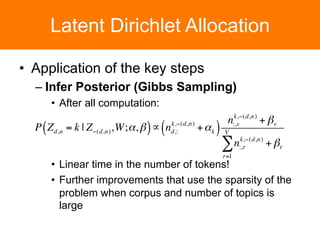
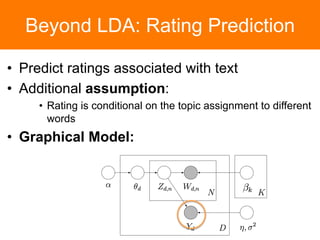
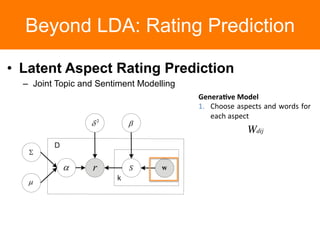
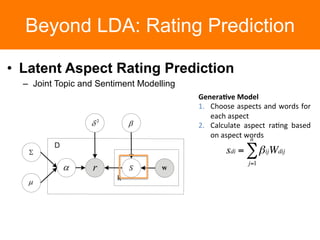
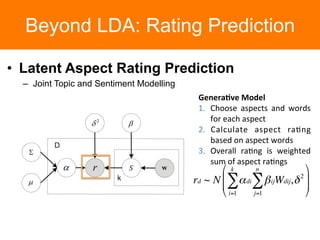
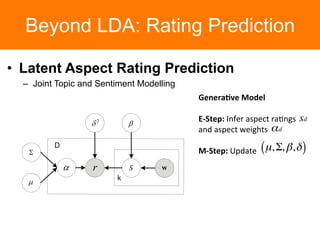
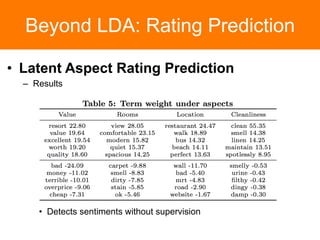
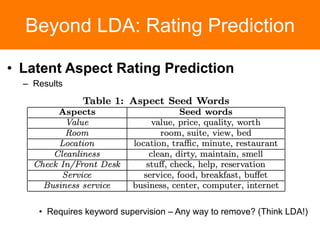
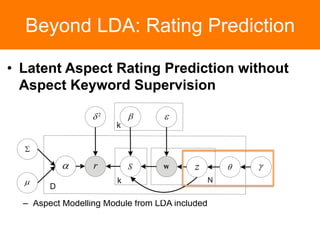
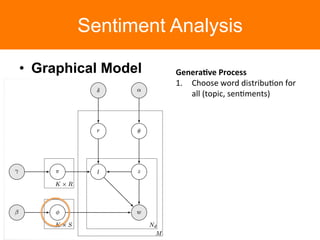
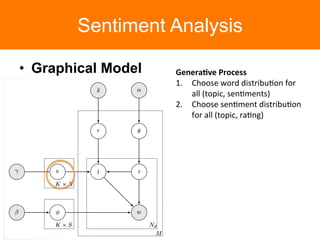
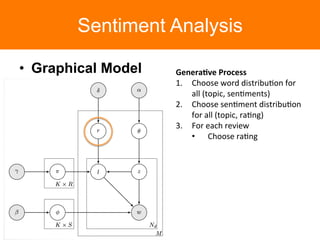
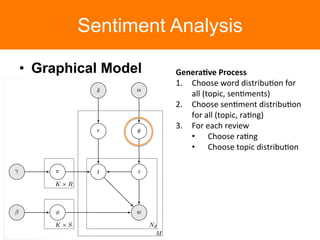
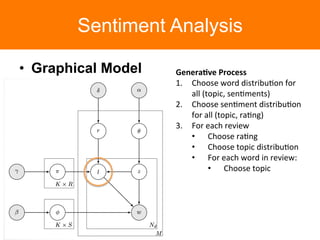
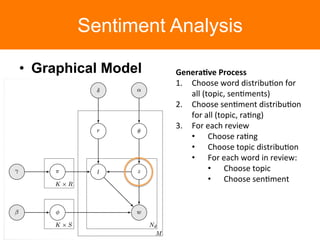
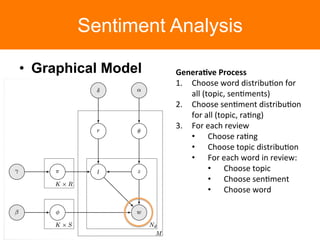
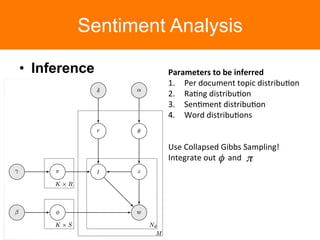
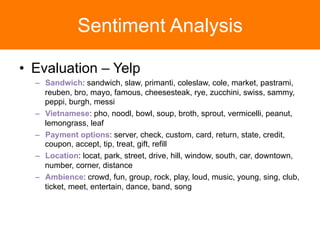
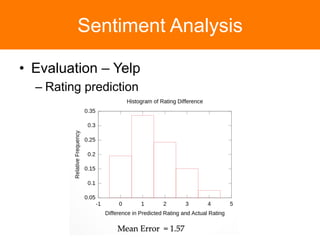
The document is a tutorial on topic modeling, covering concepts such as probabilistic topic models, their applications, and training/inference methods, particularly focusing on Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA). It discusses the evaluation of topic models and introduces advanced concepts like sentiment analysis and rating prediction. Additionally, it outlines future directions in topic modeling, emphasizing the need for model selection and incorporating linguistic structures.