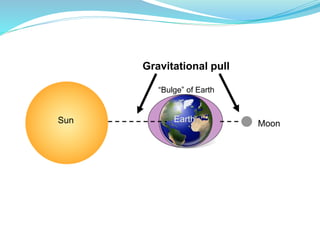
The document summarizes tides and their causes. Tides are the daily rise and fall of sea levels caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and Earth's rotation. The Moon's closer proximity to Earth means it has a stronger gravitational pull than the Sun. This pull creates tidal bulges in the oceans on the sides facing and facing away from the Moon. As Earth rotates, different locations experience high and low tides passing through these bulges. Spring tides occur during full and new Moons when the Sun and Moon pull together, creating higher tides. Neap tides happen at half Moons when the Sun and Moon pull at right angles, resulting in lower tides.