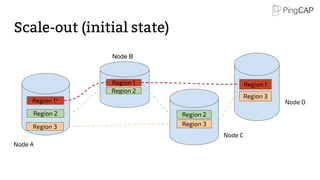
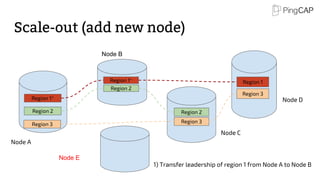
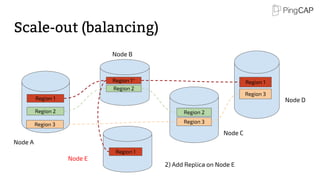
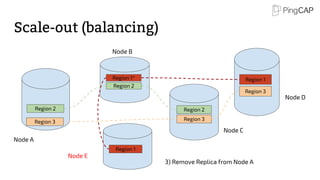
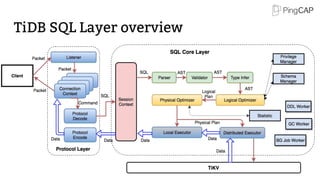
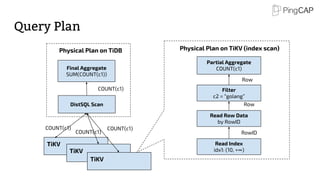
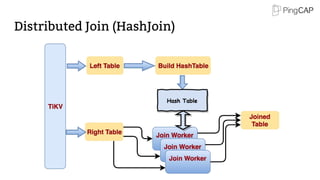
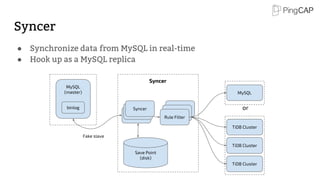
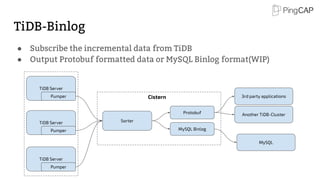
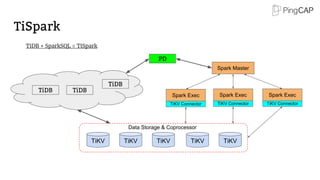
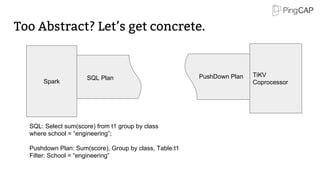
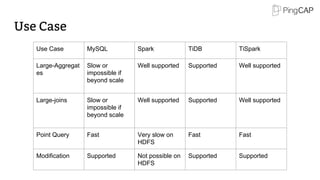
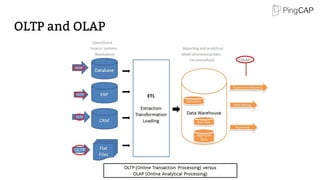
This document provides an overview of TiDB, a hybrid transactional and analytical processing (HTAP) database built to handle big data efficiently by integrating OLTP and OLAP capabilities. It details its architecture including the Tikv storage layer, the Raft consensus algorithm for data safety, and its SQL capabilities for distributed computing. The document also discusses integration with big data ecosystems and future improvements planned for TiDB.






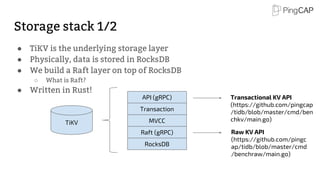
![RocksDB
Instance
Region 1:[a-e]
Region 3:[k-o]
Region 5:[u-z]
...
Region 4:[p-t]
RocksDB
Instance
Region 1:[a-e]
Region 2:[f-j]
Region 4:[p-t]
...
Region 3:[k-o]
RocksDB
Instance
Region 2:[f-j]
Region 5:[u-z]
Region 3:[k-o]
... RocksDB
Instance
Region 1:[a-e]
Region 2:[f-j]
Region 5:[u-z]
...
Region 4:[p-t]
Raft group
Storage stack 2/2
● Data is organized by Regions
● Region: a set of continuous key-value pairs
RPC (gRPC)
Transaction
MVCC
Raft
RocksDB
···](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataintidb1-171110051658/85/TiDB-for-Big-Data-9-320.jpg)
![Dynamic Multi-Raft
● What’s Dynamic Multi-Raft?
○ Dynamic split / merge
● Safe split / merge
Region 1:[a-e]
split Region 1.1:[a-c]
Region 1.2:[d-e]split](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataintidb1-171110051658/85/TiDB-for-Big-Data-10-320.jpg)
![Safe Split: 1/4
TiKV1
Region 1:[a-e]
TiKV2
Region 1:[a-e]
TiKV3
Region 1:[a-e]
raft raft
Leader Follower Follower
Raft group](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataintidb1-171110051658/85/TiDB-for-Big-Data-11-320.jpg)
![Safe Split: 2/4
TiKV2
Region 1:[a-e]
TiKV3
Region 1:[a-e]
raft raft
Leader
Follower Follower
TiKV1
Region 1.1:[a-c]
Region 1.2:[d-e]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataintidb1-171110051658/85/TiDB-for-Big-Data-12-320.jpg)
![Safe Split: 3/4
TiKV1
Region 1.1:[a-c]
Region 1.2:[d-e]
Leader
Follower Follower
Split log (replicated by Raft)
Split log
TiKV2
Region 1:[a-e]
TiKV3
Region 1:[a-e]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataintidb1-171110051658/85/TiDB-for-Big-Data-13-320.jpg)
![Safe Split: 4/4
TiKV1
Region 1.1:[a-c]
Leader
Region 1.2:[d-e]
TiKV2
Region 1.1:[a-c]
Follower
Region 1.2:[d-e]
TiKV3
Region 1.1:[a-c]
Follower
Region 1.2:[d-e]
raft
raft
raft
raft](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataintidb1-171110051658/85/TiDB-for-Big-Data-14-320.jpg)