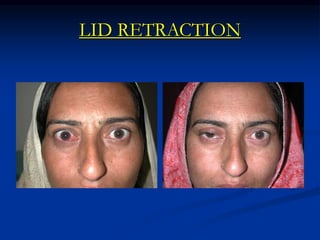
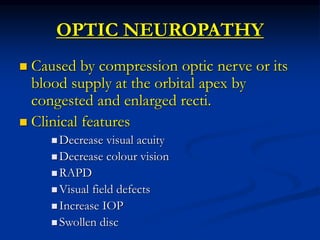
This document discusses thyroid ophthalmopathy, an autoimmune disorder where the thyroid gland and eye muscles are attacked. It causes inflammation and swelling of the eye muscles and surrounding tissues. The main symptoms are soft tissue involvement around the eyes, lid retraction, proptosis (bulging eyes), optic neuropathy, restrictive myopathy, and corneal exposure. The condition progresses through inflammatory and fibrotic stages and is usually treated with lubricants, steroids, radiation therapy, or surgery depending on the severity and location of symptoms.