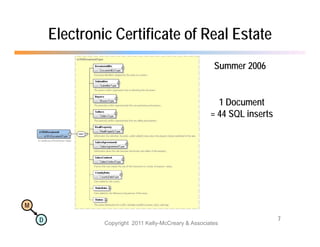
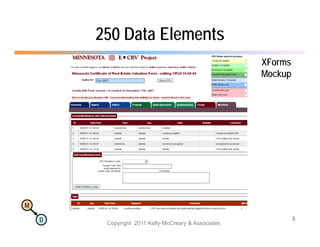
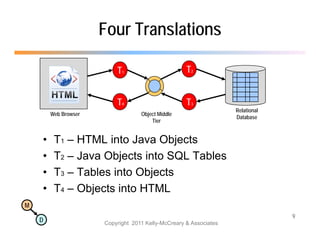
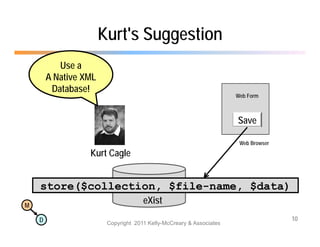
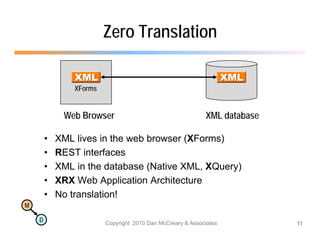
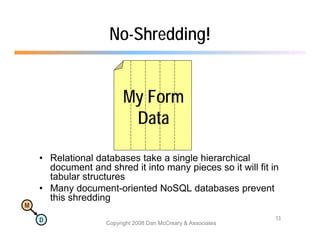
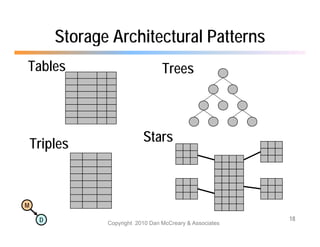
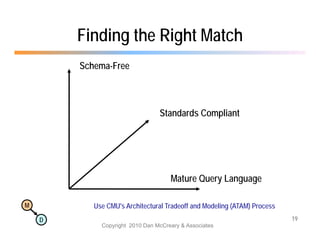
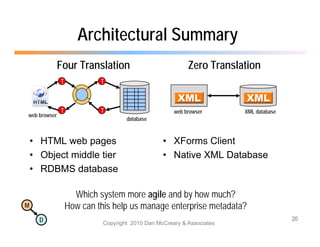
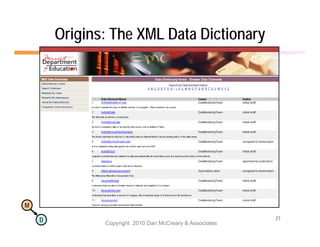
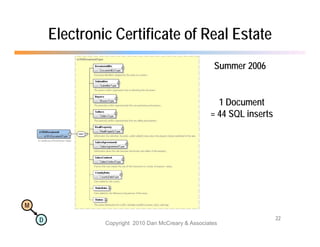
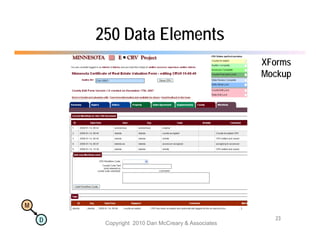
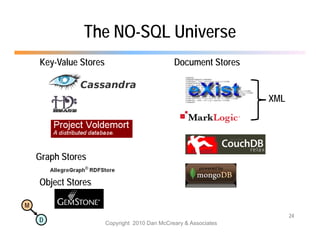
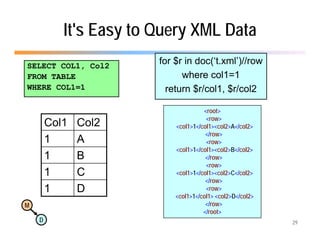
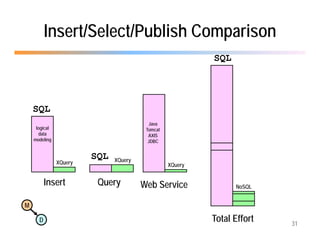
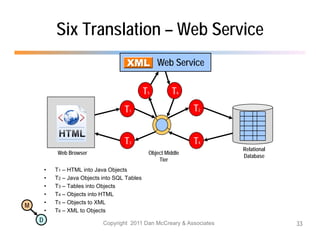
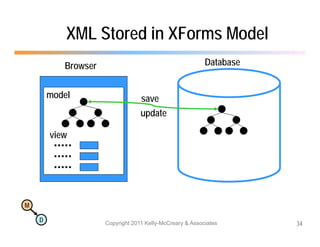
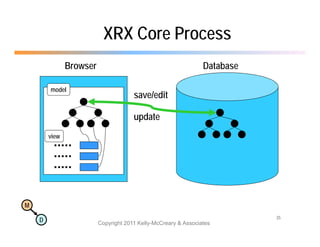
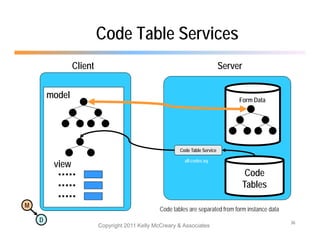
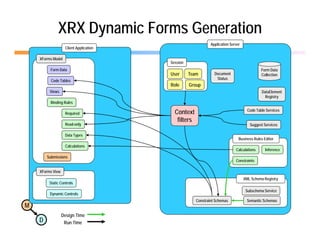
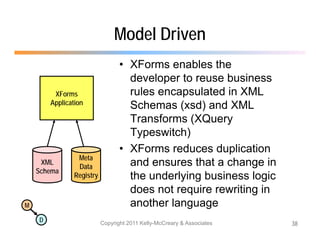
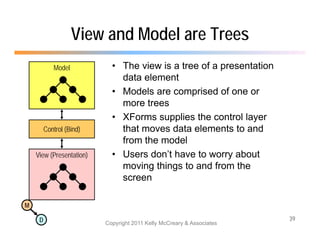
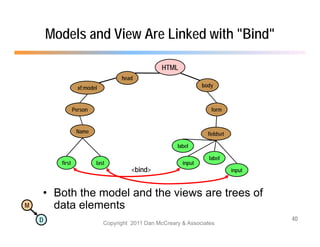
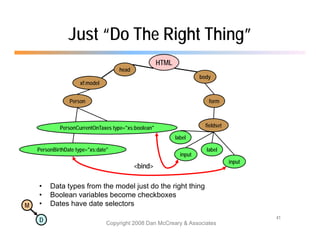
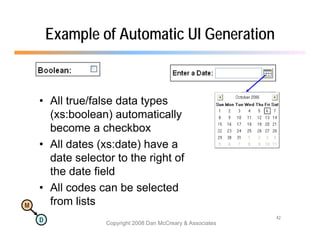
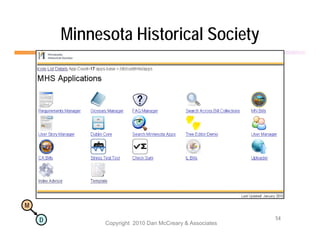
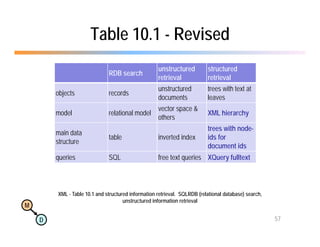
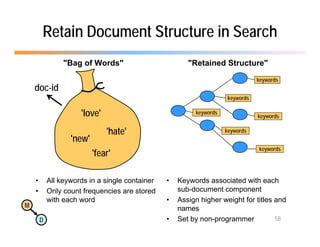
The document discusses the benefits of using agile NoSQL systems and the XRX architecture, which facilitates web application development without the need for complex data translation. It emphasizes how schema-free, zero-translation systems can increase overall system agility, allowing non-programmers to participate in application development. The presentation outlines key components of XRX, challenges with traditional systems, and various architectural options for leveraging these modern data management techniques.