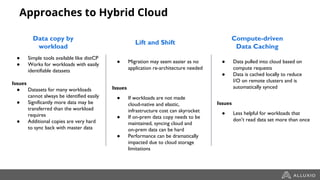
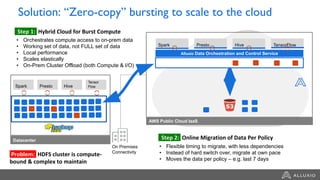
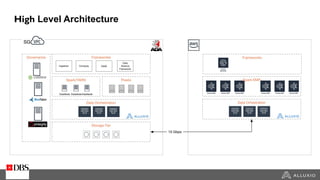
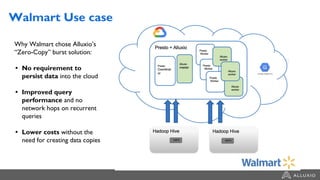
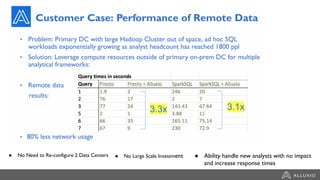
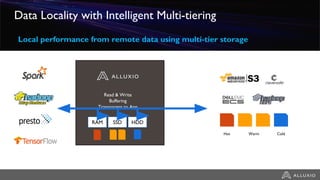
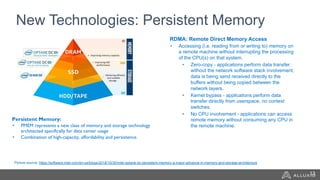
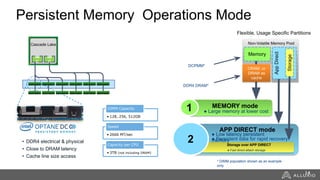
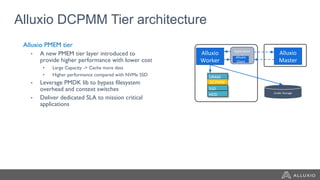
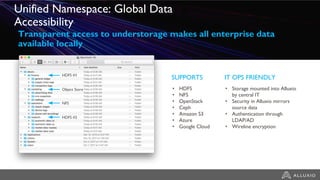
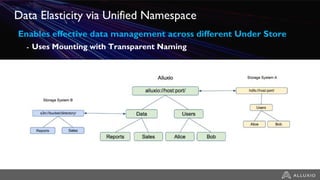
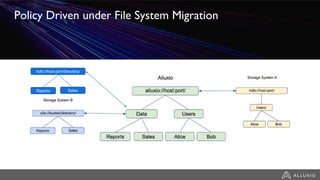
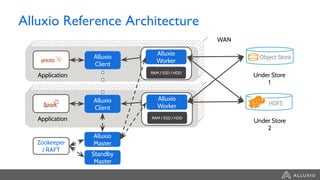
The document discusses the benefits and strategies for using hybrid cloud solutions to accelerate queries on cloud data lakes, emphasizing compute capacity expansion and reducing overload on existing infrastructure. It outlines challenges such as network latency, data copying difficulties, and the need for efficient data synchronization. The use of Alluxio's 'zero-copy' bursting solution is highlighted as a means to improve query performance and reduce costs by avoiding data persistence in the cloud.