The document provides a comprehensive overview of threat hunting in cybersecurity, detailing methodologies, terminologies, and practical techniques for detecting advanced threats that evade existing security measures. It emphasizes the importance of proactive and intelligent hunting, leveraging both manual and automated approaches, including the use of machine learning and threat intelligence. The content is structured into various sections, including hunting processes, network and endpoint hunting techniques, and the application of frameworks such as MITRE ATT&CK.














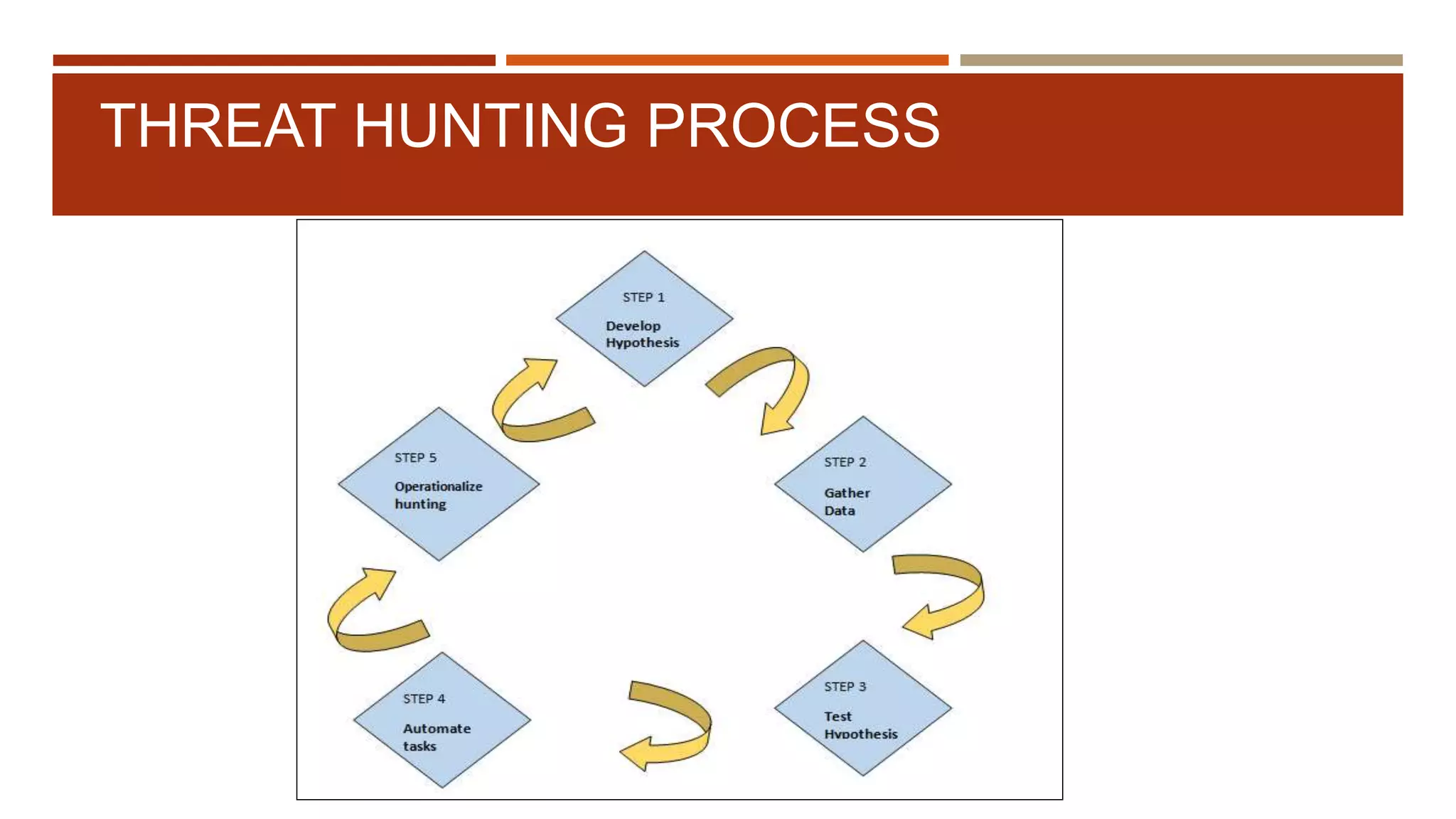
![THREAT HUNTING PROCESS
Hypothesis driven approach
What is Hypotheses ?
Assumption on attack behavior.
Actionable use case based on observations, intelligence, and experience
Three types of hypotheses:
Analytics-Driven: "Machine-learning and UEBA, used to develop aggregated risk scores
that can also serve as hunting hypotheses"[5]
Situational-Awareness Driven: "Crown Jewel analysis, enterprise risk assessments,
company- or employee-level trends"[5]
Intelligence-Driven: "Threat intelligence reports, threat intelligence feeds, malware
analysis, vulnerability scans"[
Hypothesis can be developed using any public APT report, twitter, security news, articles etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/threathuntingincyberworld-201109120616/75/Threat-hunting-in-cyber-world-15-2048.jpg)