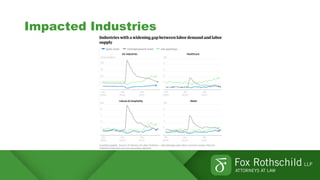
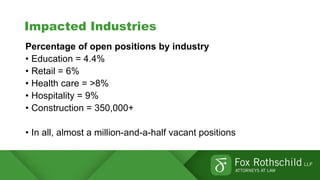
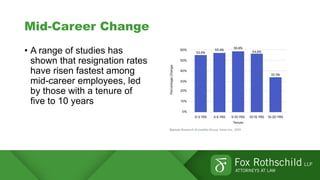
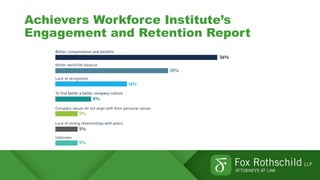
This document summarizes key points from a discussion on retention and recruitment in the current labor market conditions referred to as the "Great Resignation".
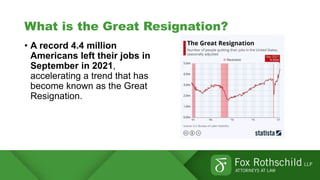
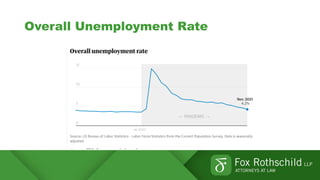
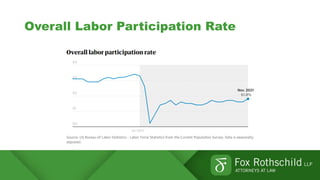
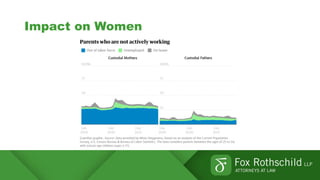
The Great Resignation refers to a record number of Americans voluntarily quitting their jobs in 2021. Over 4 million people quit their jobs each month in 2021. Reasons for quitting include burnout, desire for flexibility, and reevaluation of work-life priorities. Employers are facing challenges retaining existing employees and recruiting new talent due to the competitive job market. Retention strategies discussed include identifying the root causes of resignations, conducting stay interviews, and developing tailored programs. Recruitment strategies include strengthening employer brand, reimagining hiring processes, and expanding talent sourcing