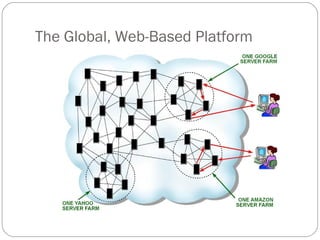
The document summarizes Thomas Friedman's book "The World is Flat" and its description of the stages of globalization: Globalization 1.0 from 1492 to 1800 driven by exploration, Globalization 2.0 from 1800 to 2000 driven by industrialization and developments like railroads and satellites, and Globalization 3.0 from 2000 to present driven by technologies like computers, the Internet, fiber optics, outsourcing, and offshoring that allow more countries and people to connect and collaborate globally in real-time. It also outlines Friedman's "Ten Flatteners" that defined Globalization 3.0, like the fall of the Berlin Wall, Netscape going public, and the rise of digital technologies, wireless networks, and the