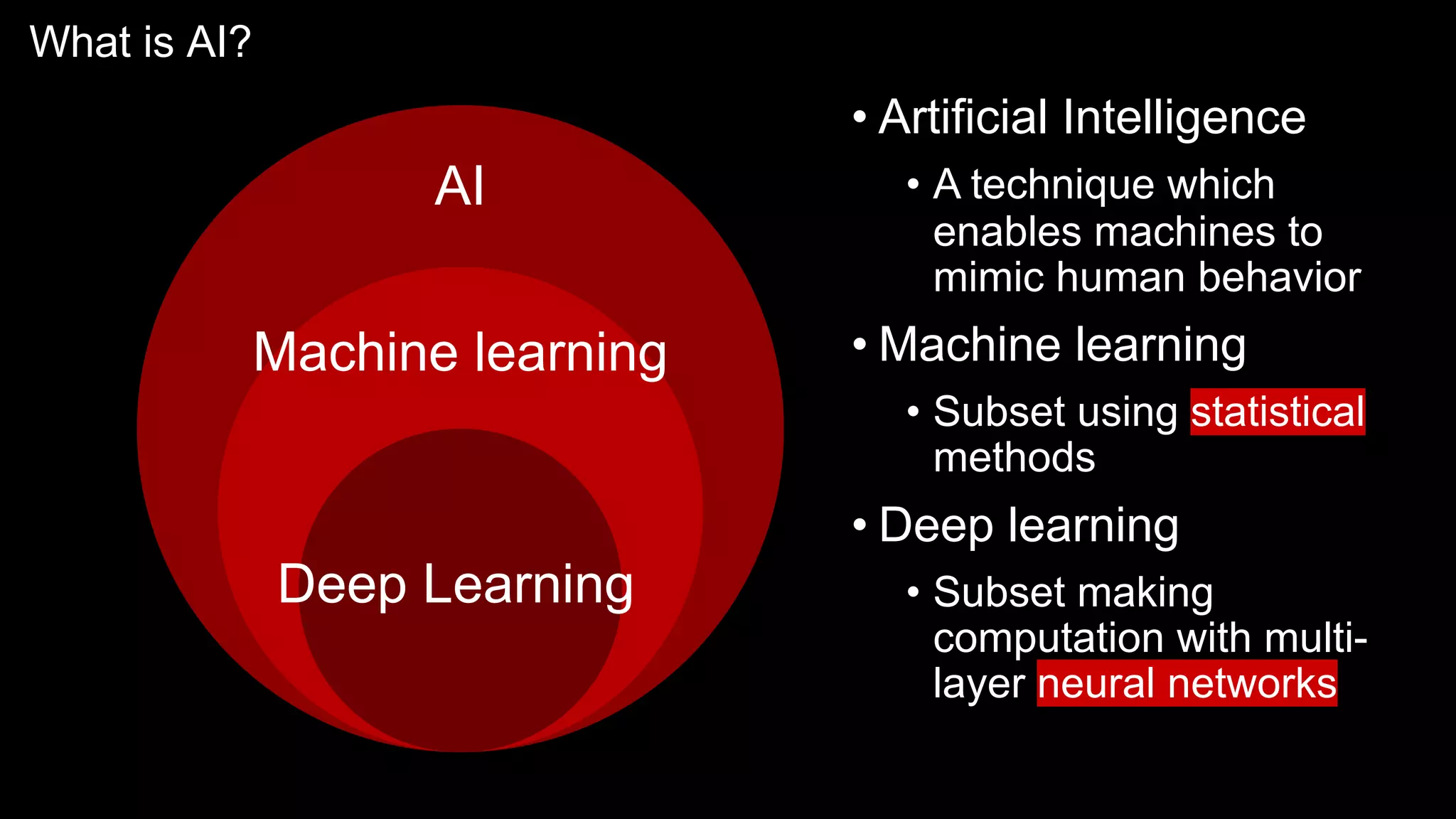
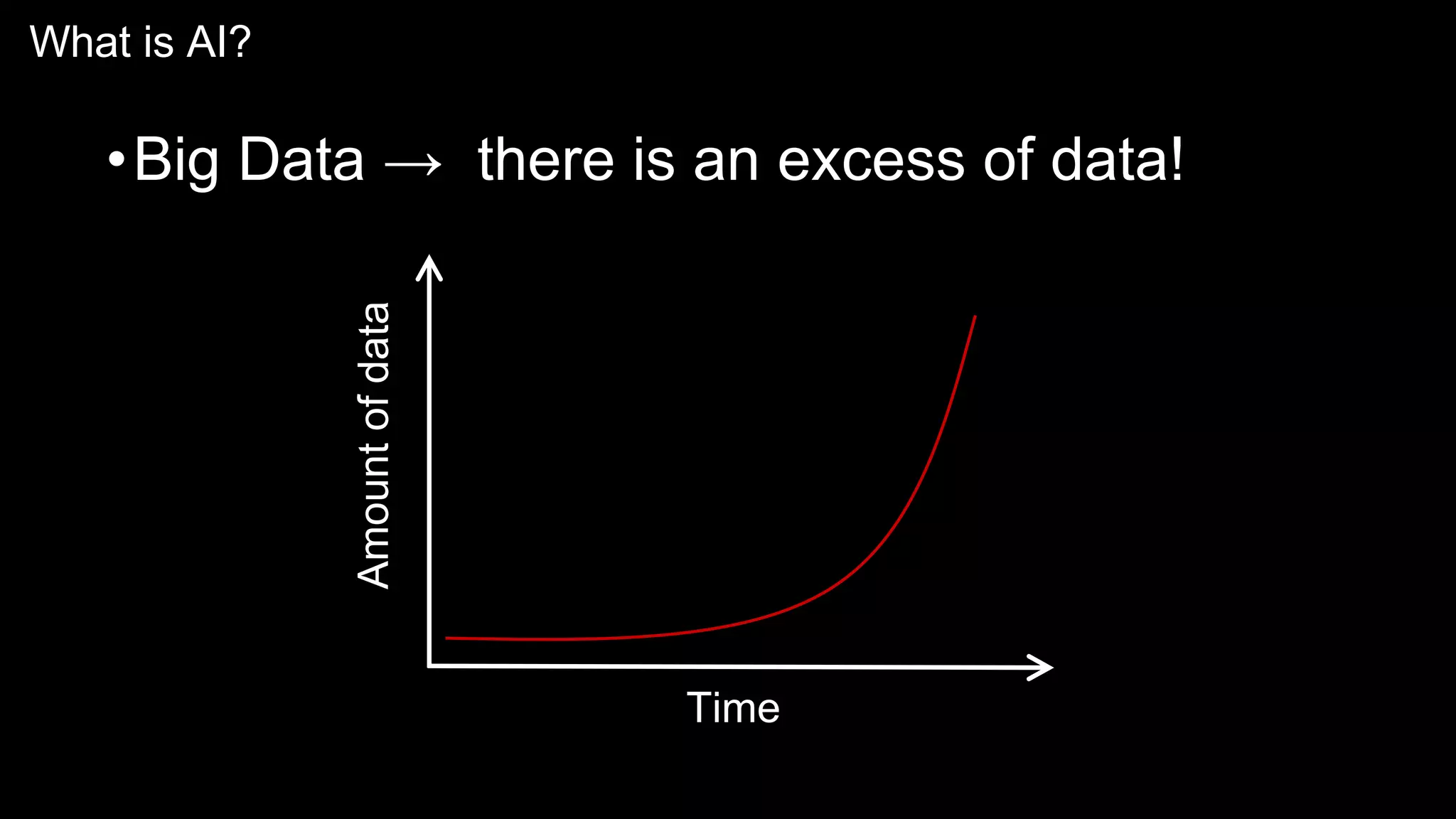
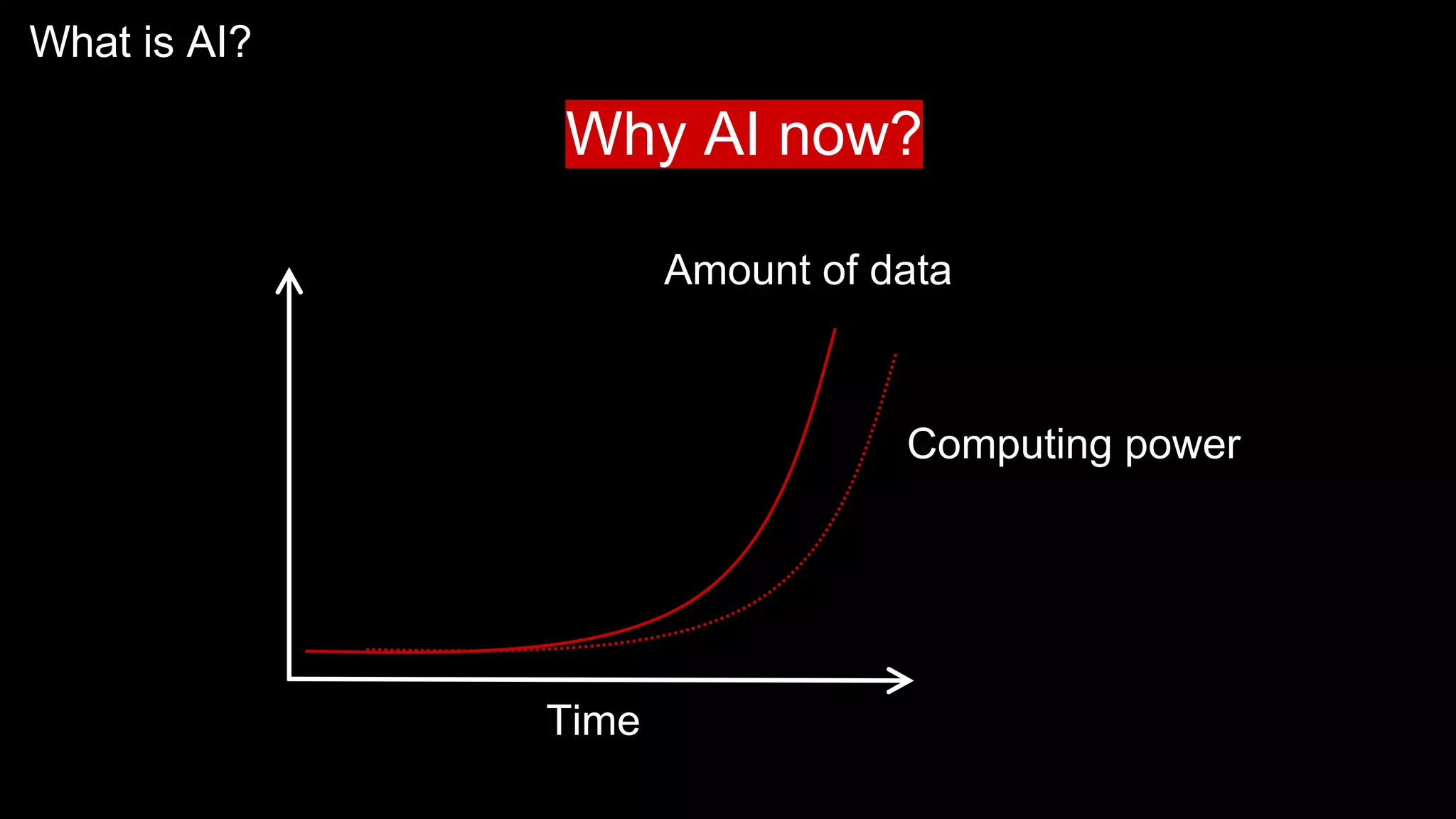
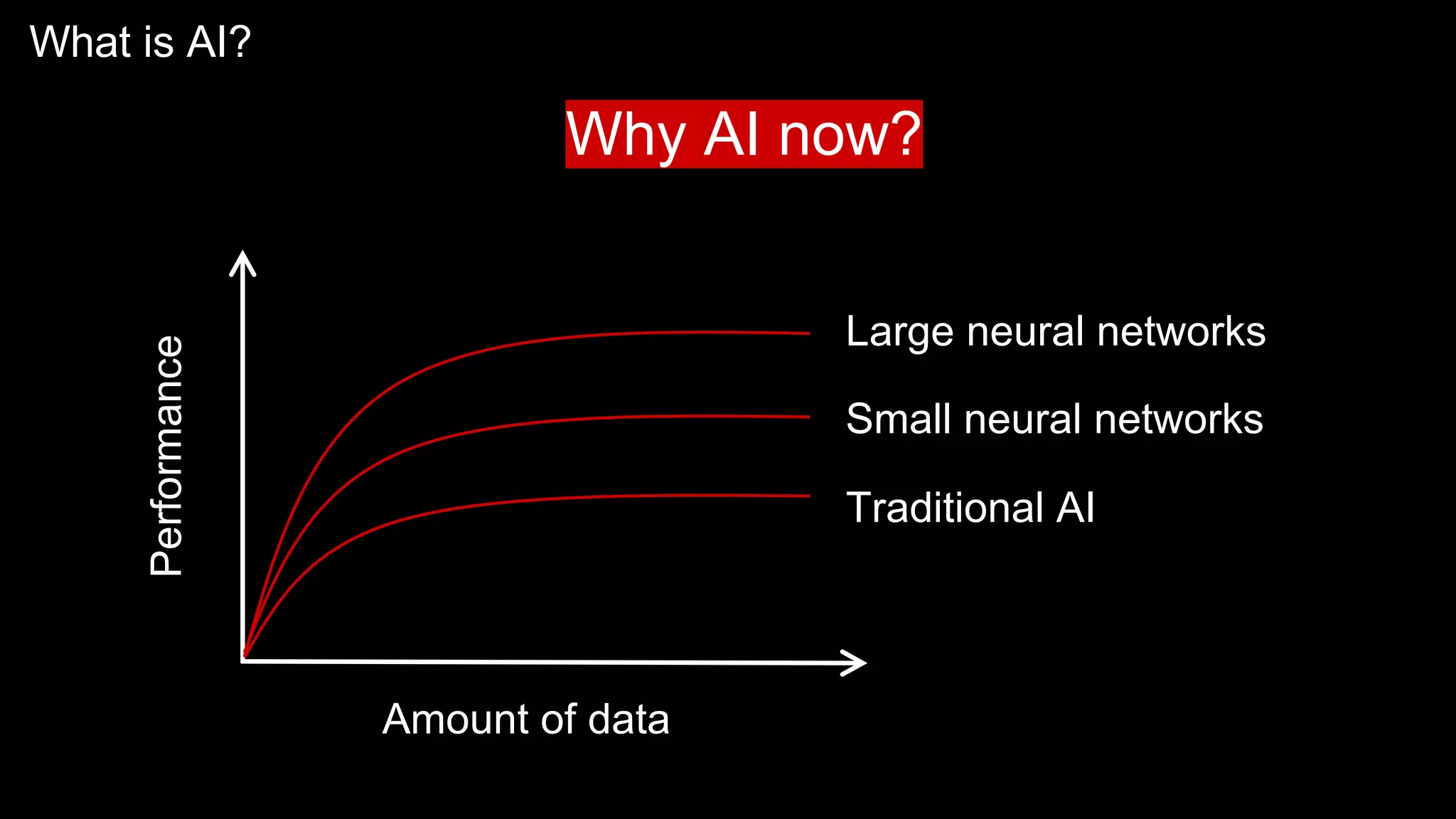
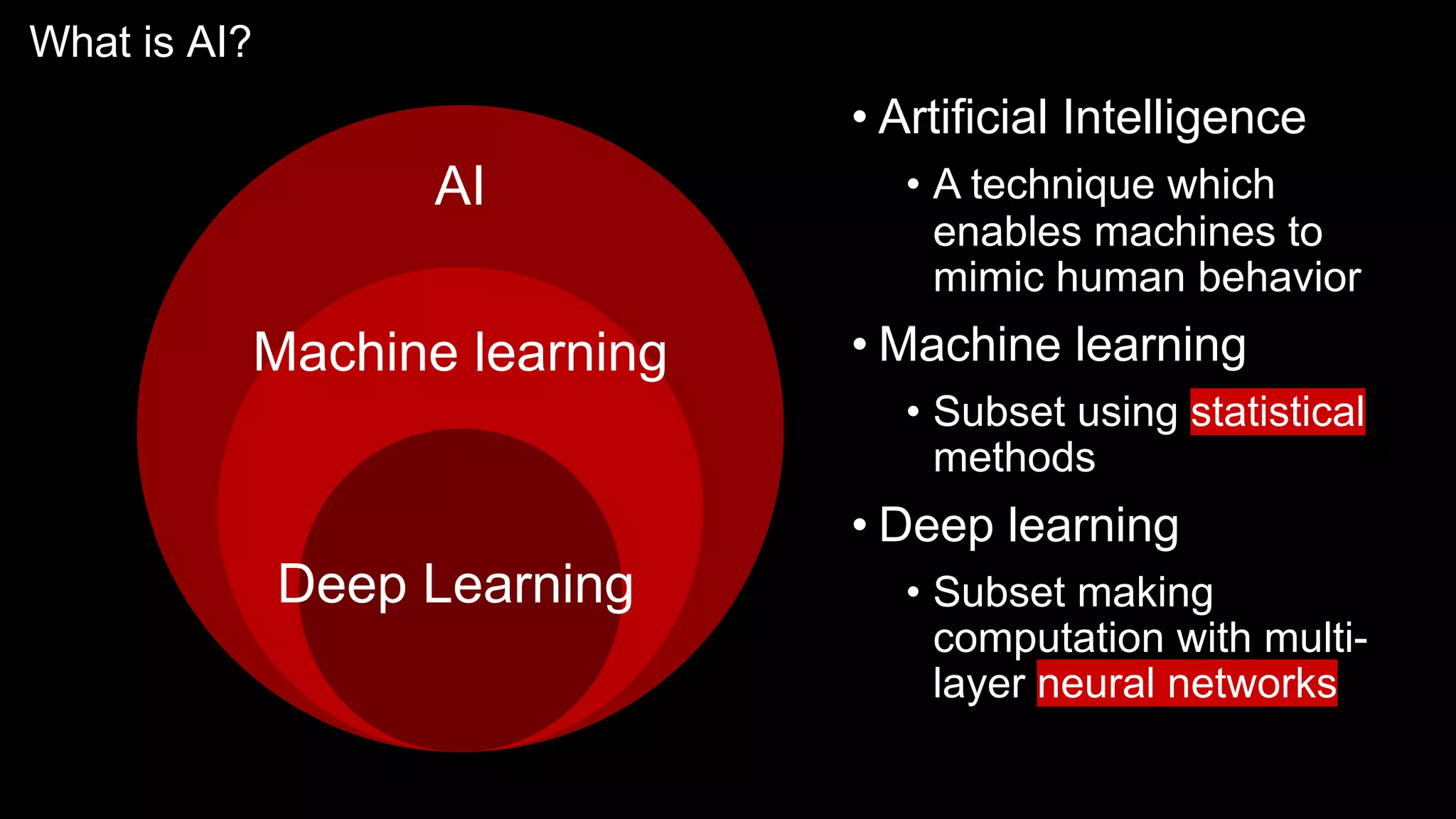
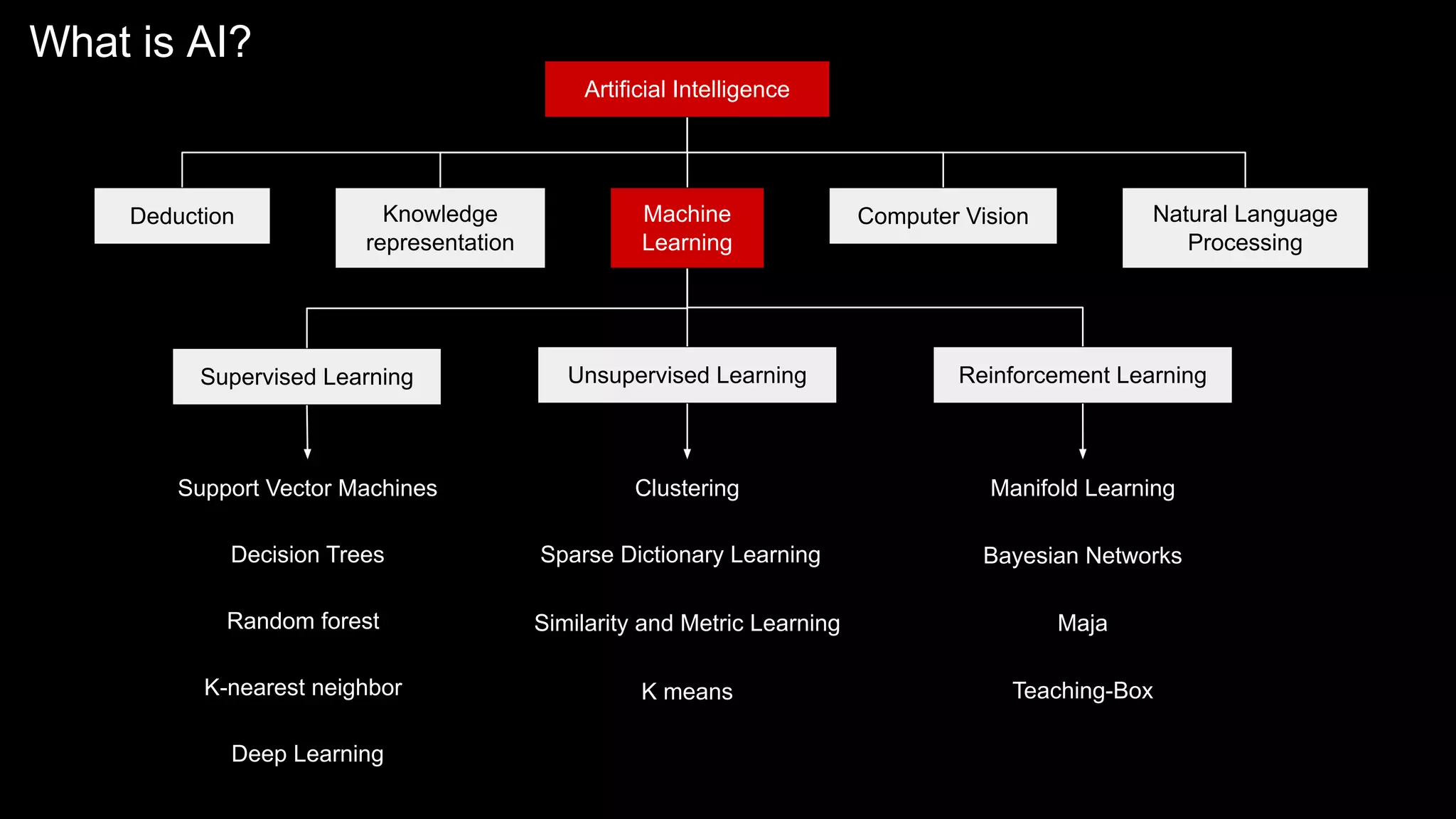
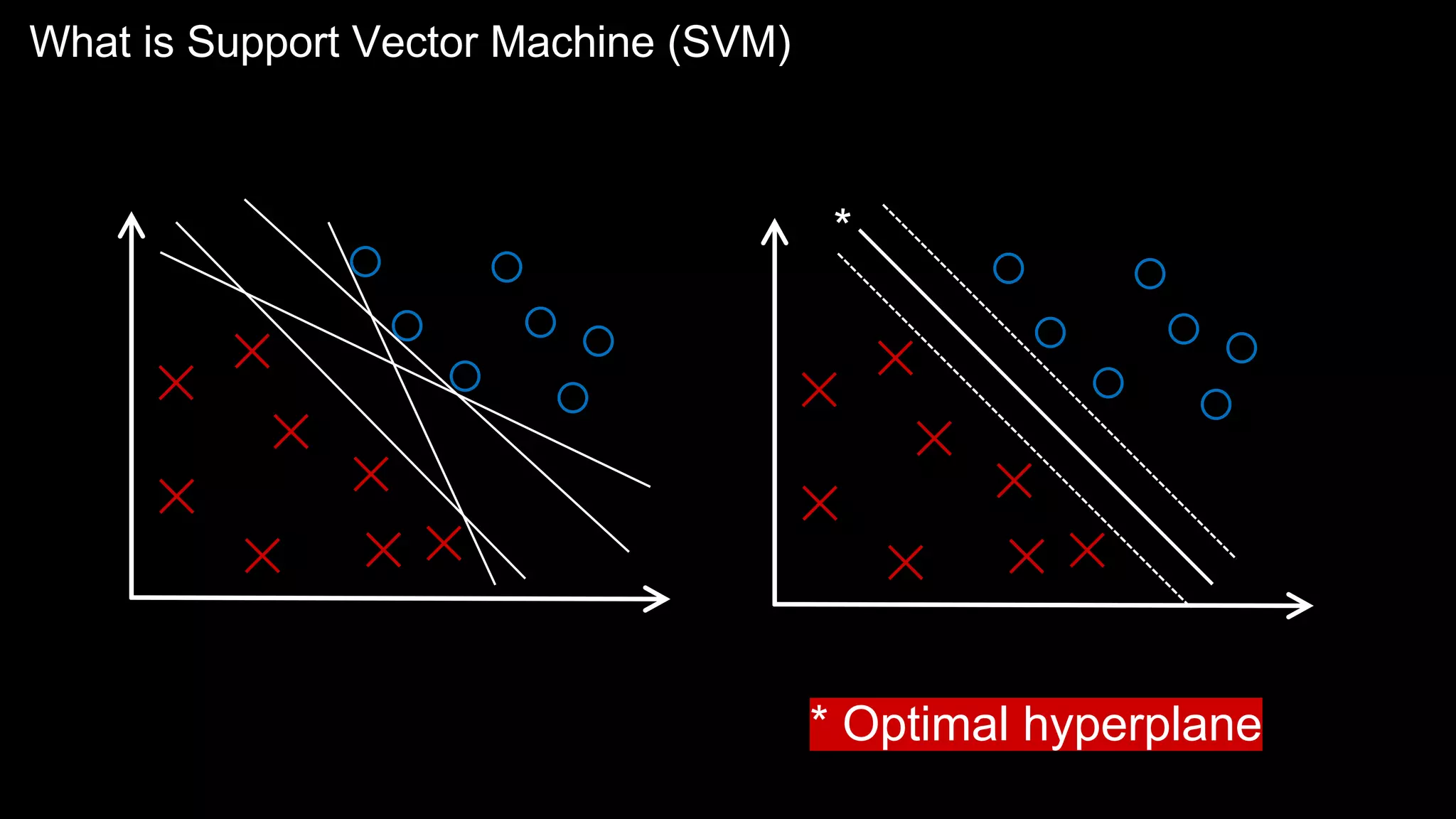
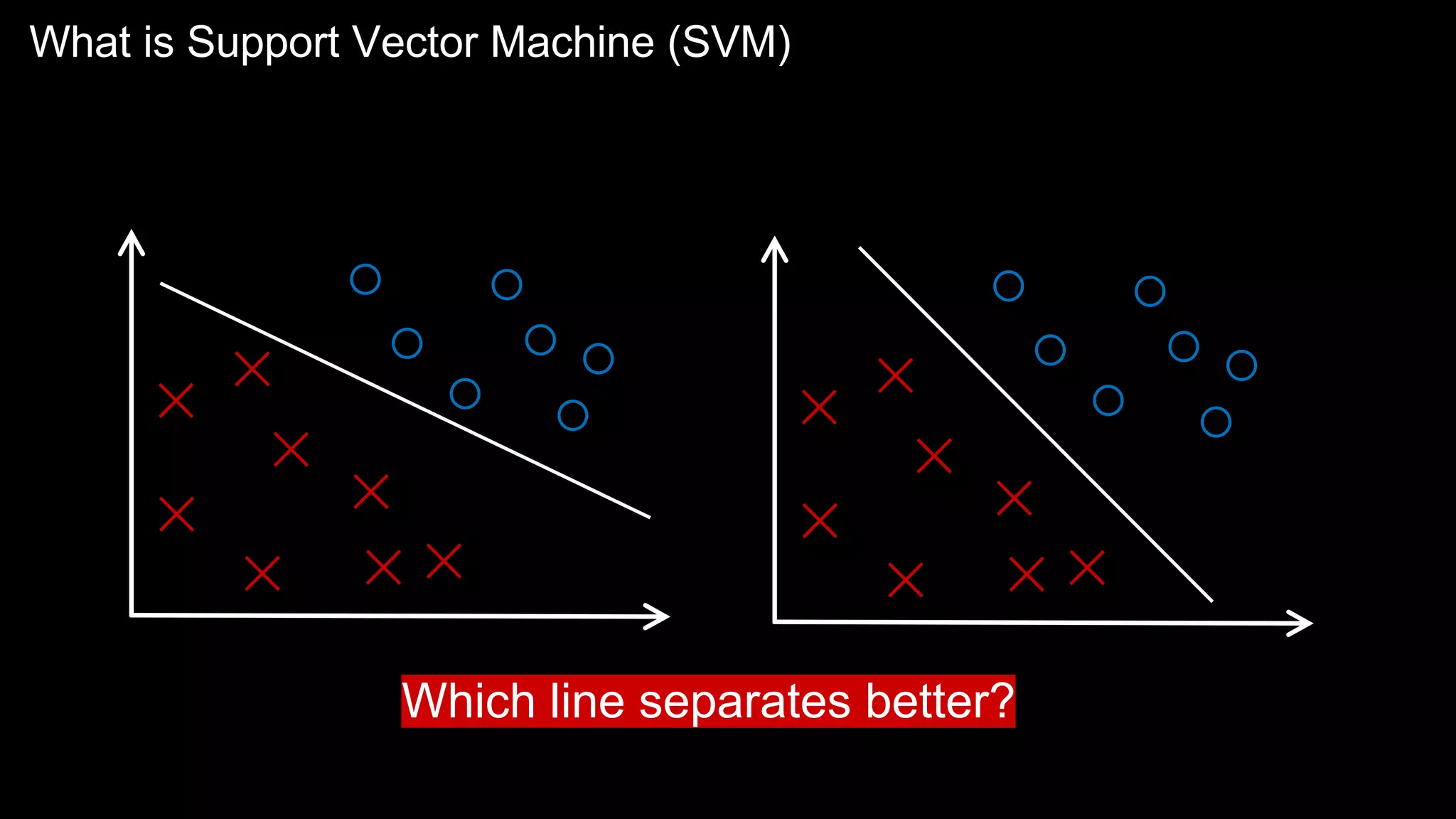
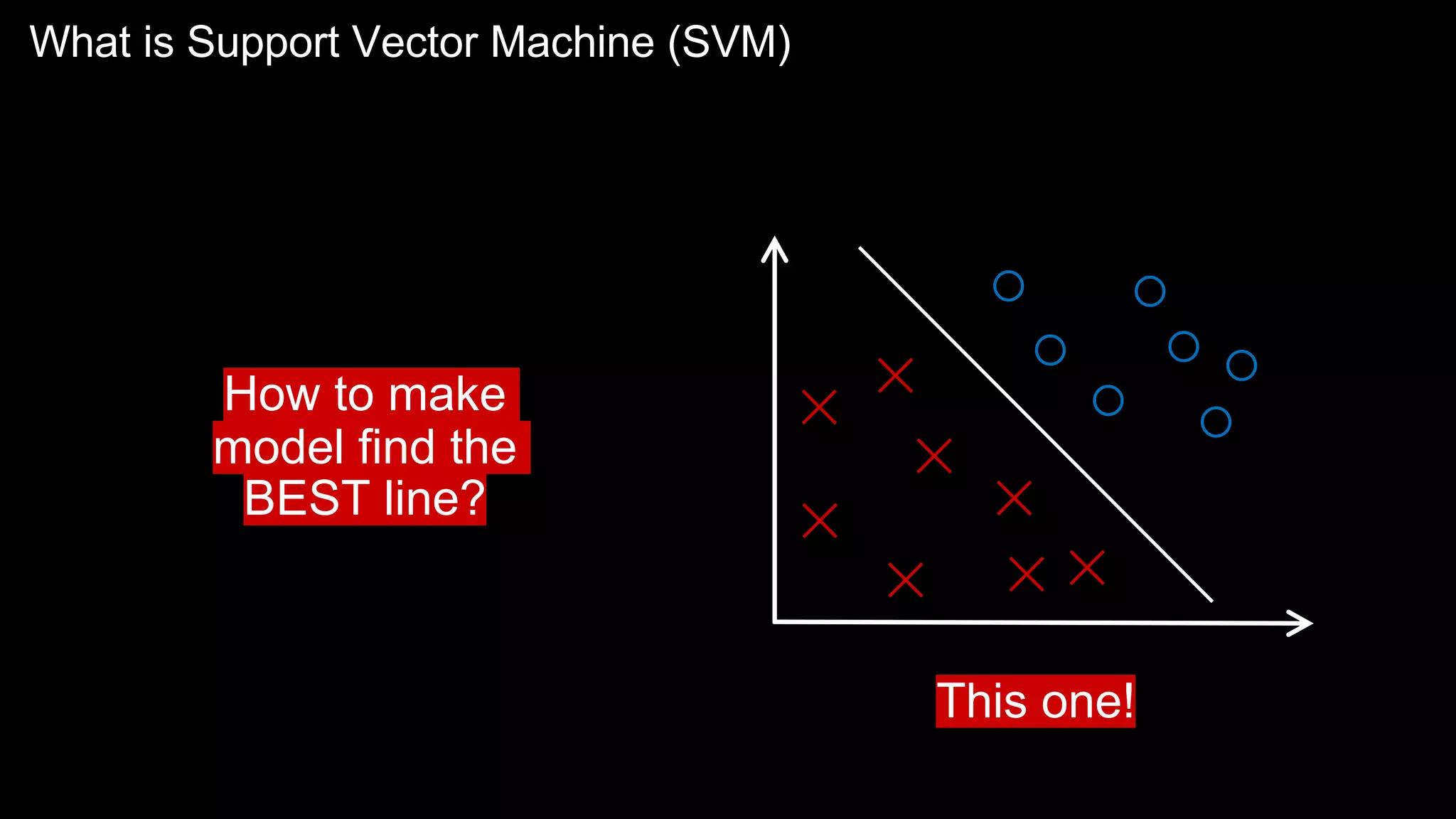
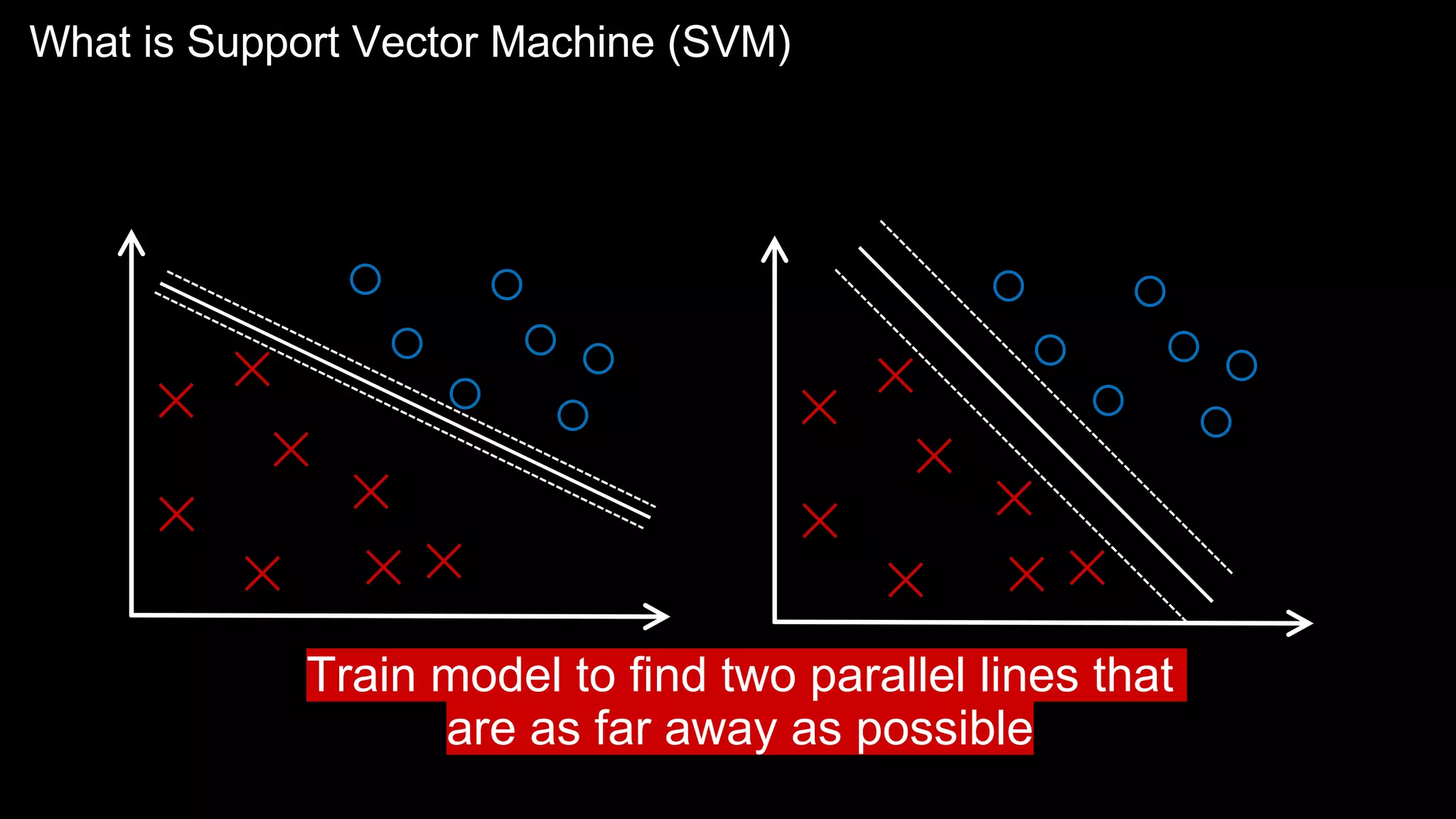
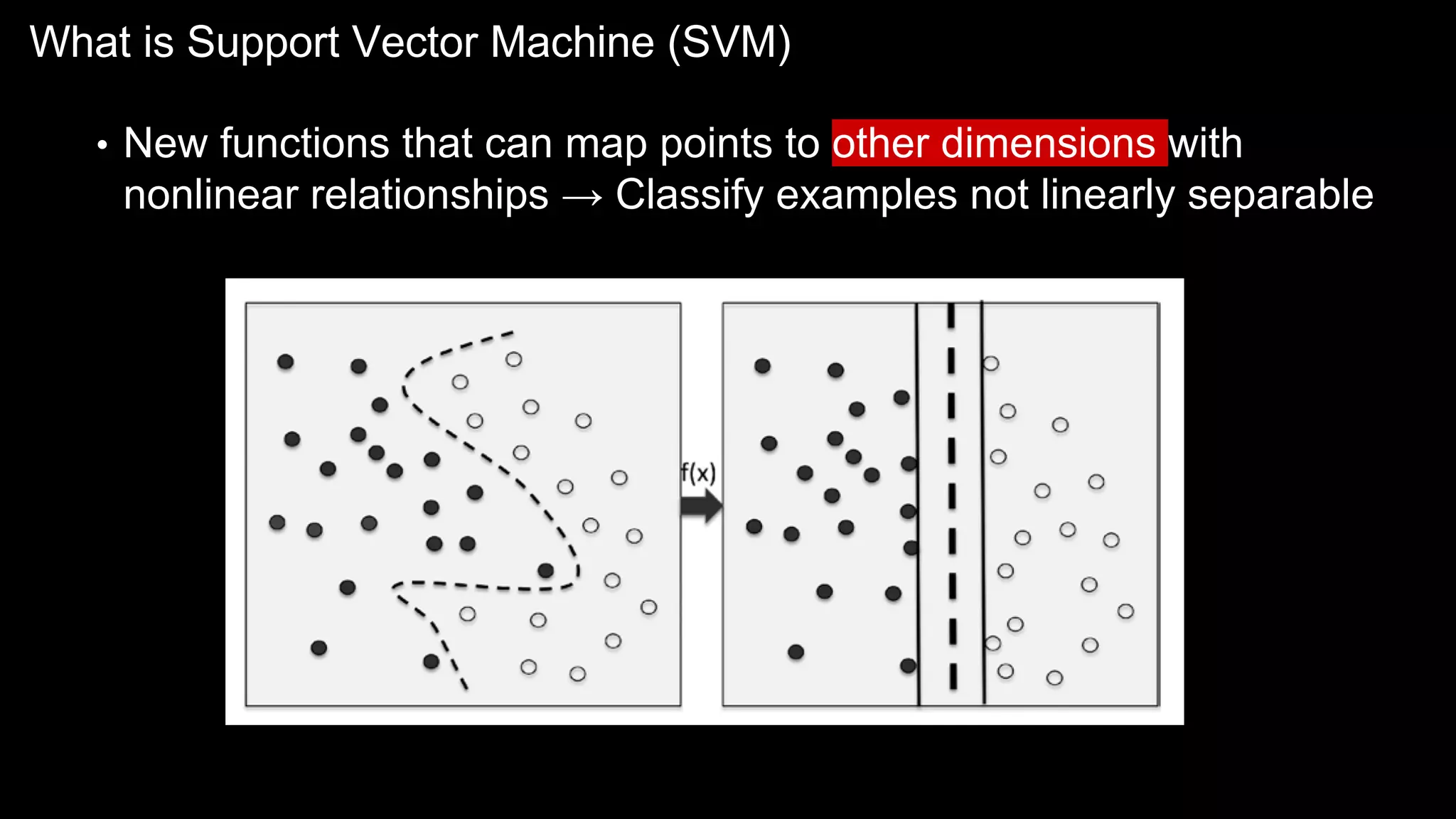
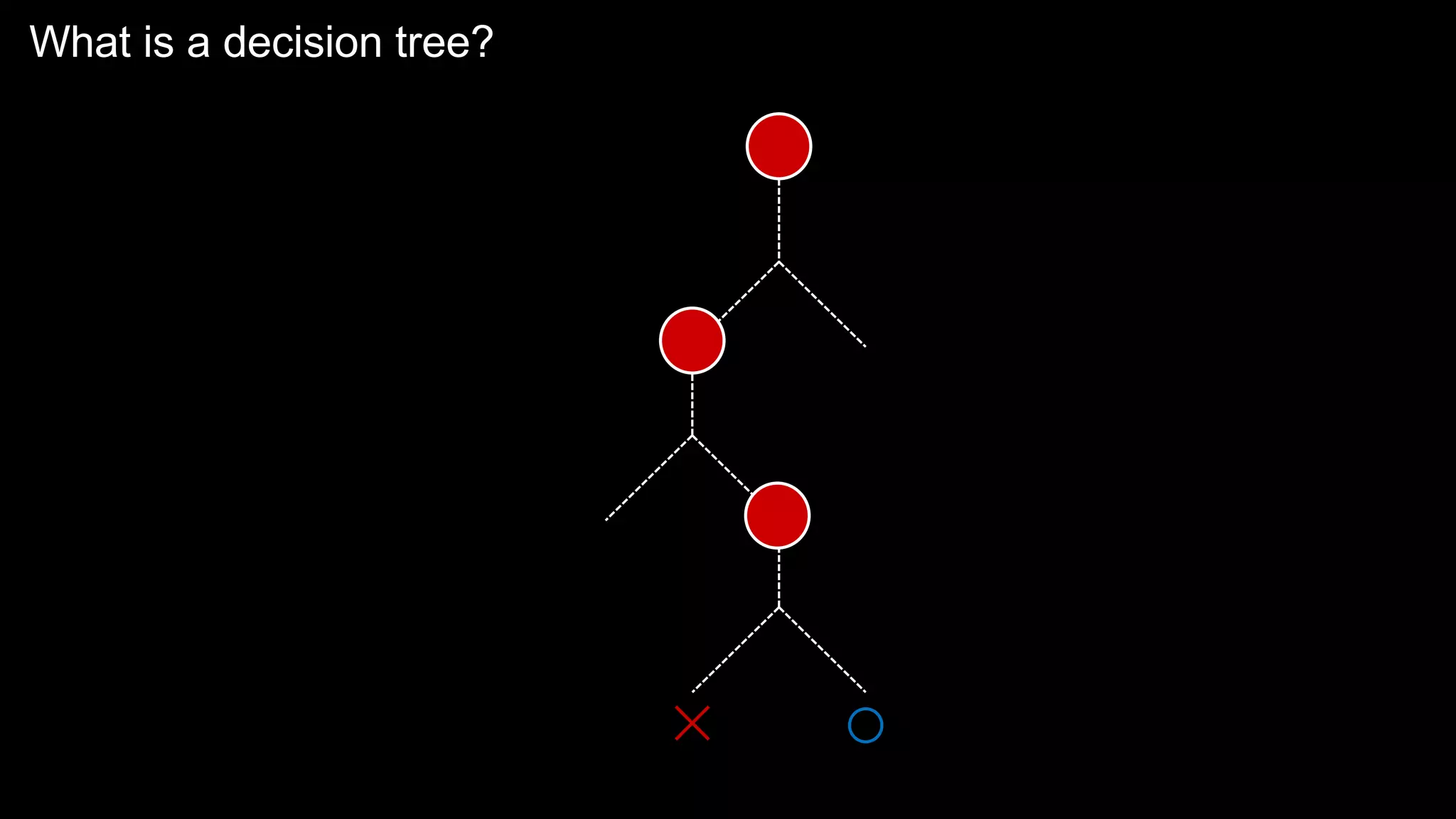
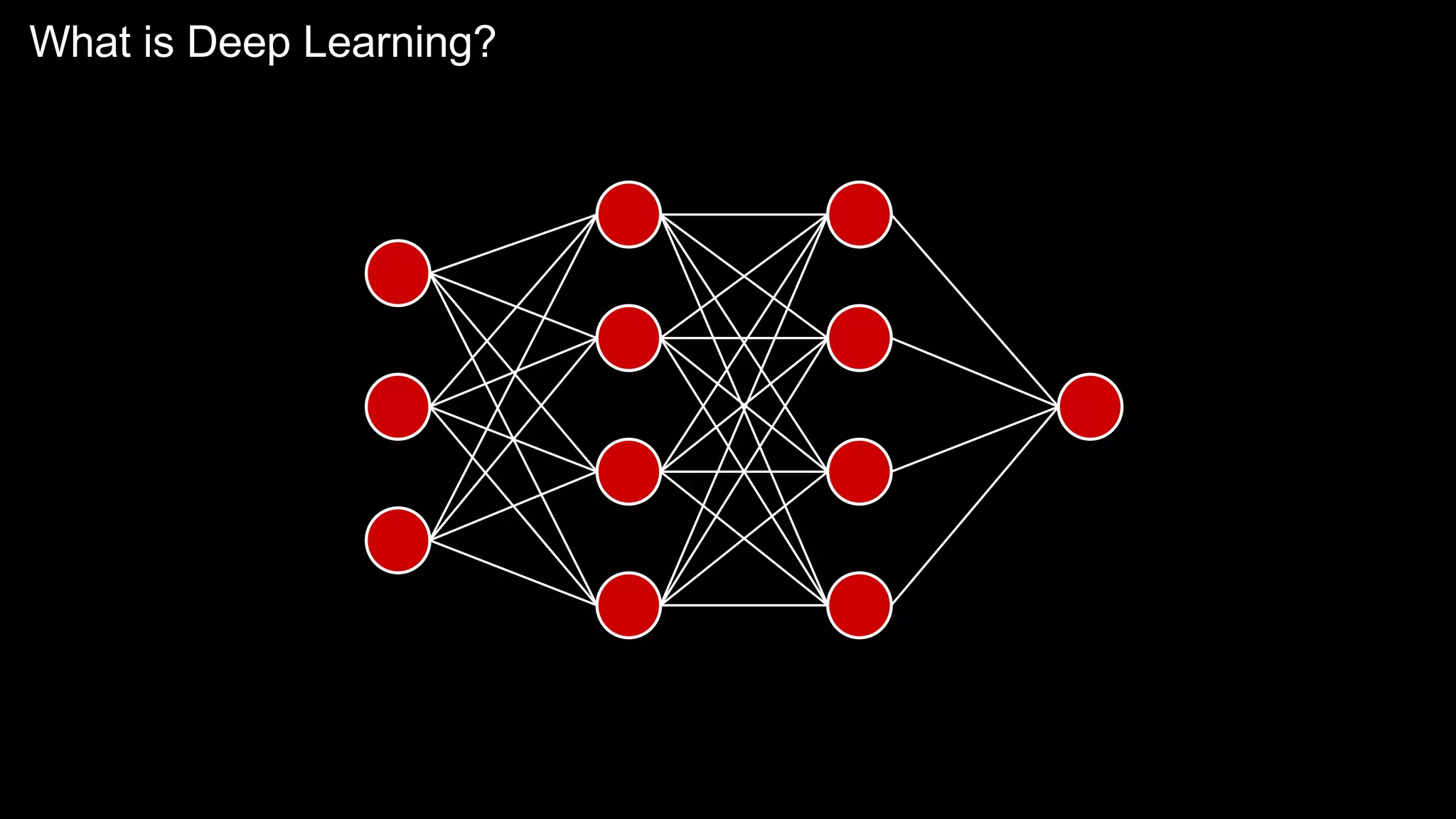
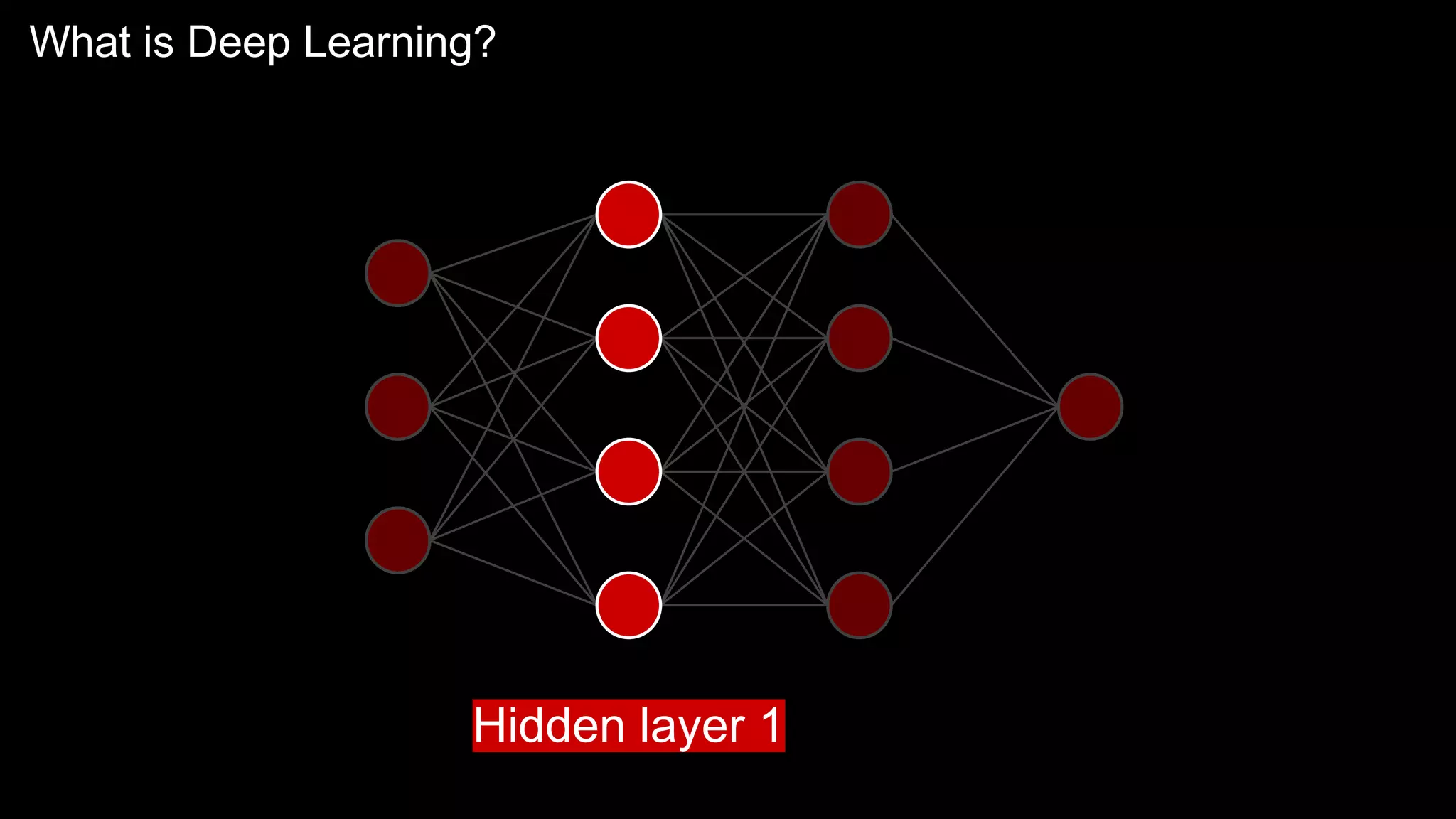
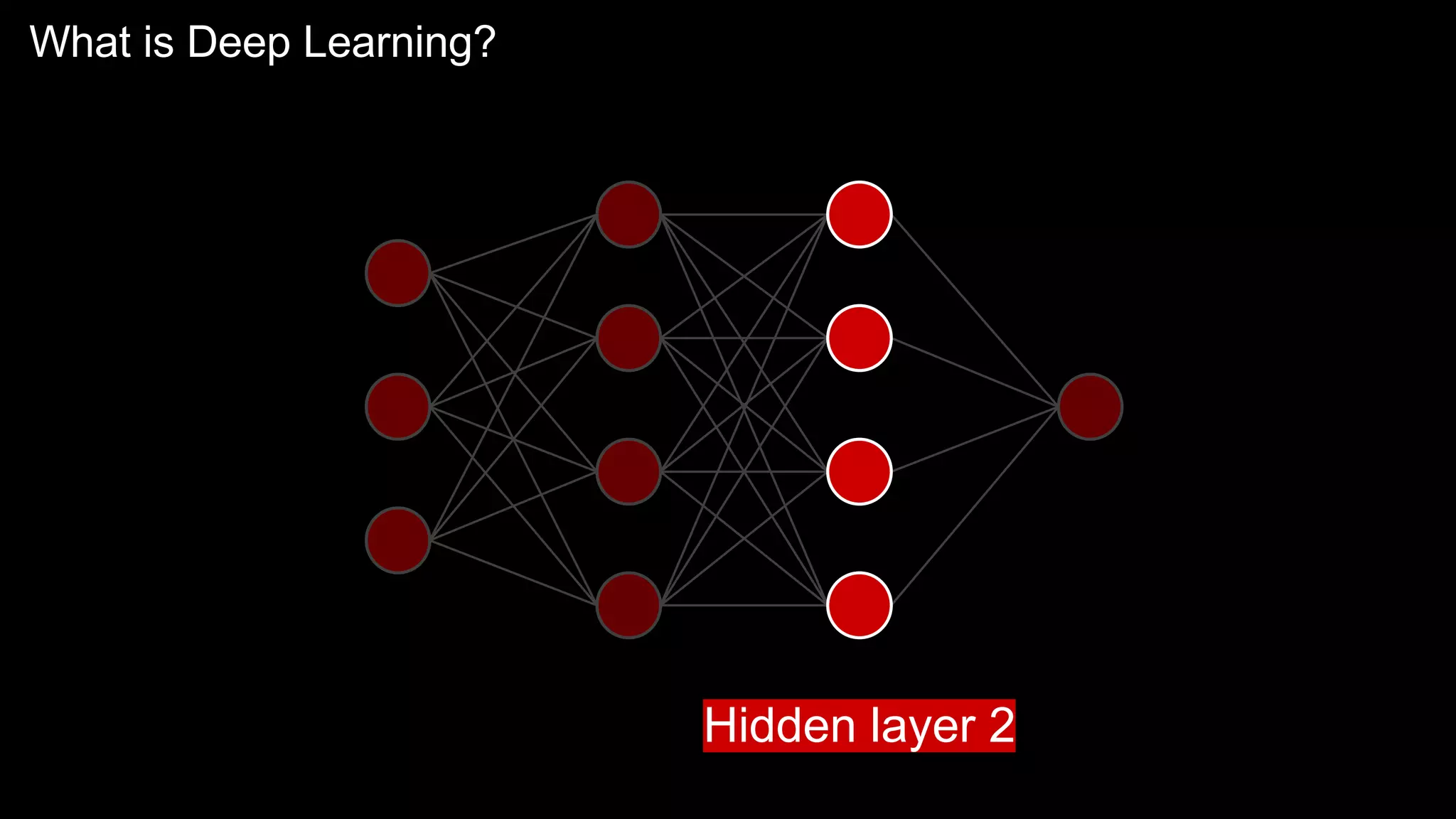
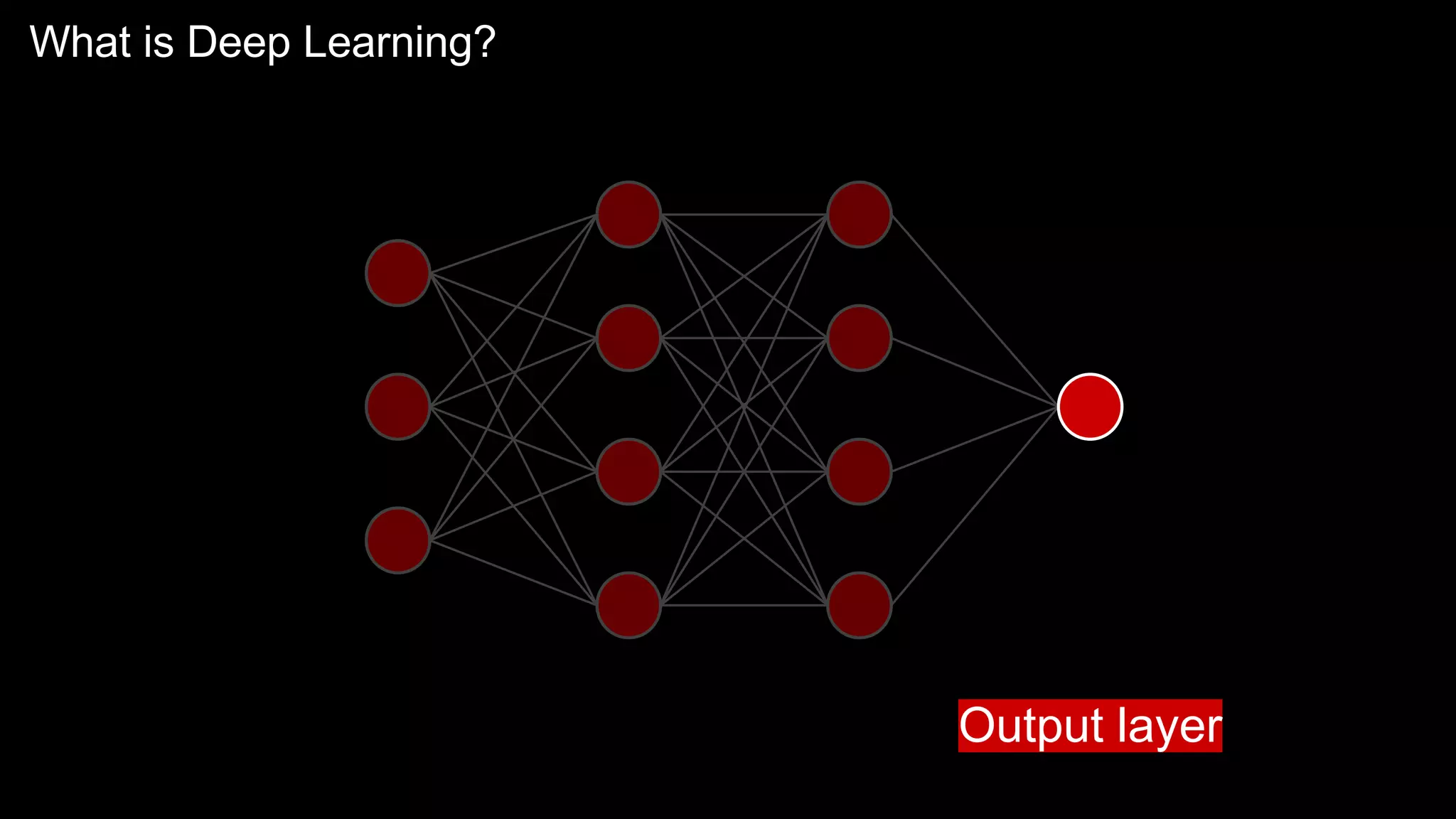
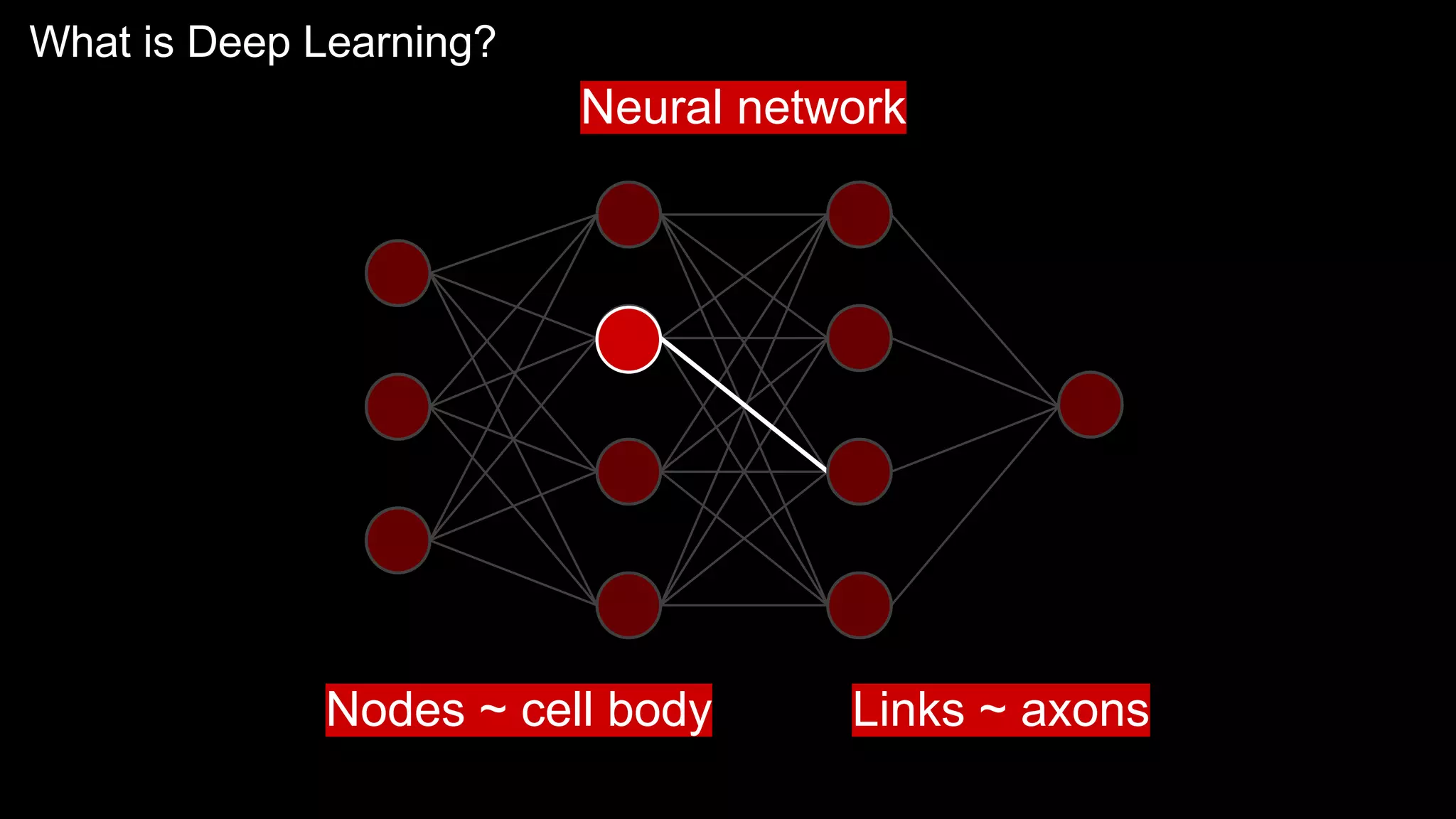
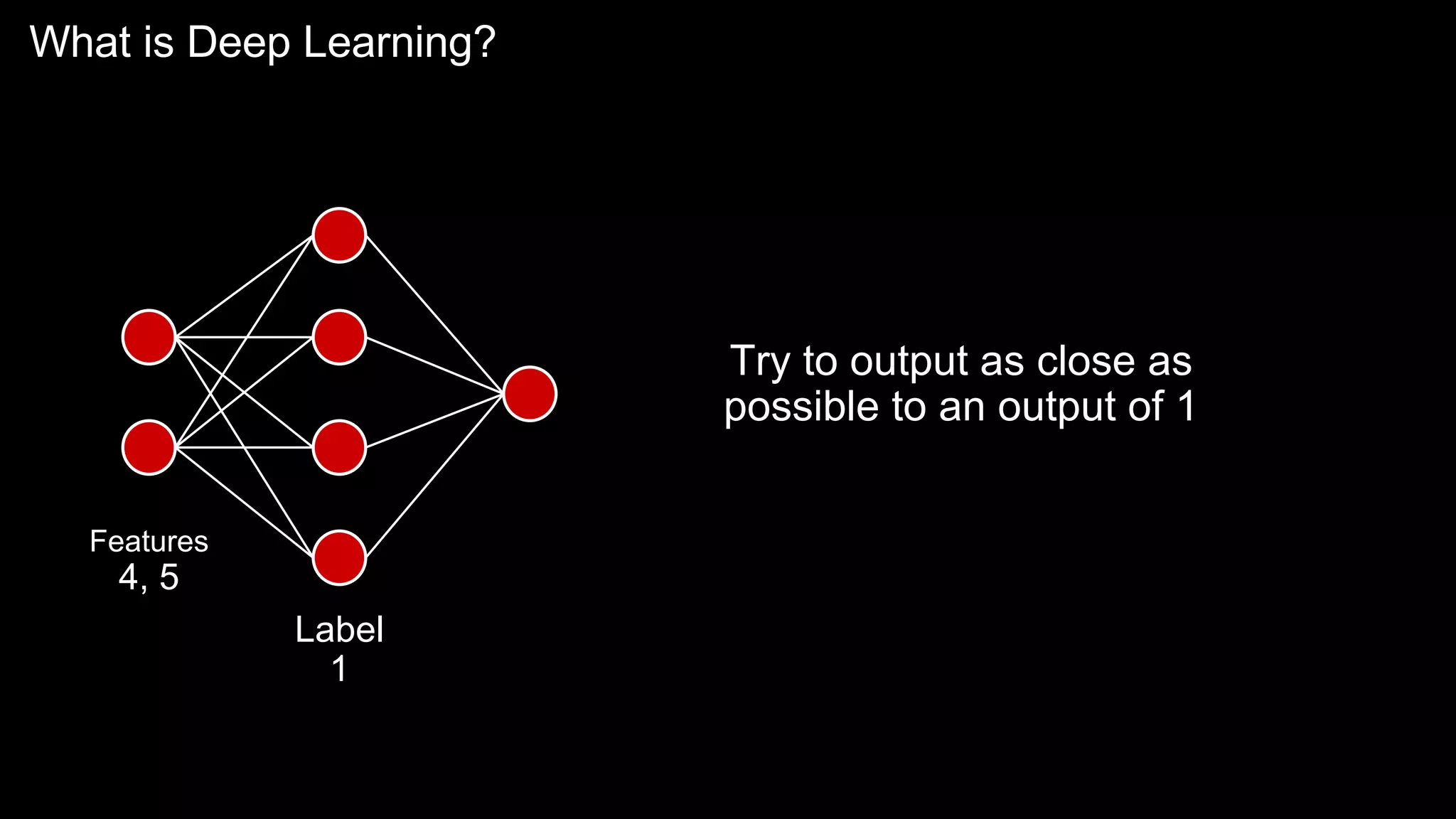
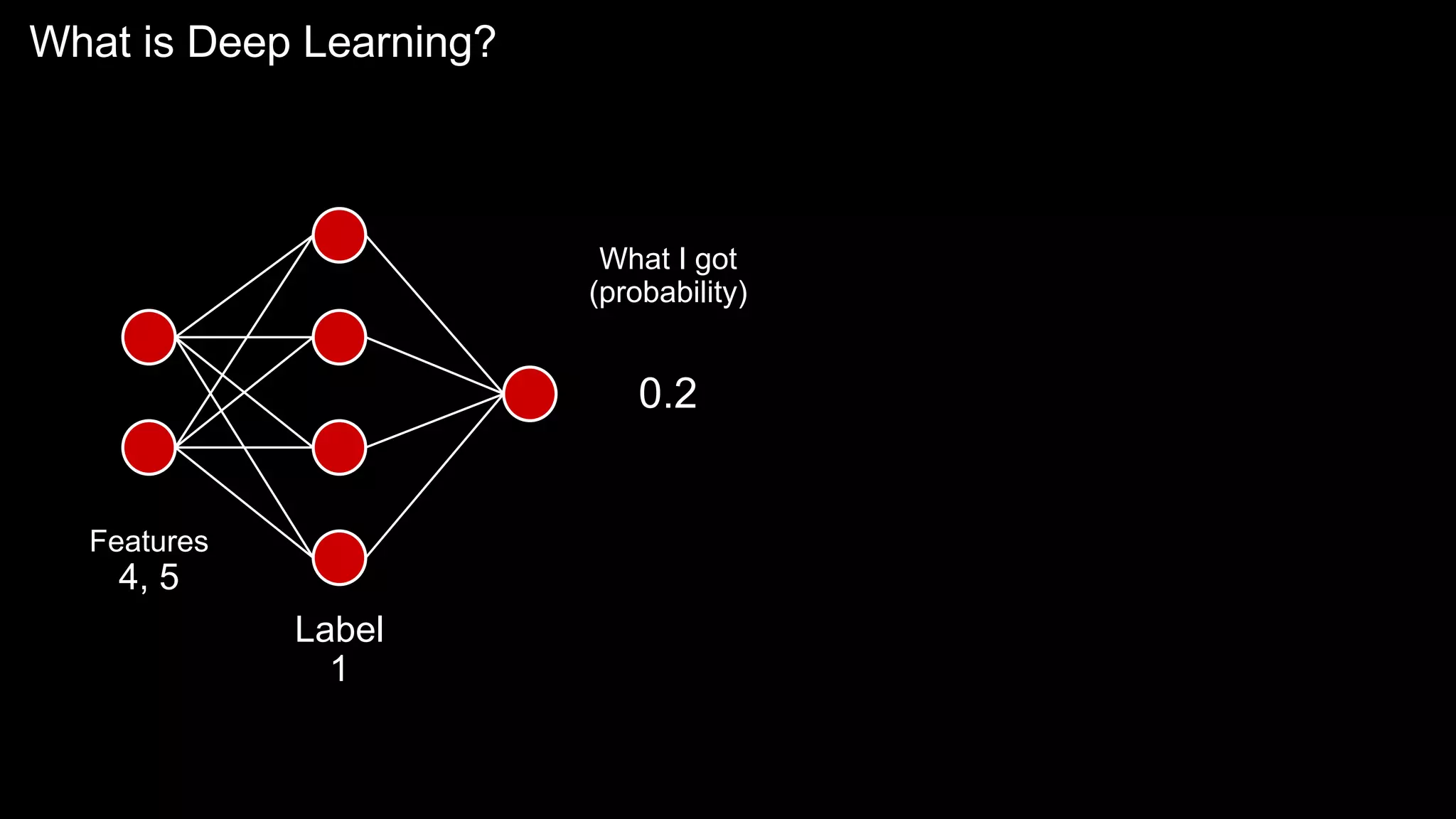
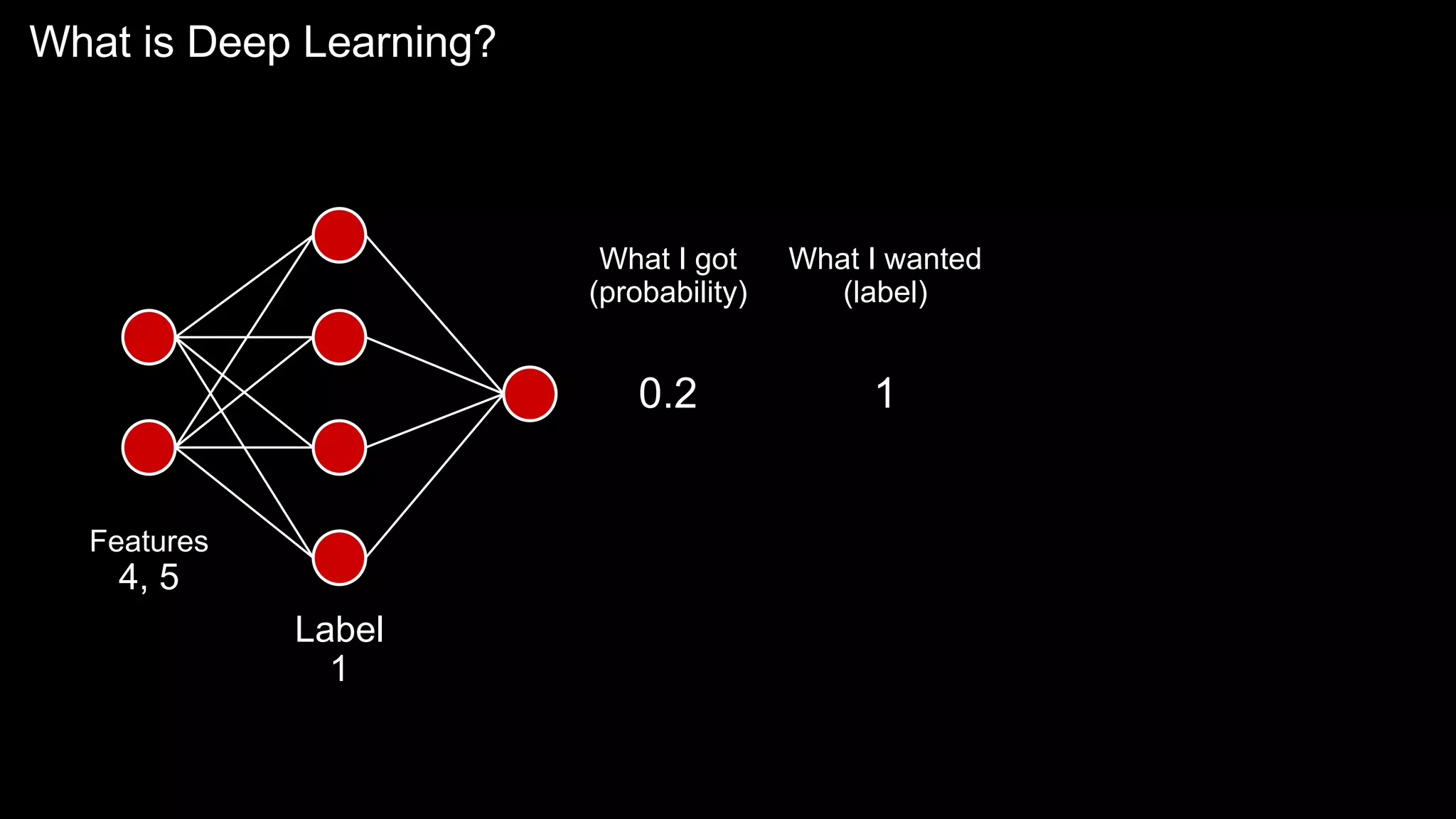
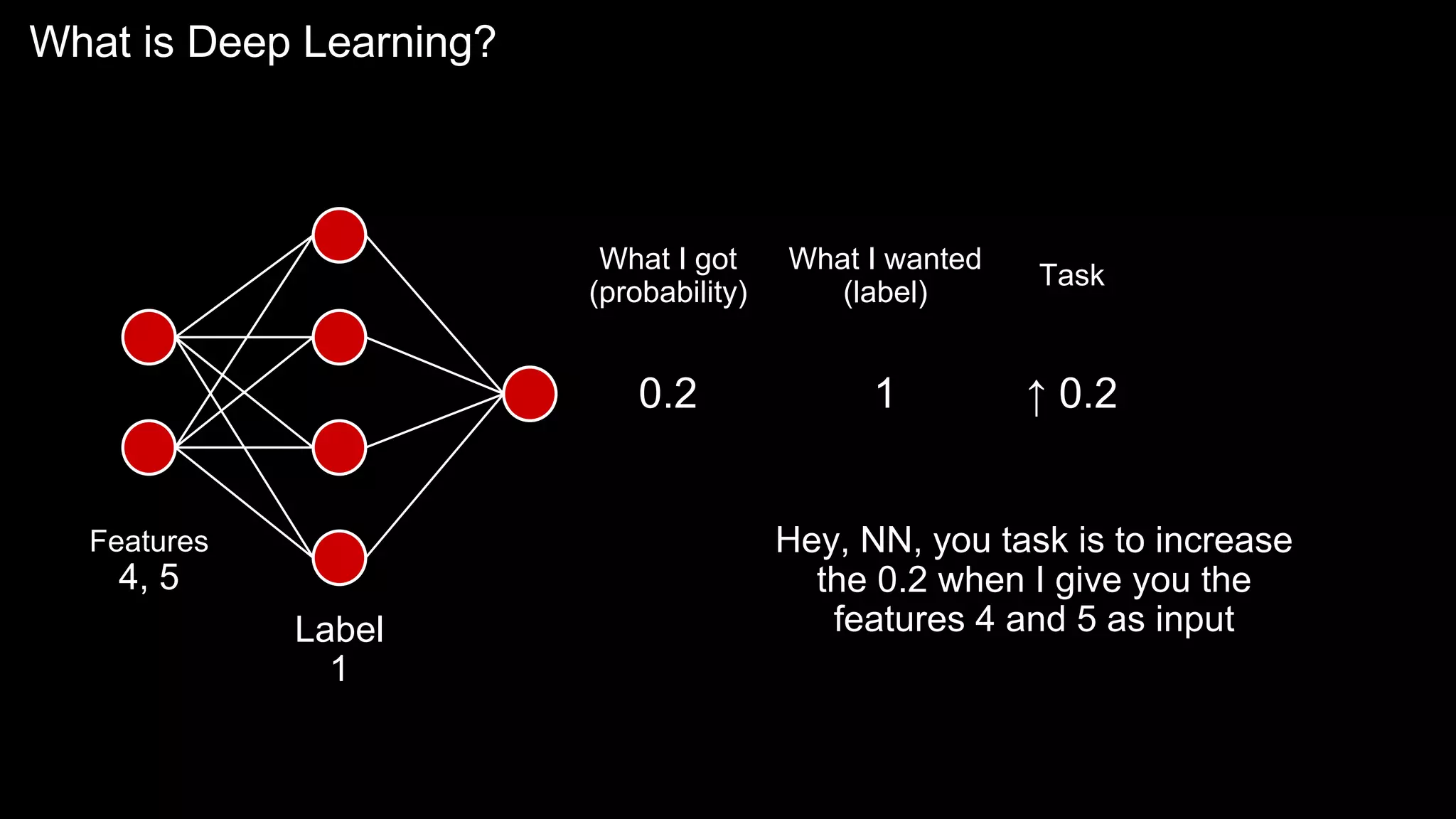
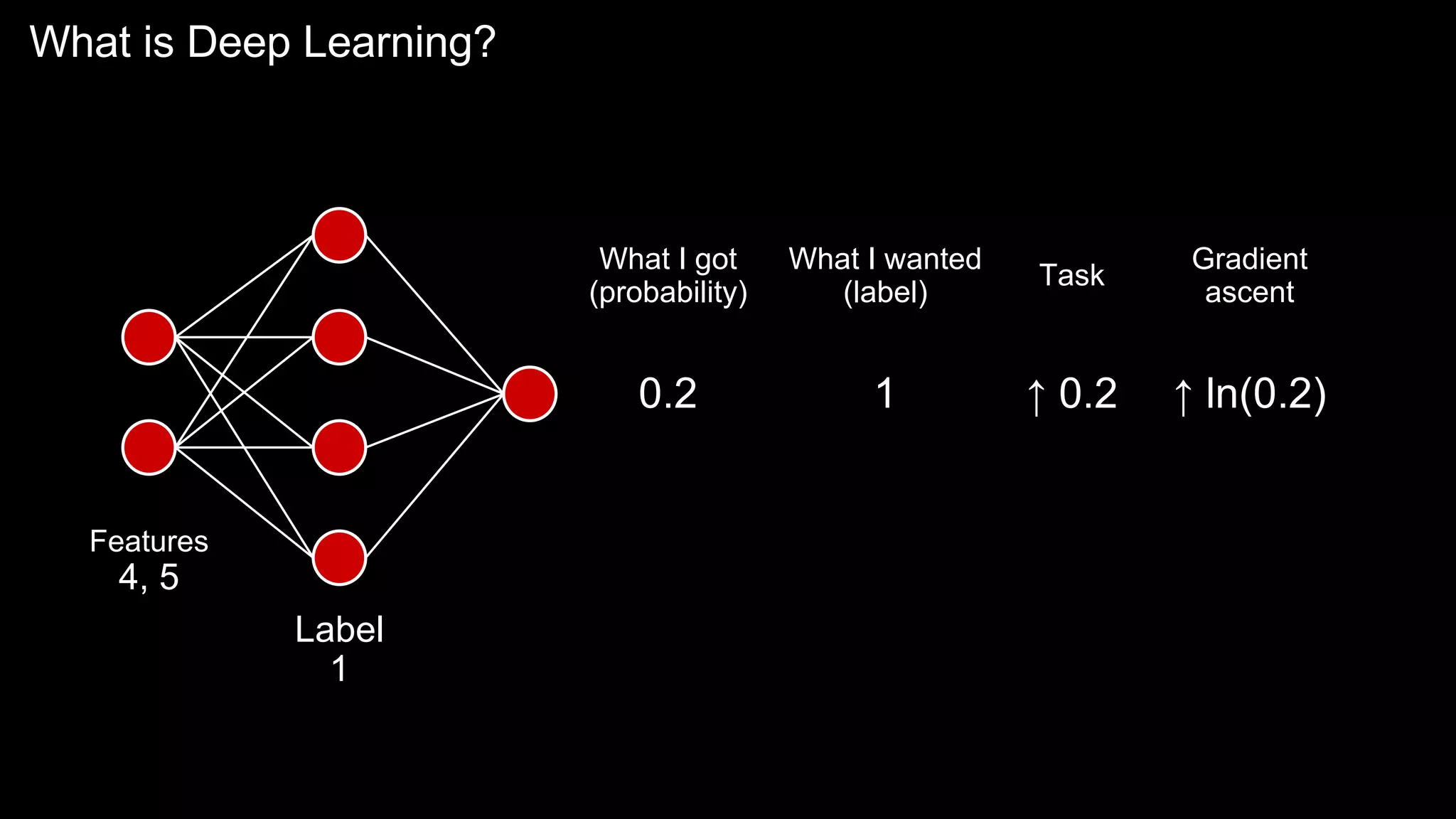
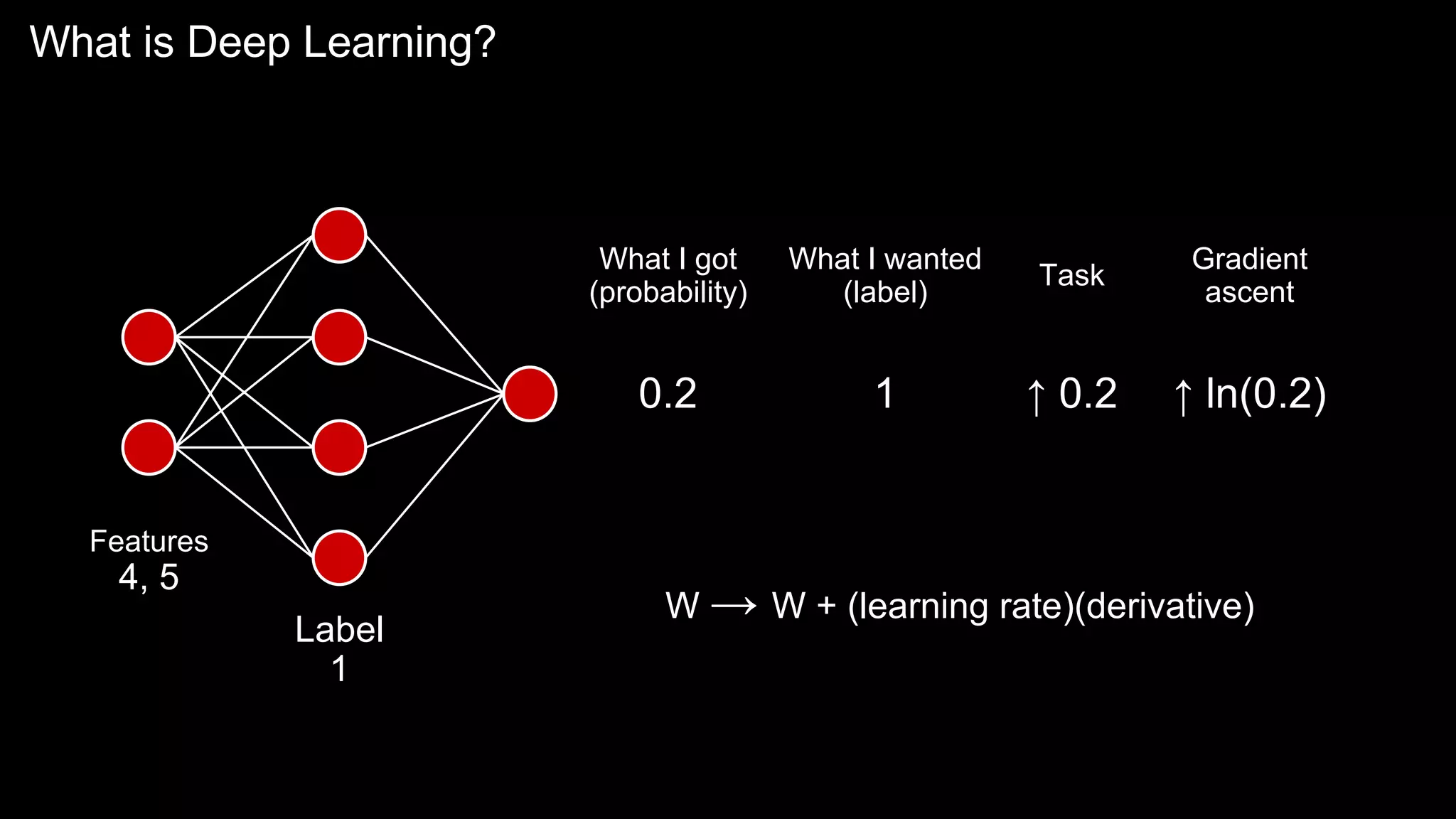
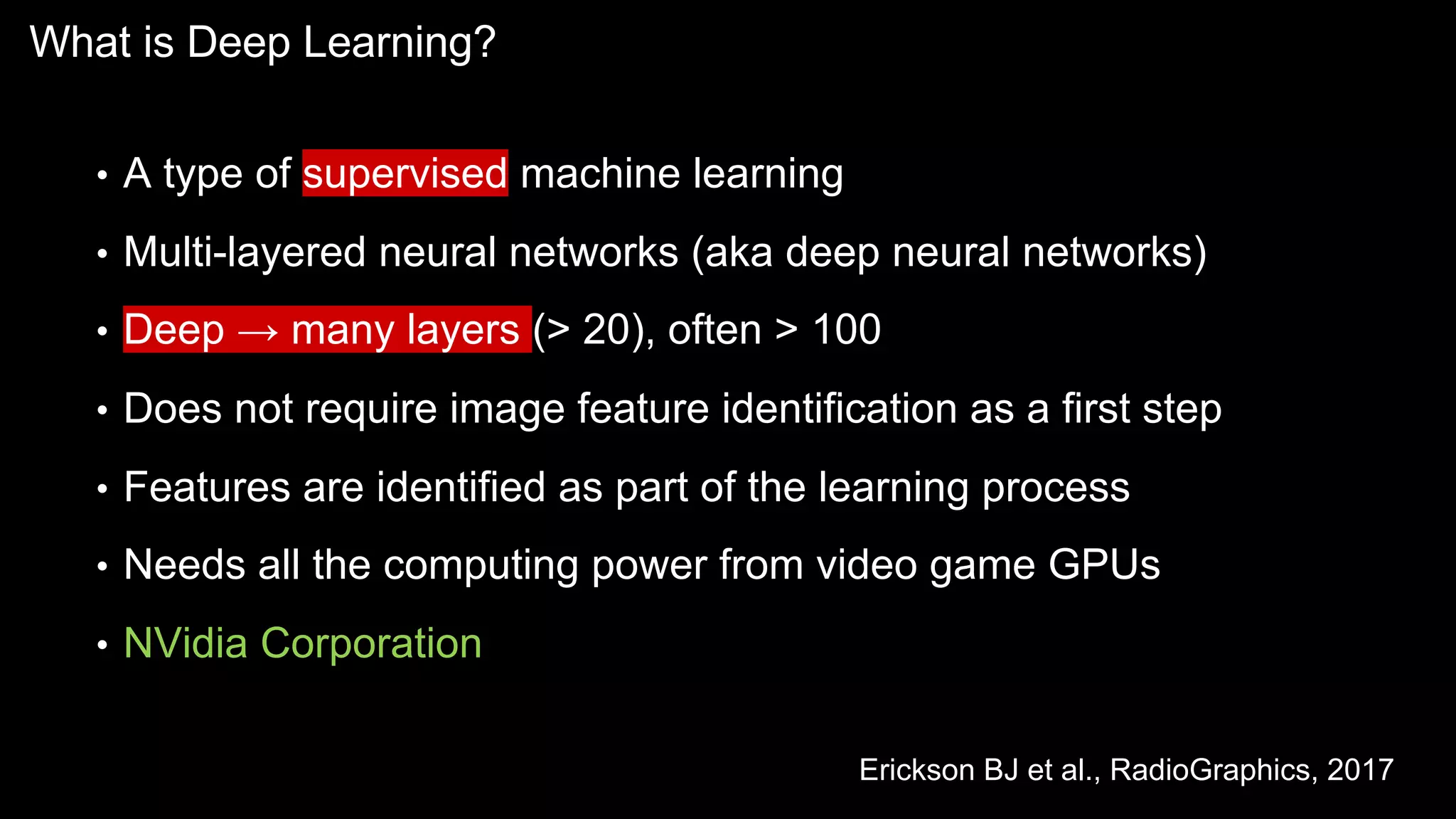
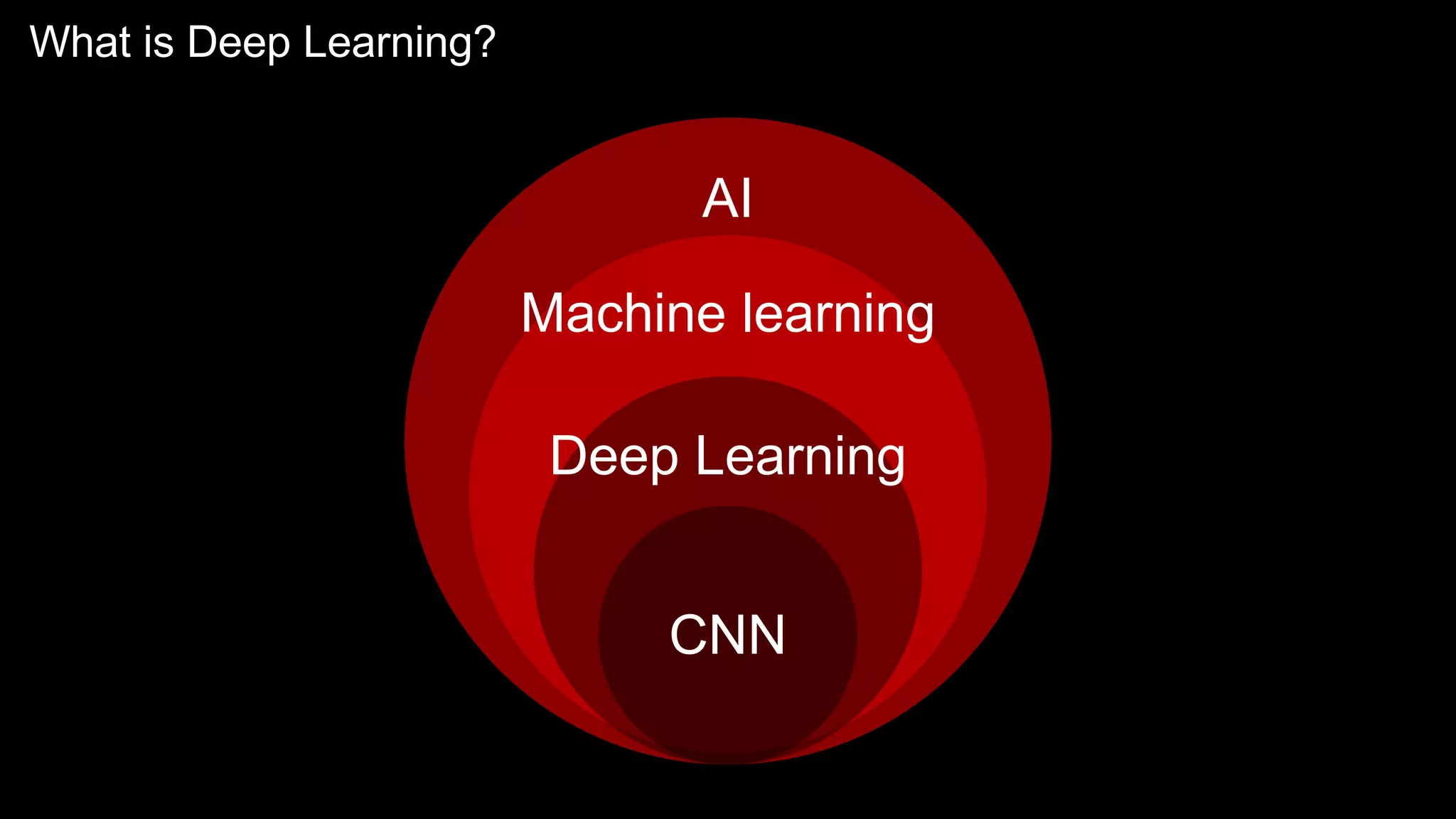
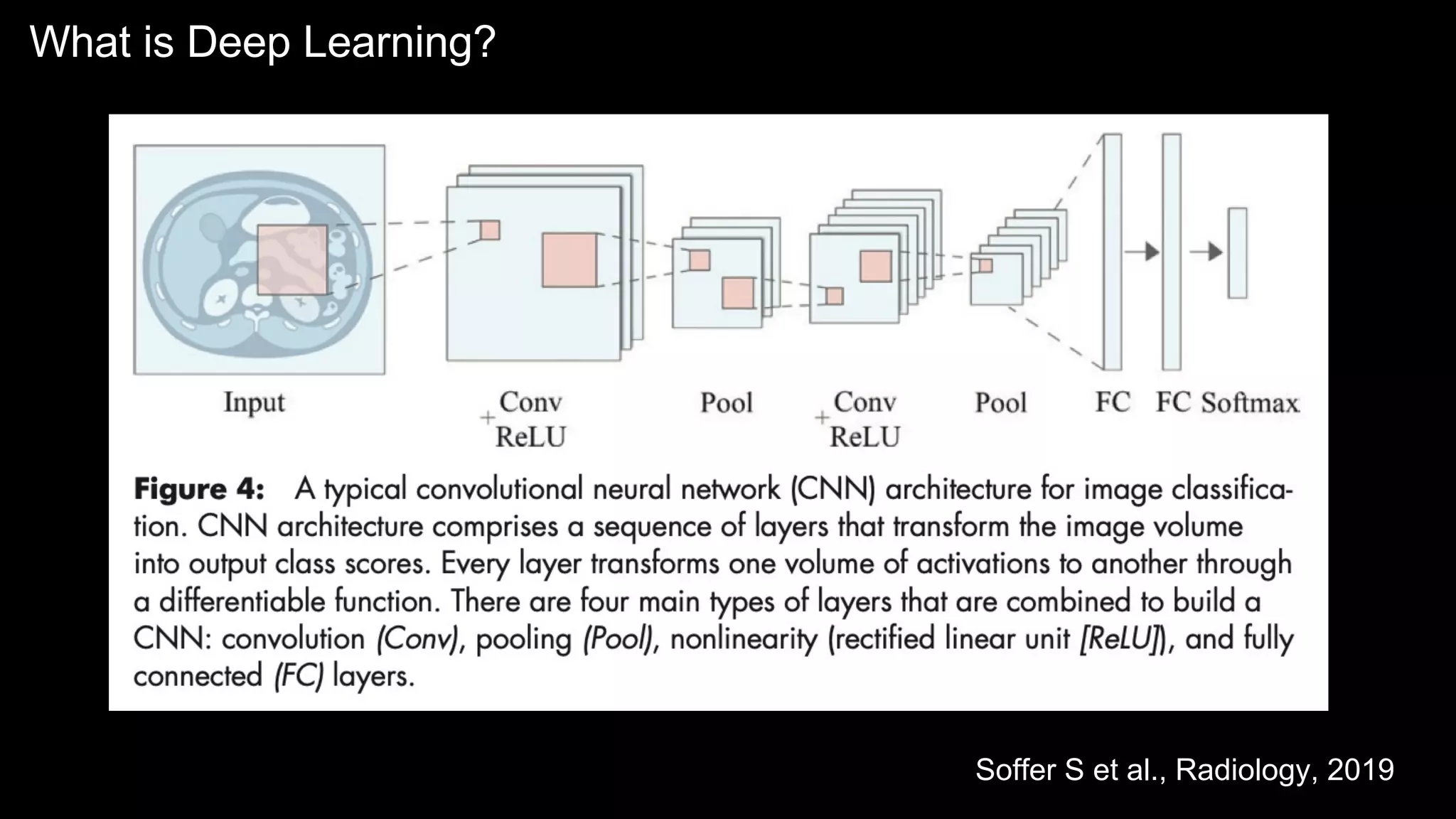
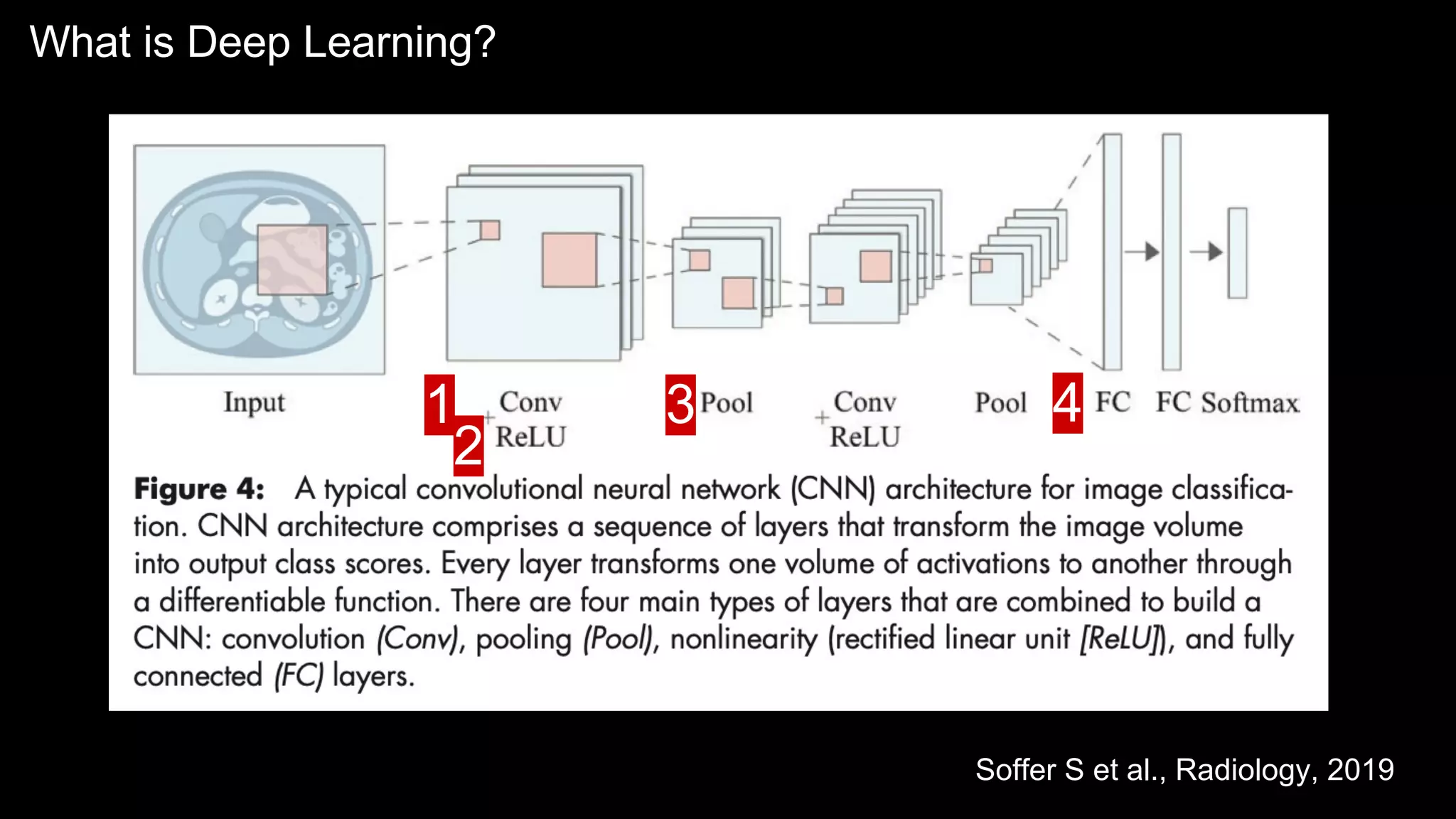
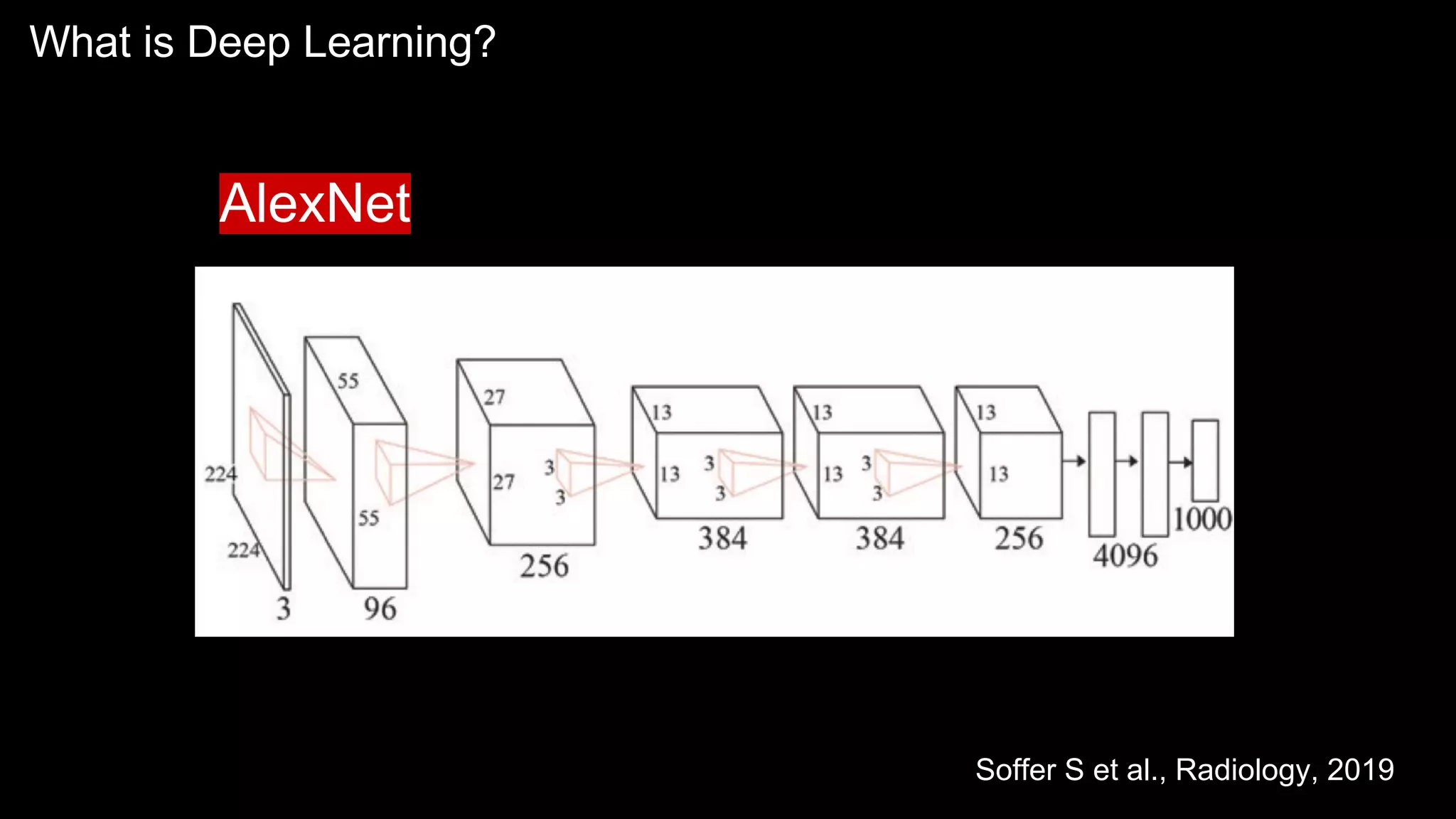
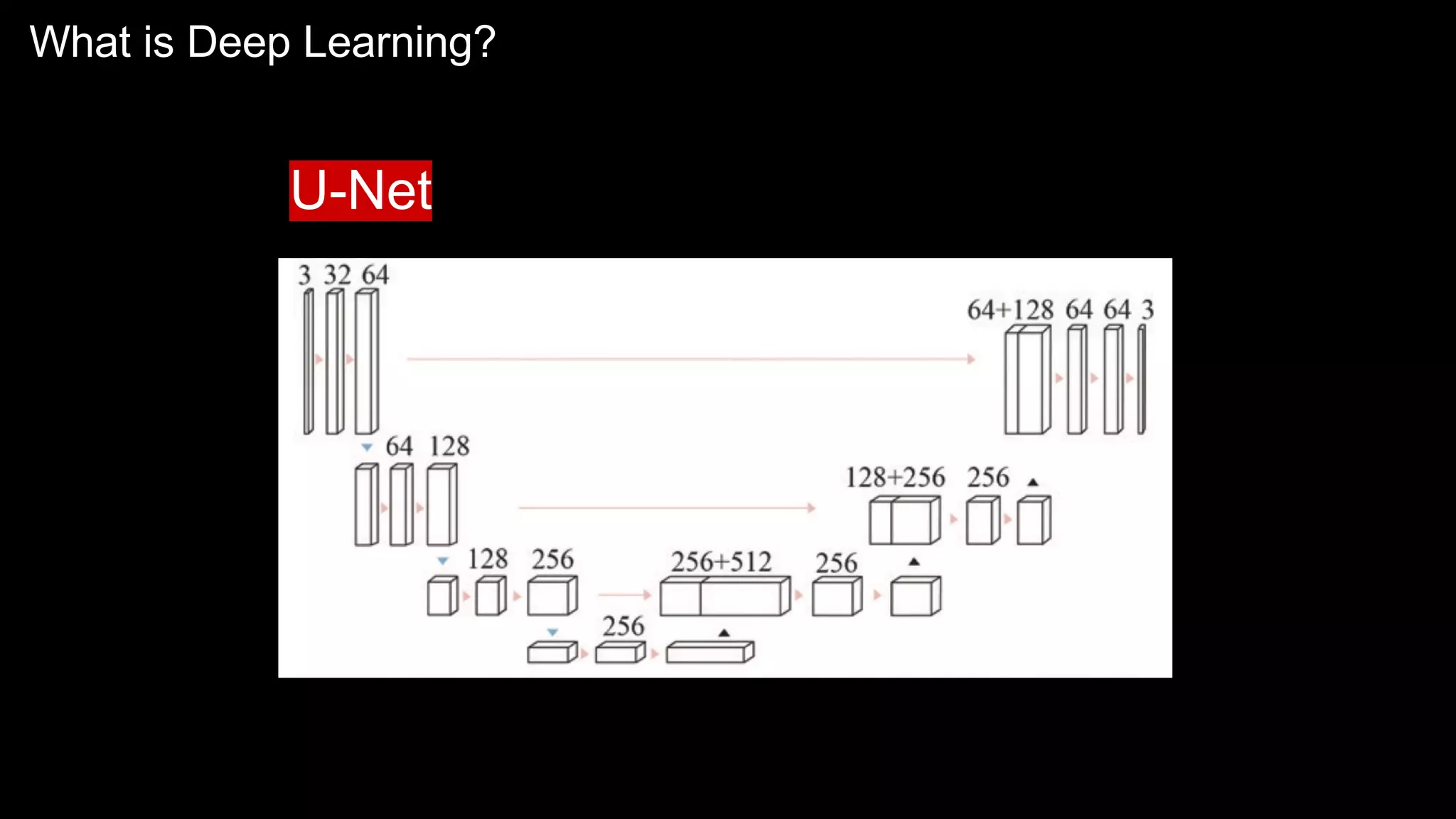
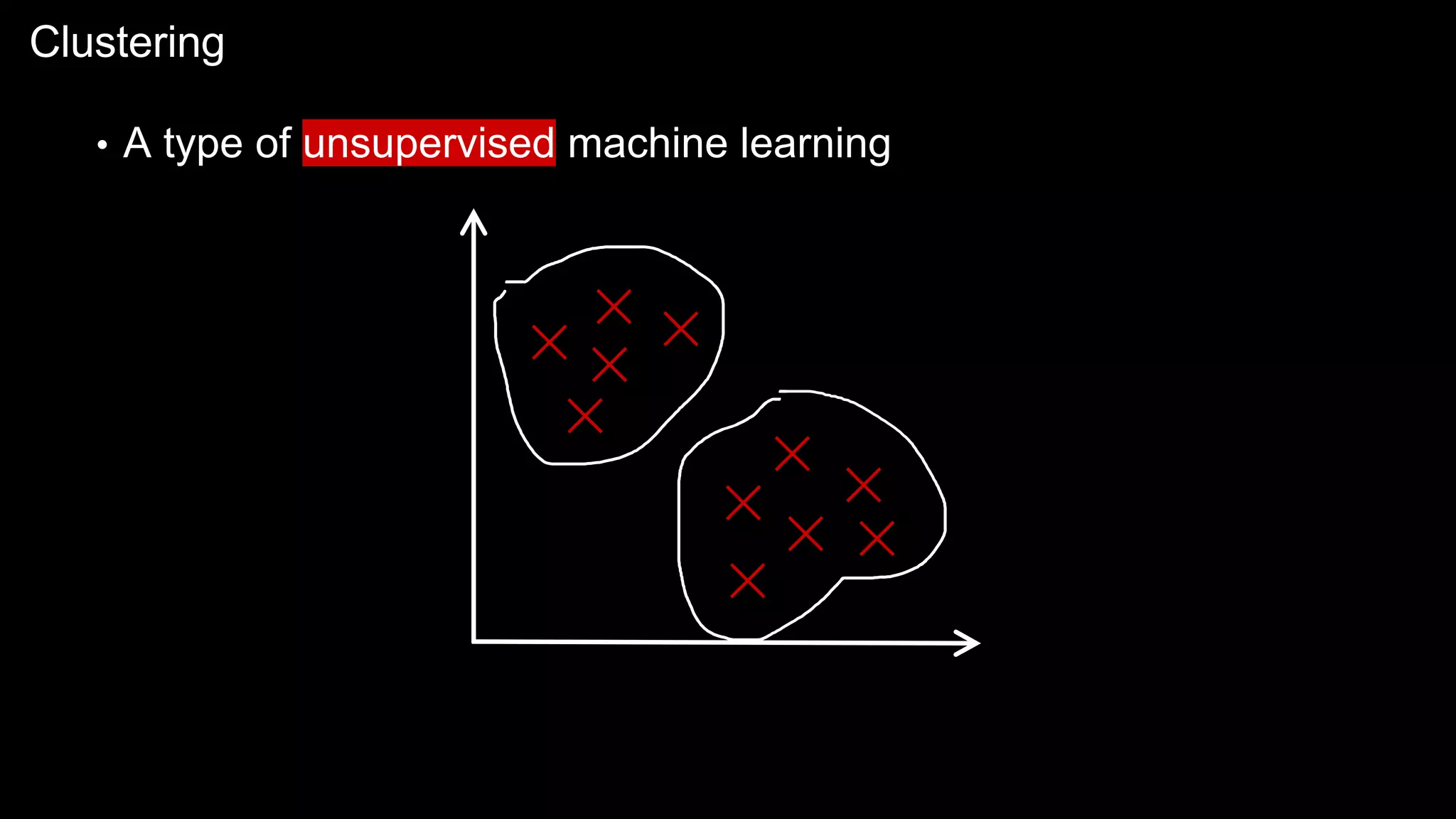
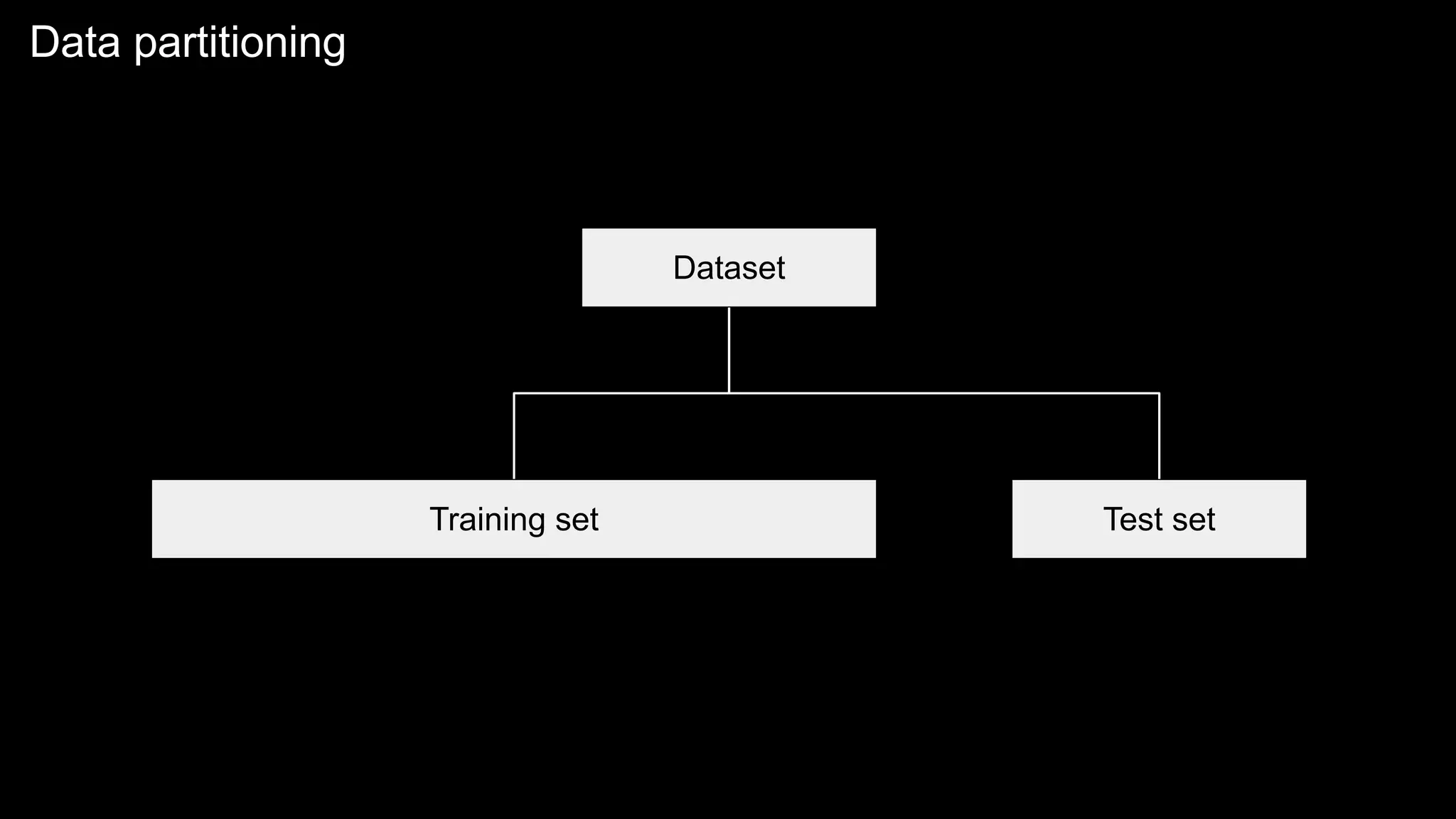
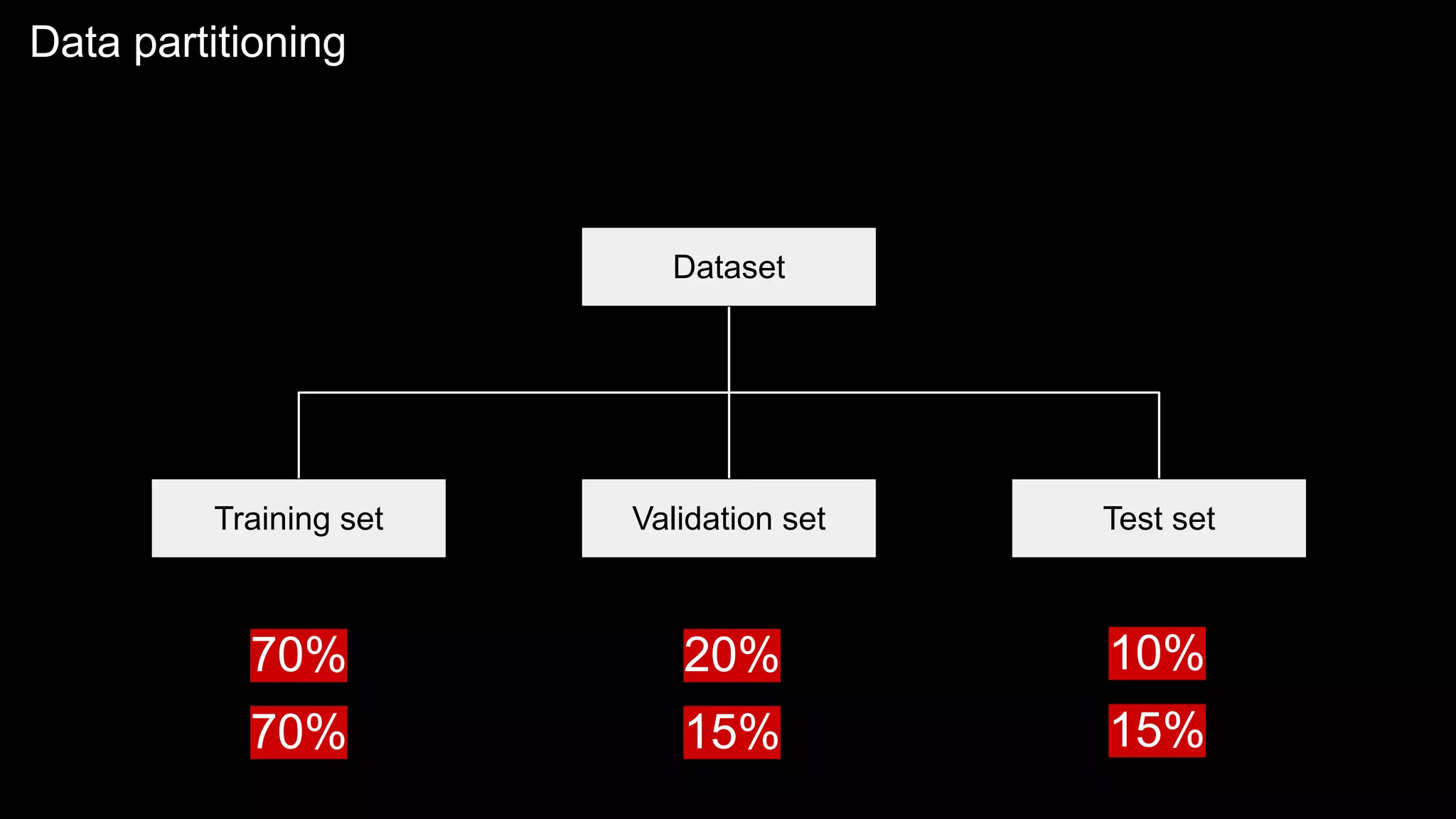
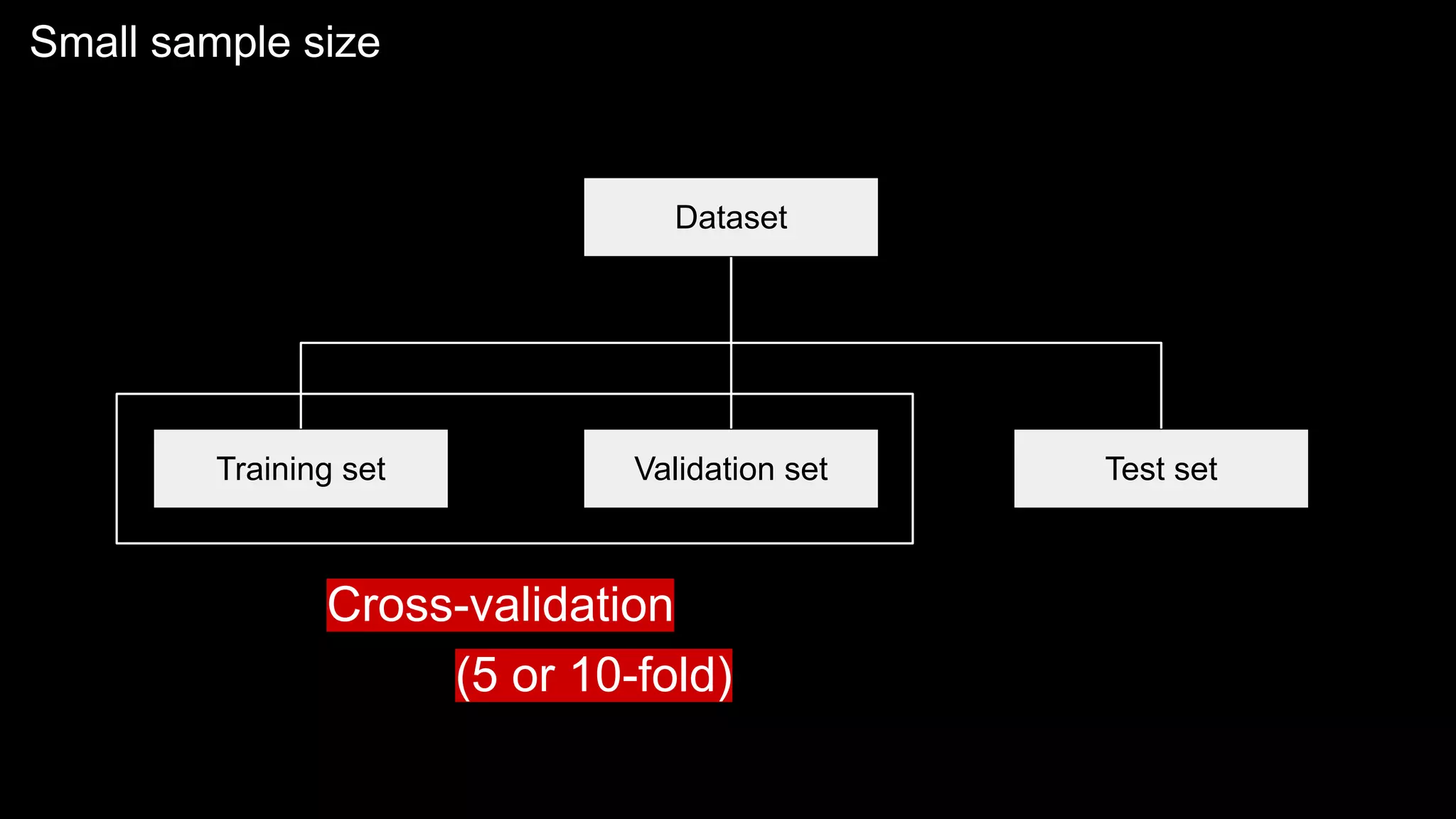
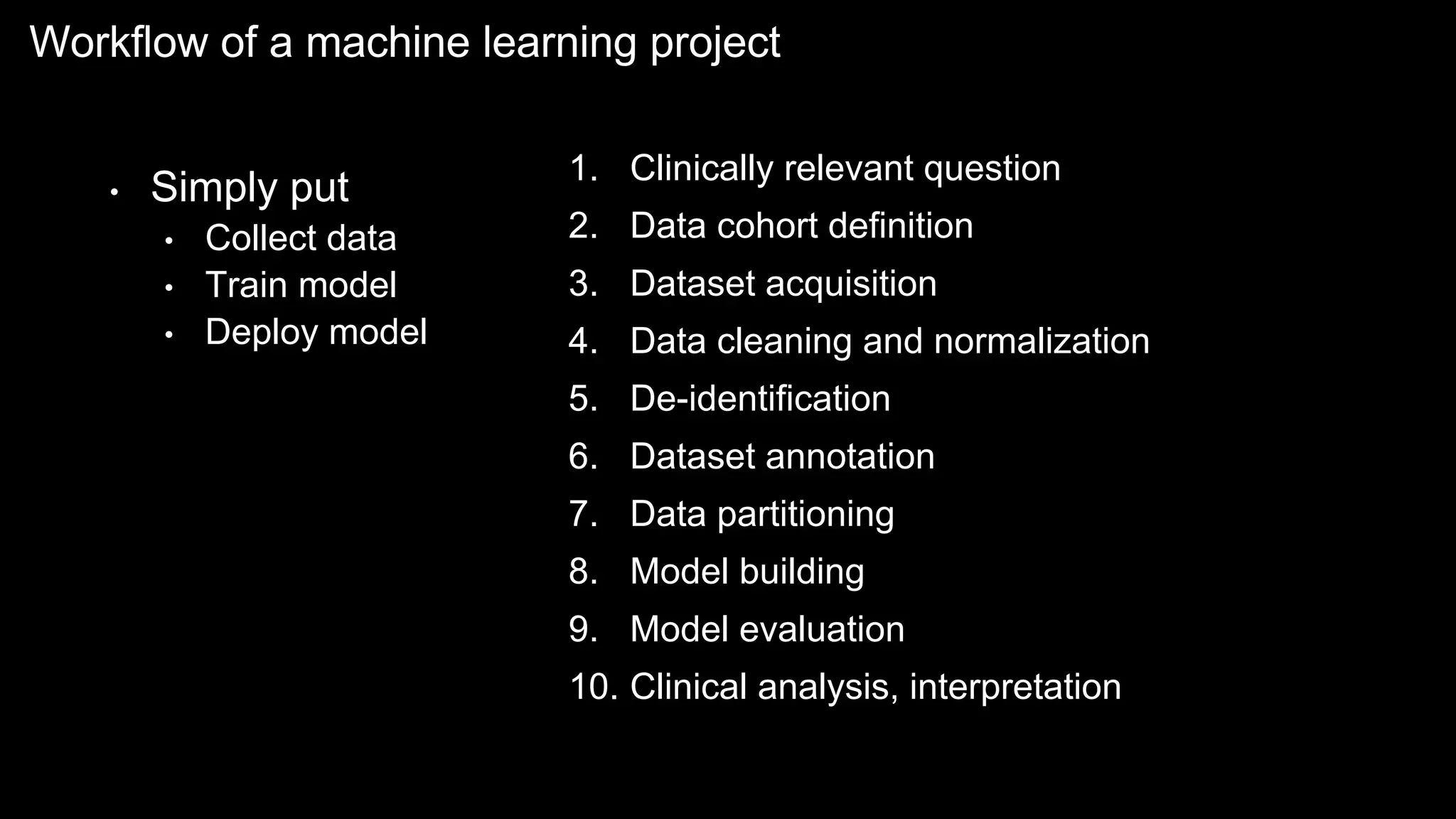
The document provides an overview of the basics of artificial intelligence (AI) relevant to radiology residents, detailing essential concepts like machine learning and deep learning. It emphasizes the need for radiologists to adapt to AI for clinical practice, algorithm evaluation, and collaboration across disciplines. Highlighted are key resources for learning AI, the principles of various machine learning techniques, and the workflow involved in AI projects.