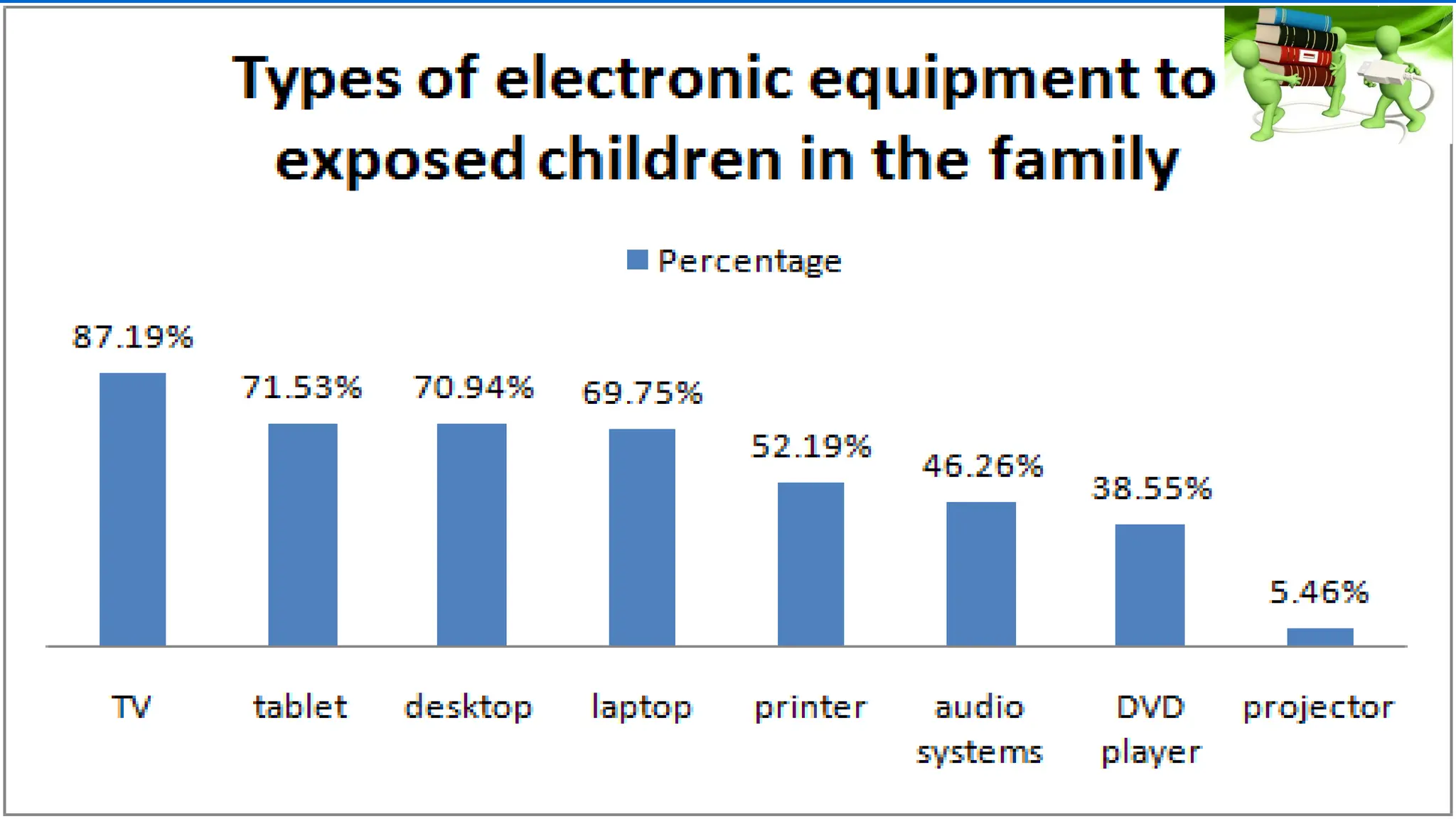
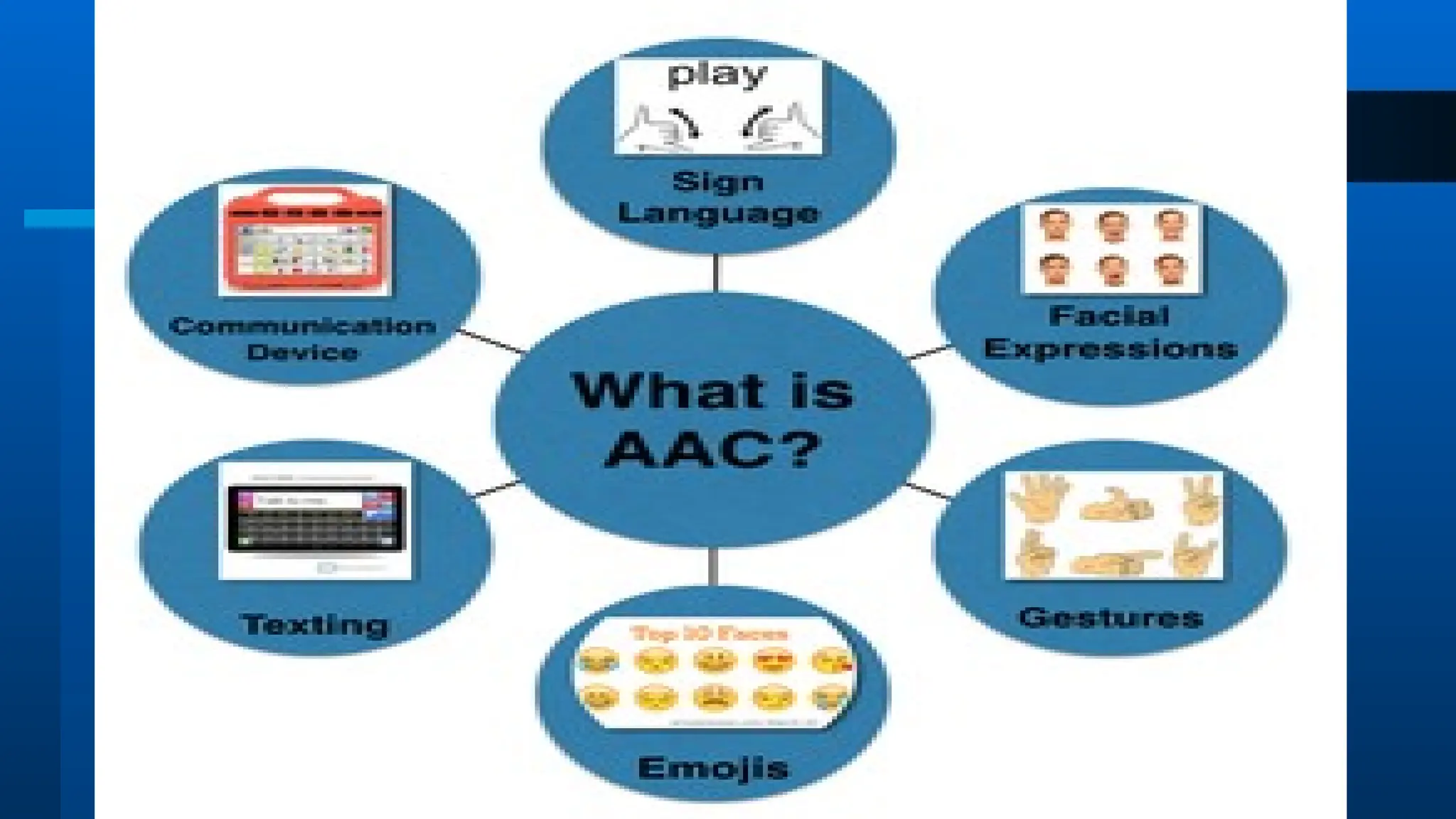
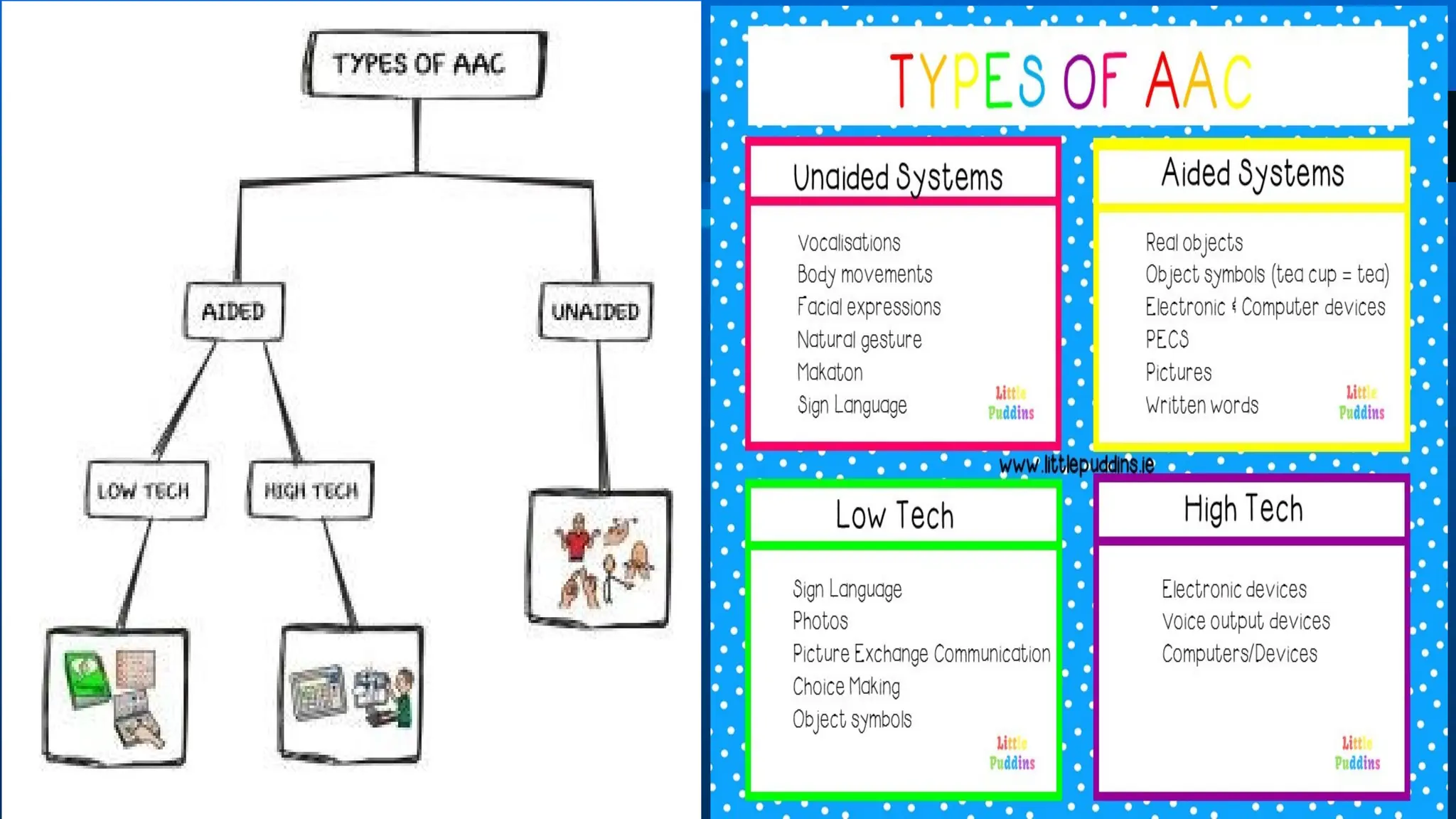
The document outlines the objectives and importance of educational technology in enhancing learning outcomes, addressing barriers in educational settings, and the application of universal design for learning. It details various technological tools and methods used in education to support personalized learning and accommodate students with disabilities. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of educational technology in fostering relevant learning environments and preparing students for modern workforce demands.