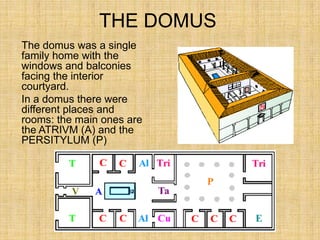
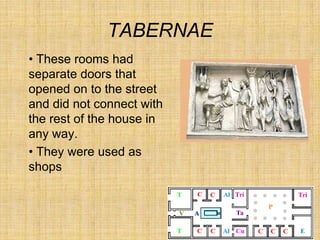
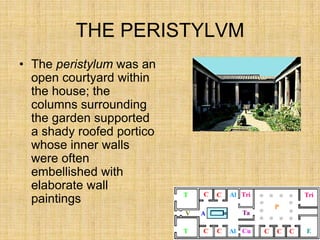
Roman houses came in different types - the domus for wealthy families, multi-story apartment buildings called insulae for the poor, and rural villas. The domus centered around an interior courtyard and usually included rooms for receiving guests (atrium, tablinum), living spaces (cubicula, triclinium), and a garden (peristylum). Poorer Romans lived crammed together in poorly-built insulae that lacked amenities, while wealthy owners resided in luxurious rural villas or divided their urban homes between housing and businesses.