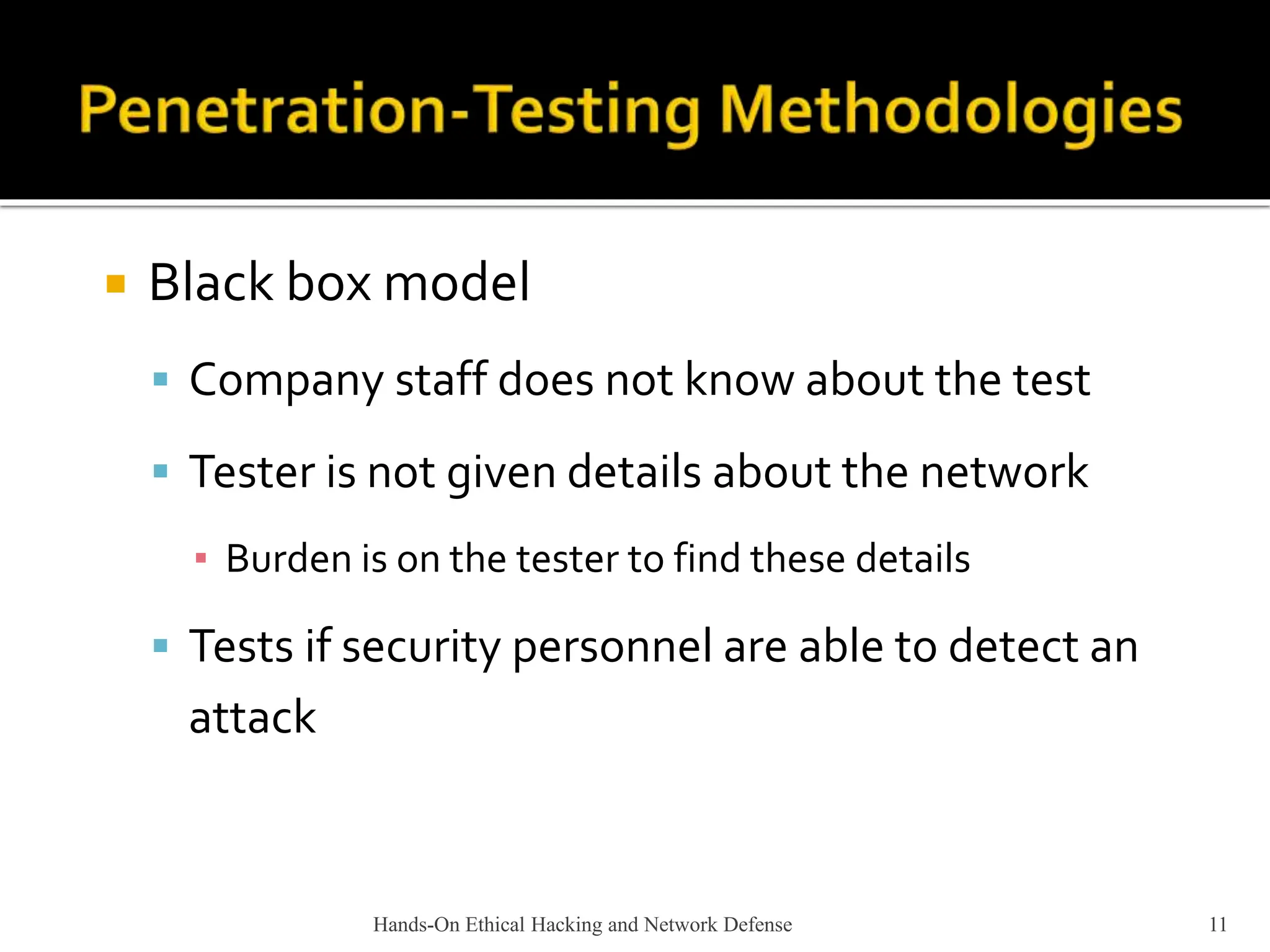
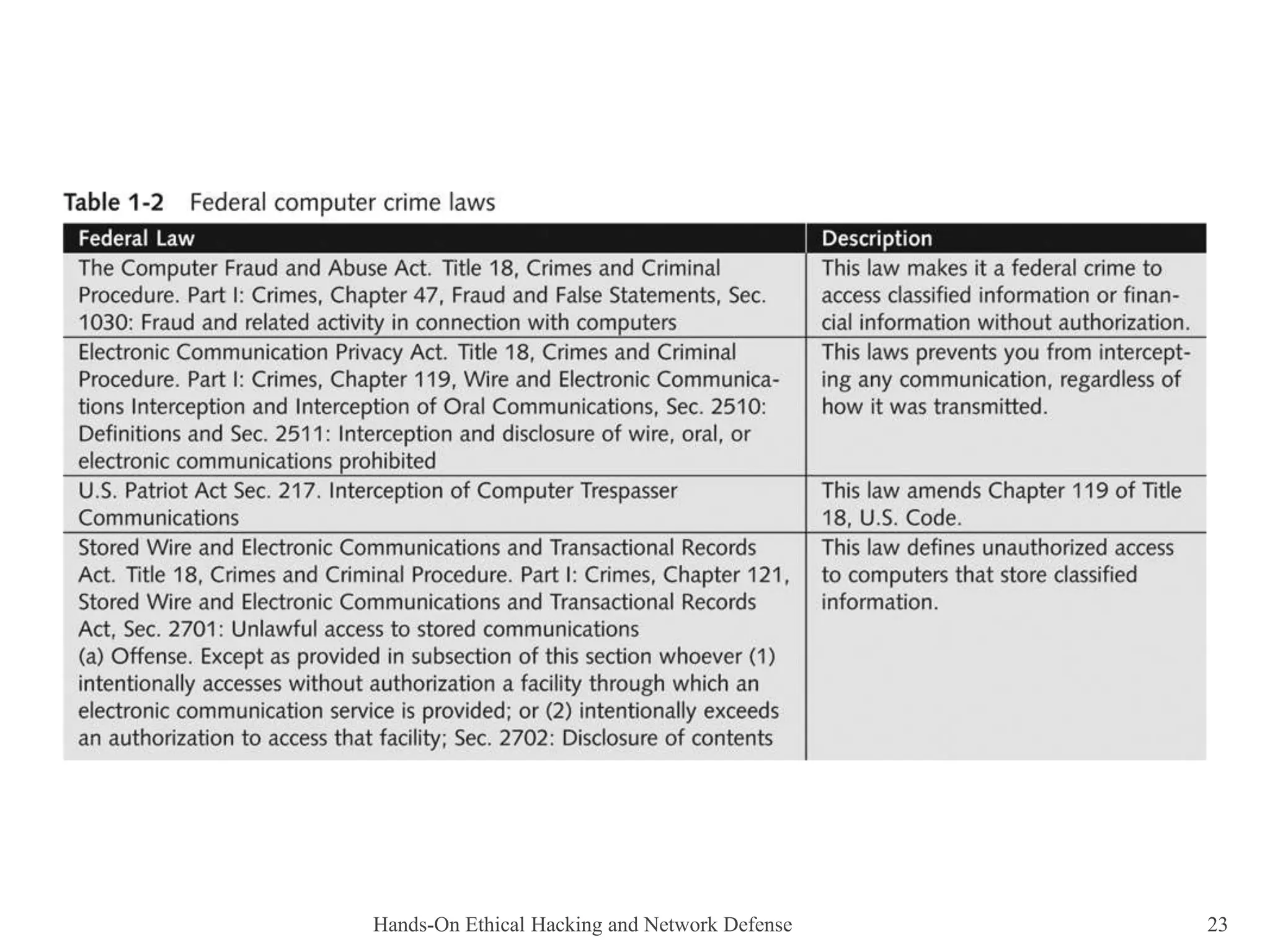
This document provides an overview of ethical hacking. It describes the role of an ethical hacker as someone who performs penetration tests or security tests with a company's permission to find weaknesses. Ethical hackers may be employed by companies, and only report their findings without solving problems themselves. The document contrasts ethical hackers with illegal hackers and crackers who access systems without authorization. It also discusses certification programs, legal and illegal activities for ethical hackers, and using contracts when working as an independent security tester.