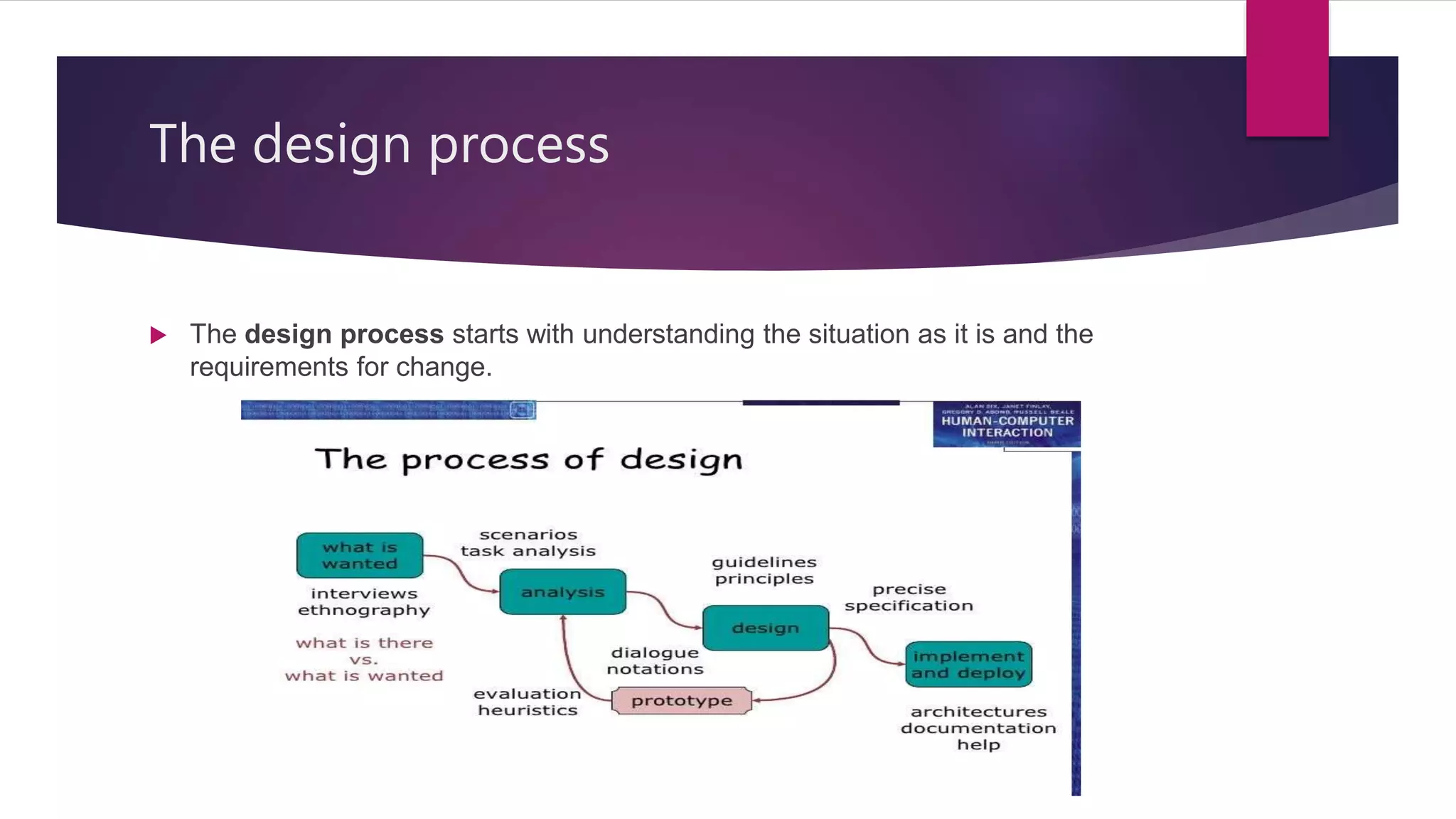
The document outlines the design process, emphasizing the importance of understanding user requirements, analyzing current practices, and focusing on user engagement through observation and persona creation. It discusses various phases of design, including iteration, prototyping, and navigation design, while highlighting the role of scenarios in exploring and communicating design ideas. Additionally, it addresses the necessity of both local and global structure in application design for enhanced user experience.