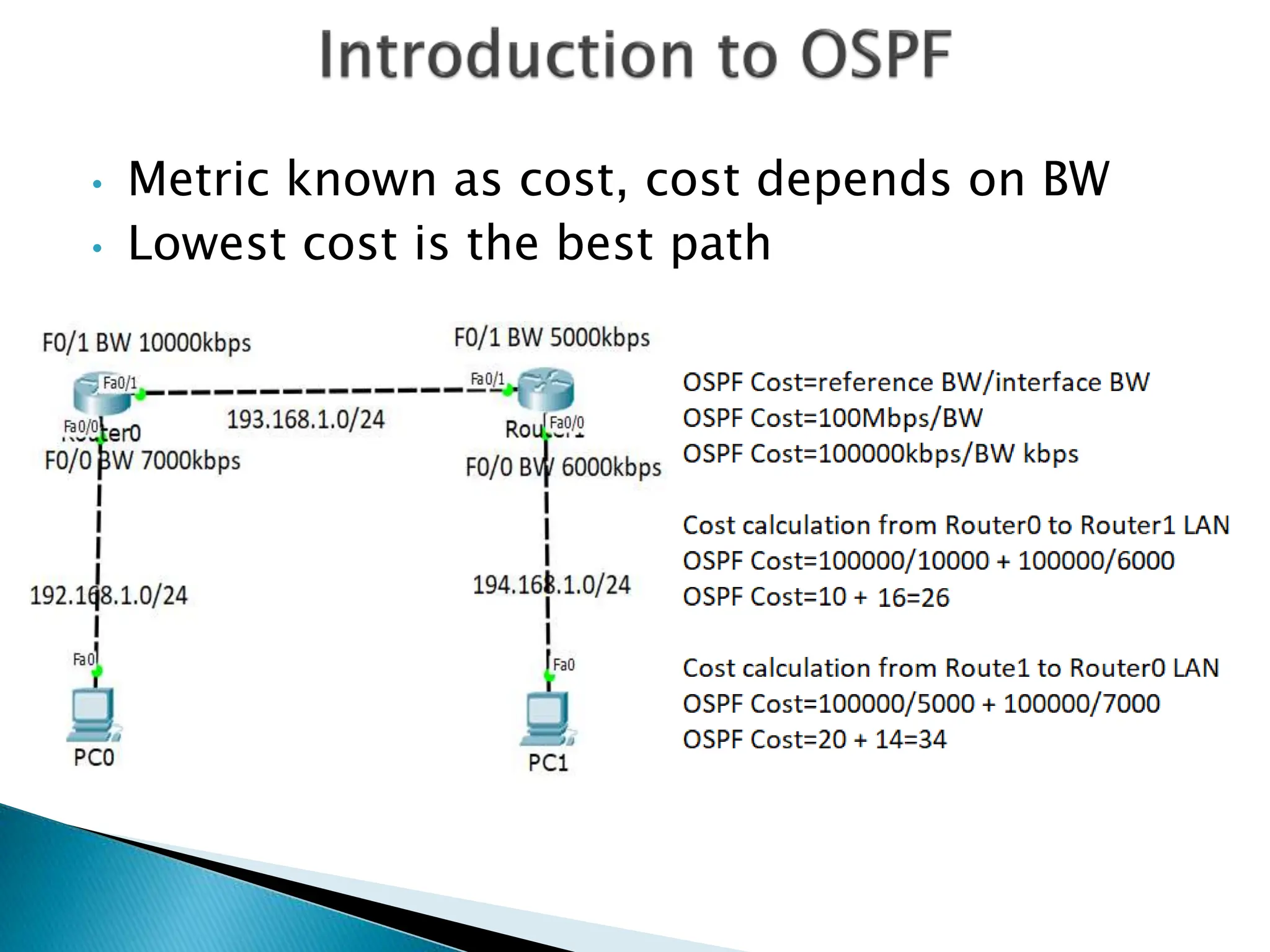
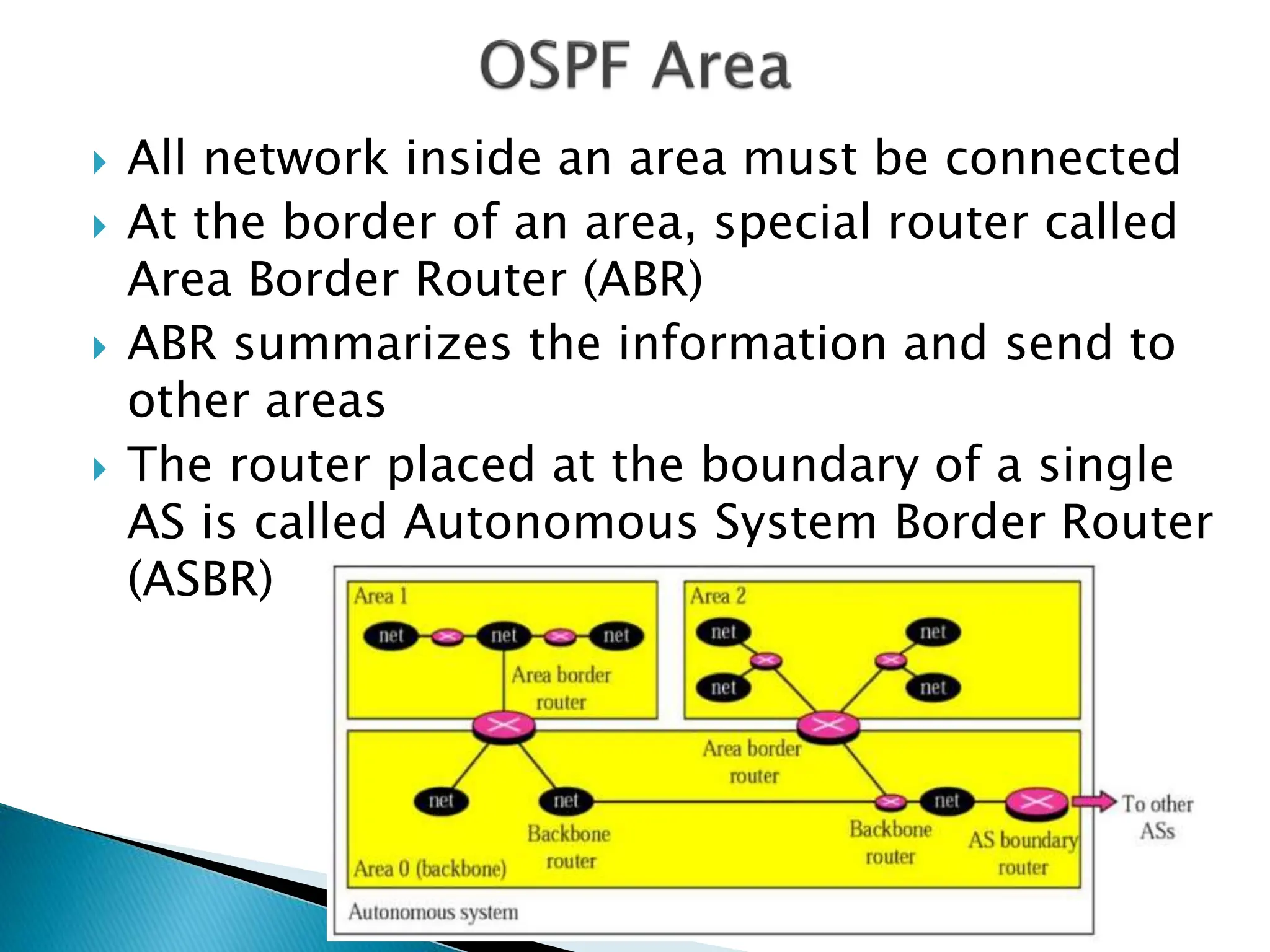
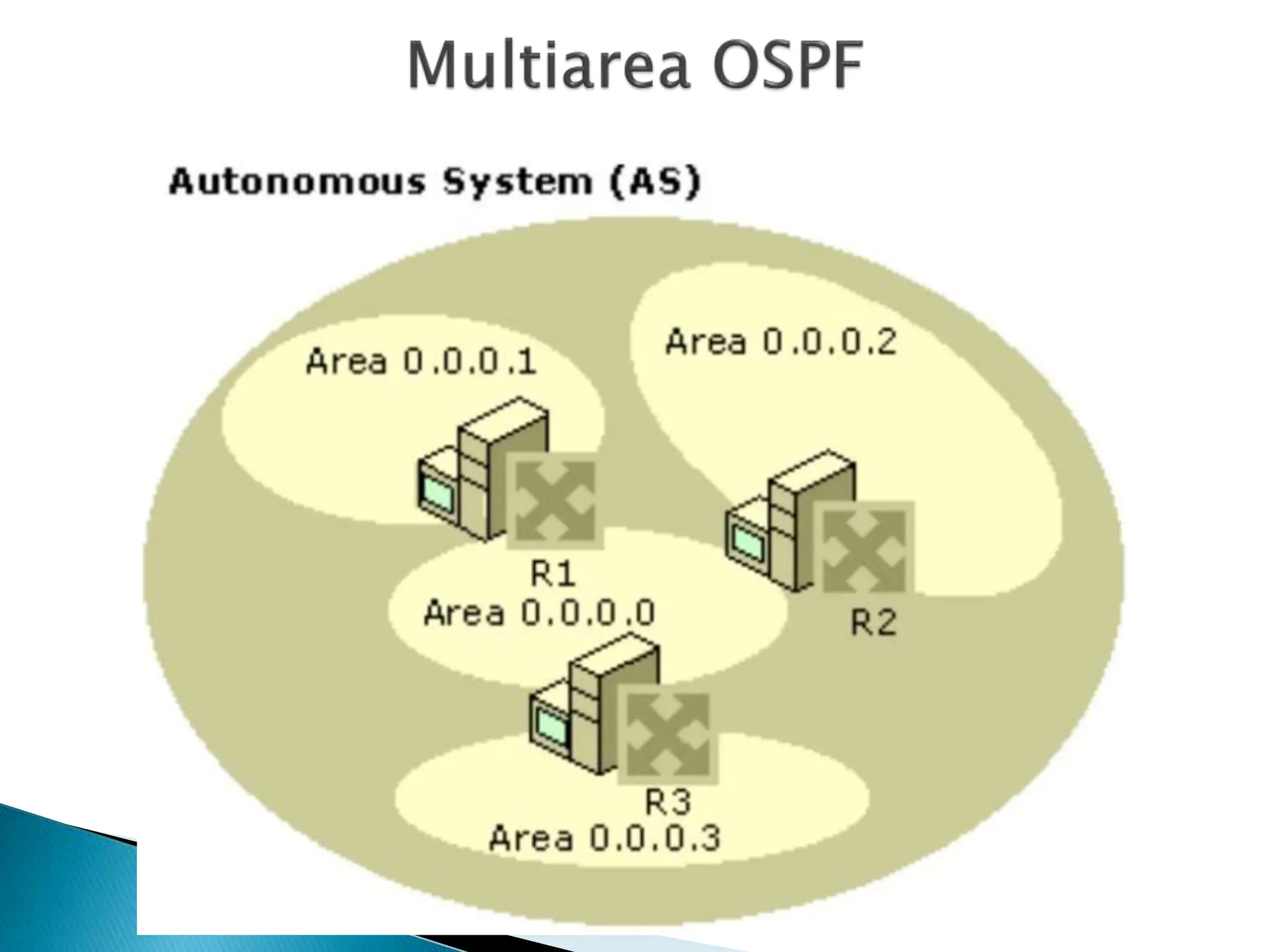
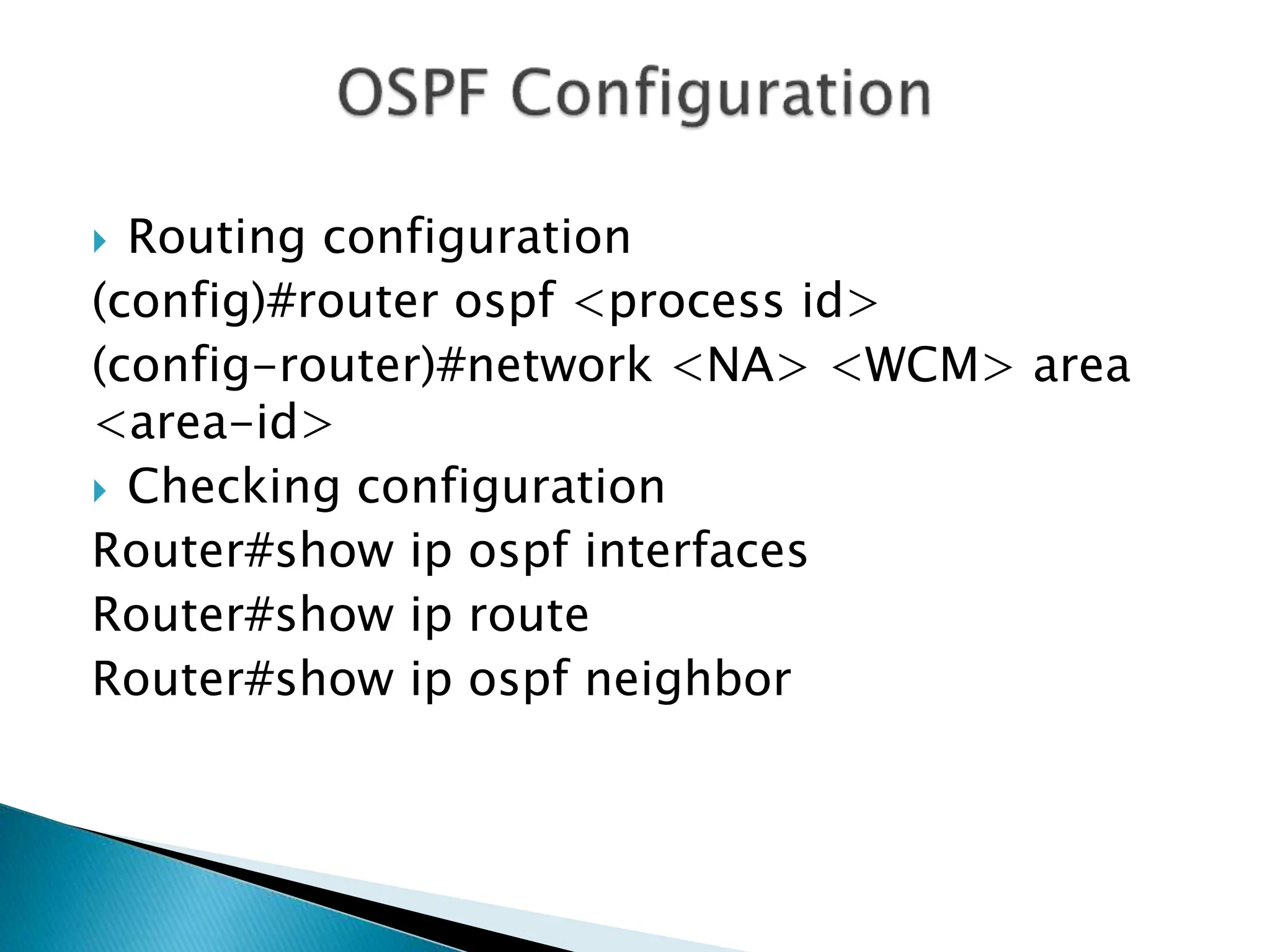
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a link-state intra-domain routing protocol using the Dijkstra algorithm, characterized by unlimited hop count and classless routing. It requires loopback interfaces for stable router identification and organizes networks into areas to optimize route information distribution. Configuration involves specifying process IDs and area IDs, with designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers (BDR) managing multi-access networks.