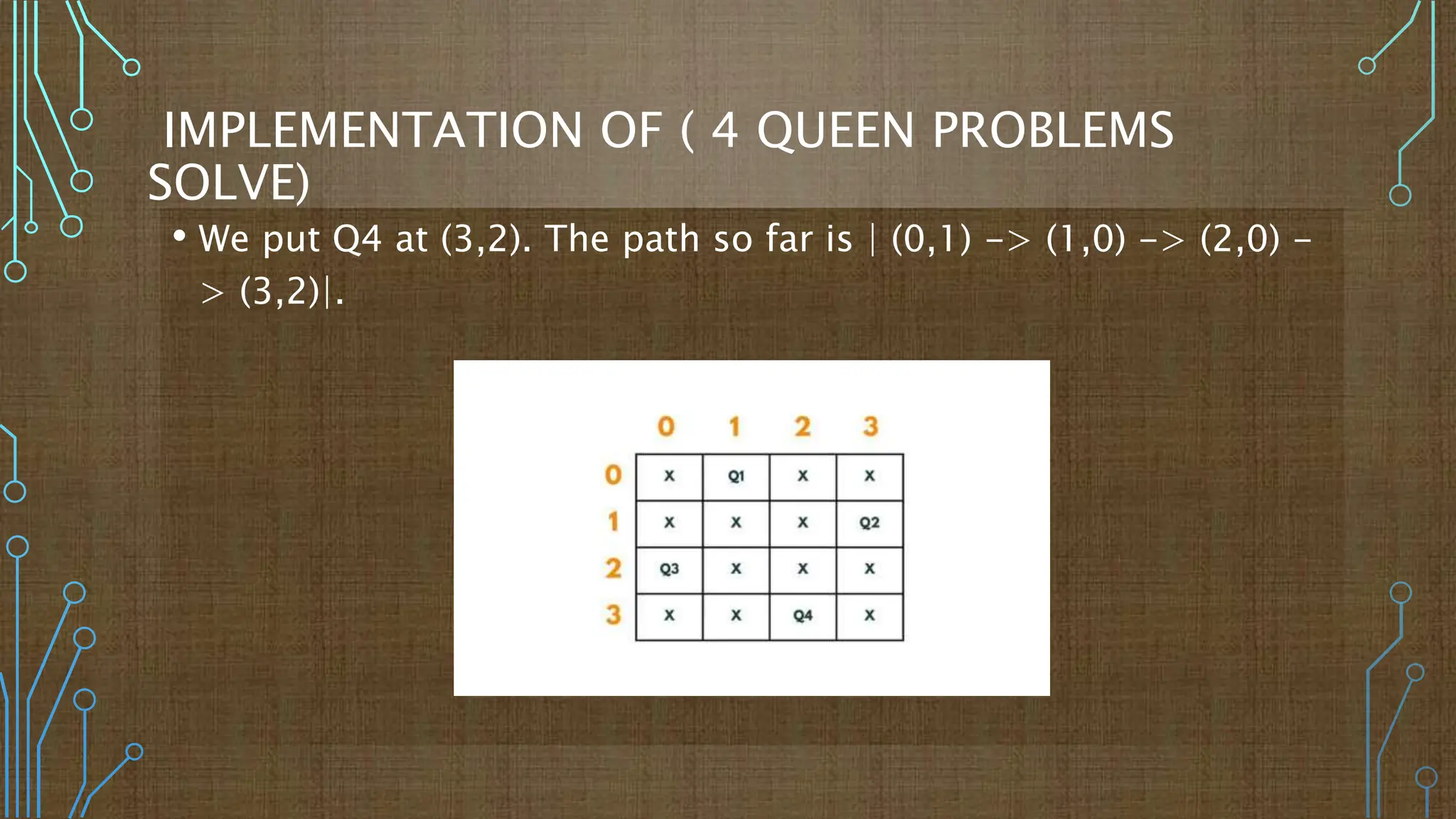
The n-queens problem is a classic puzzle where the objective is to place n queens on an n×n chessboard without any two queens threatening each other. The solution often utilizes backtracking, a method where one explores potential placements of queens, retracing steps if conflicts arise. An example implementation using a 4x4 chessboard demonstrates this backtracking process to find valid arrangements of queens.