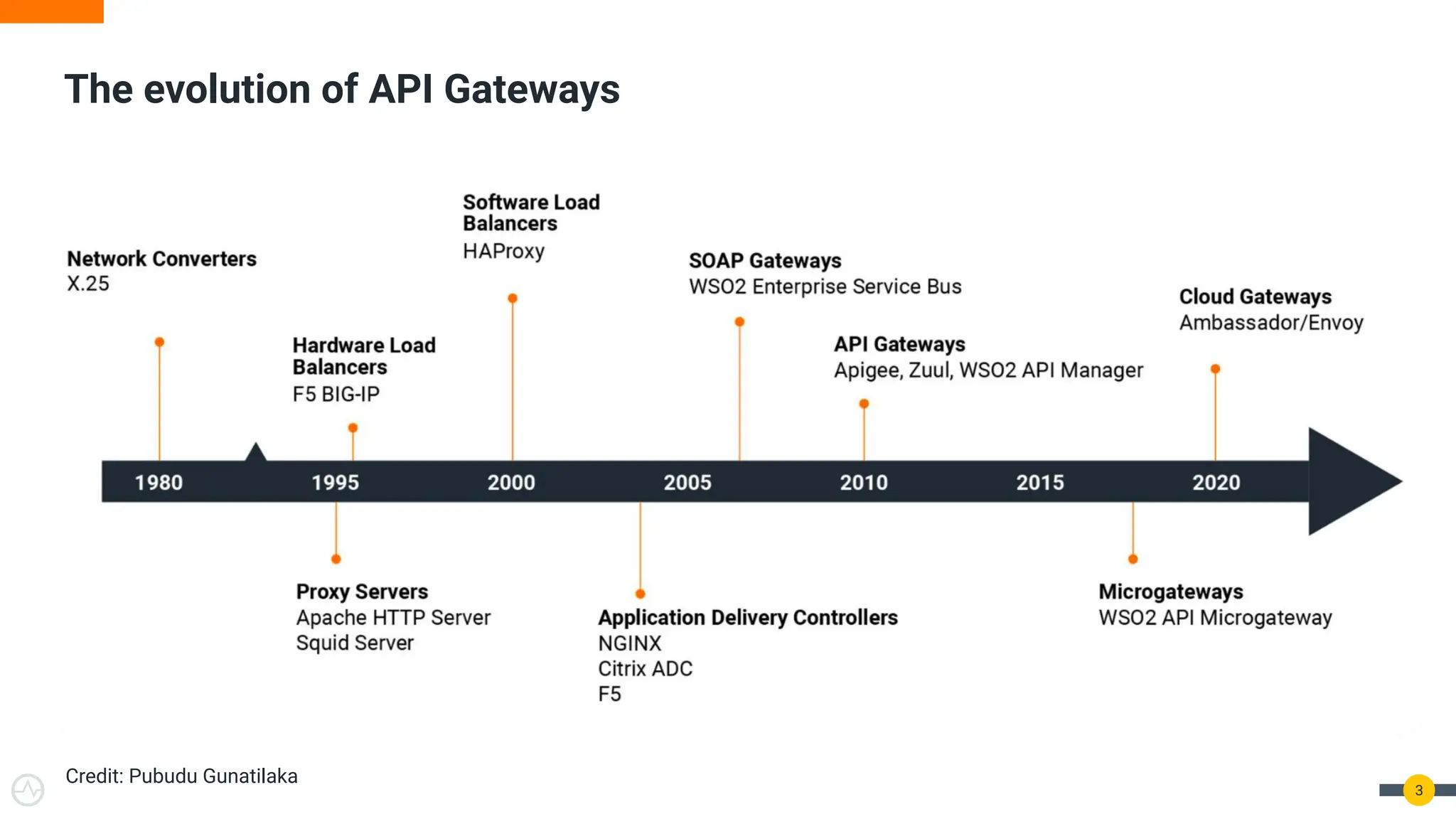
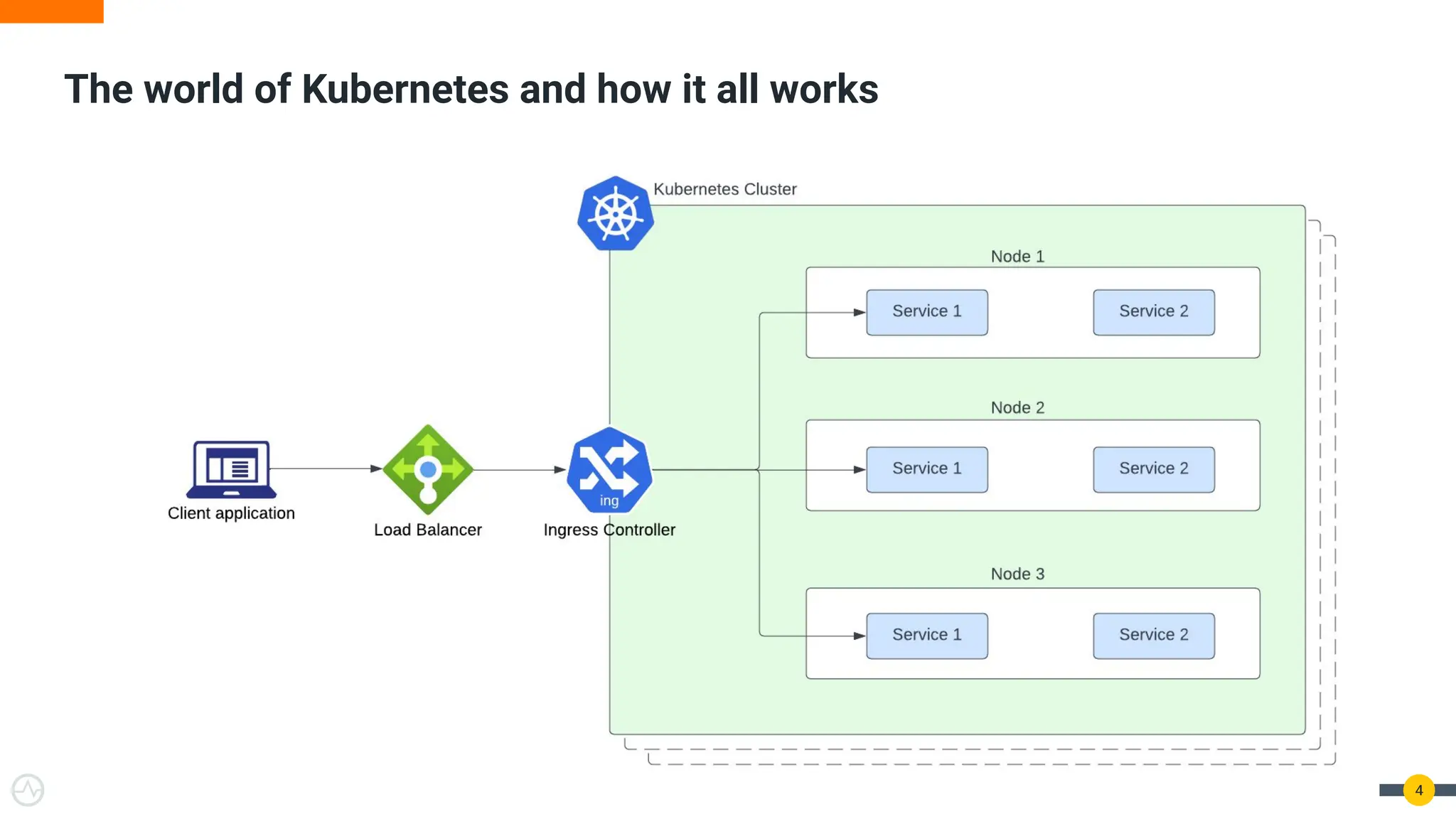
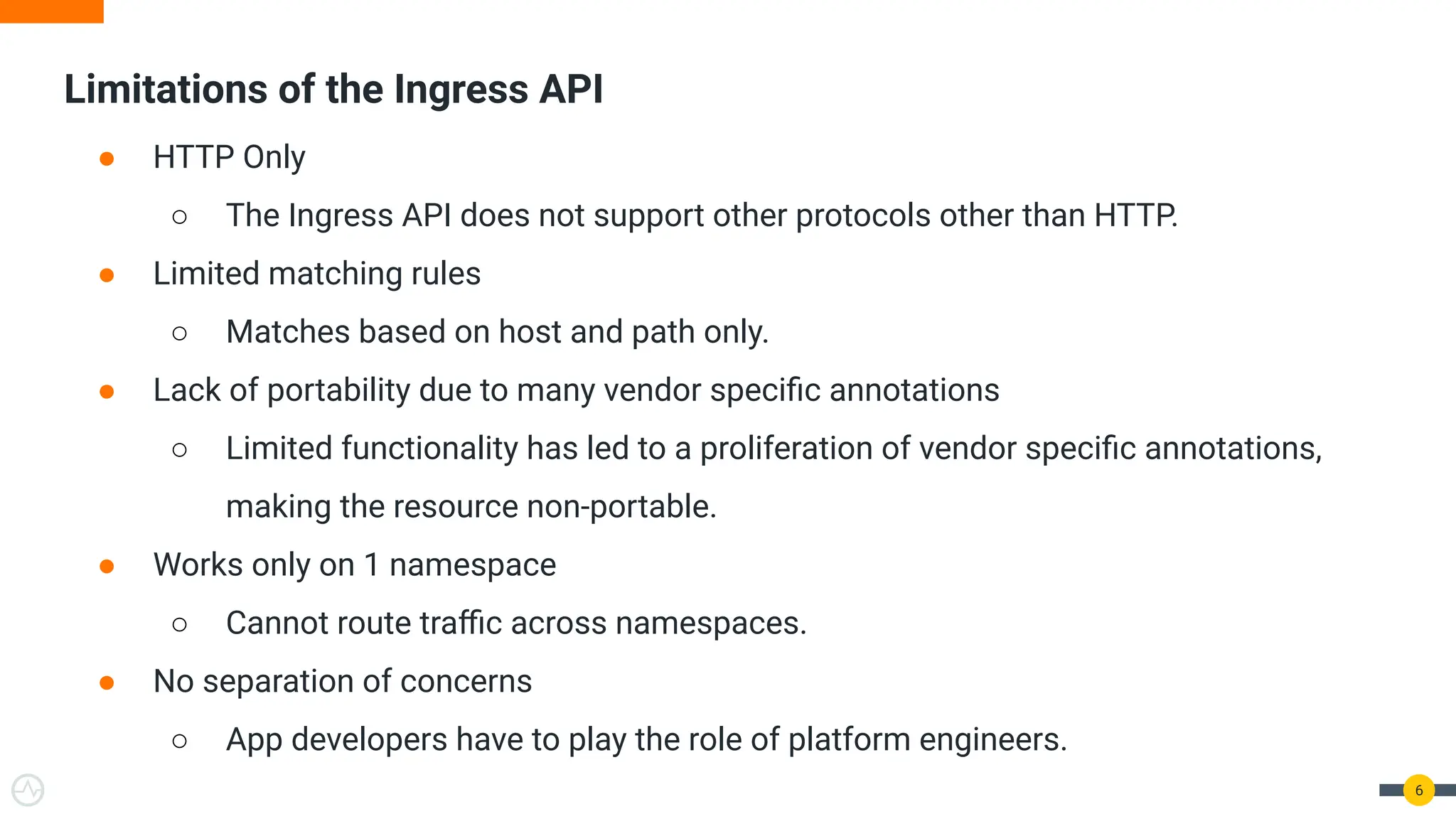
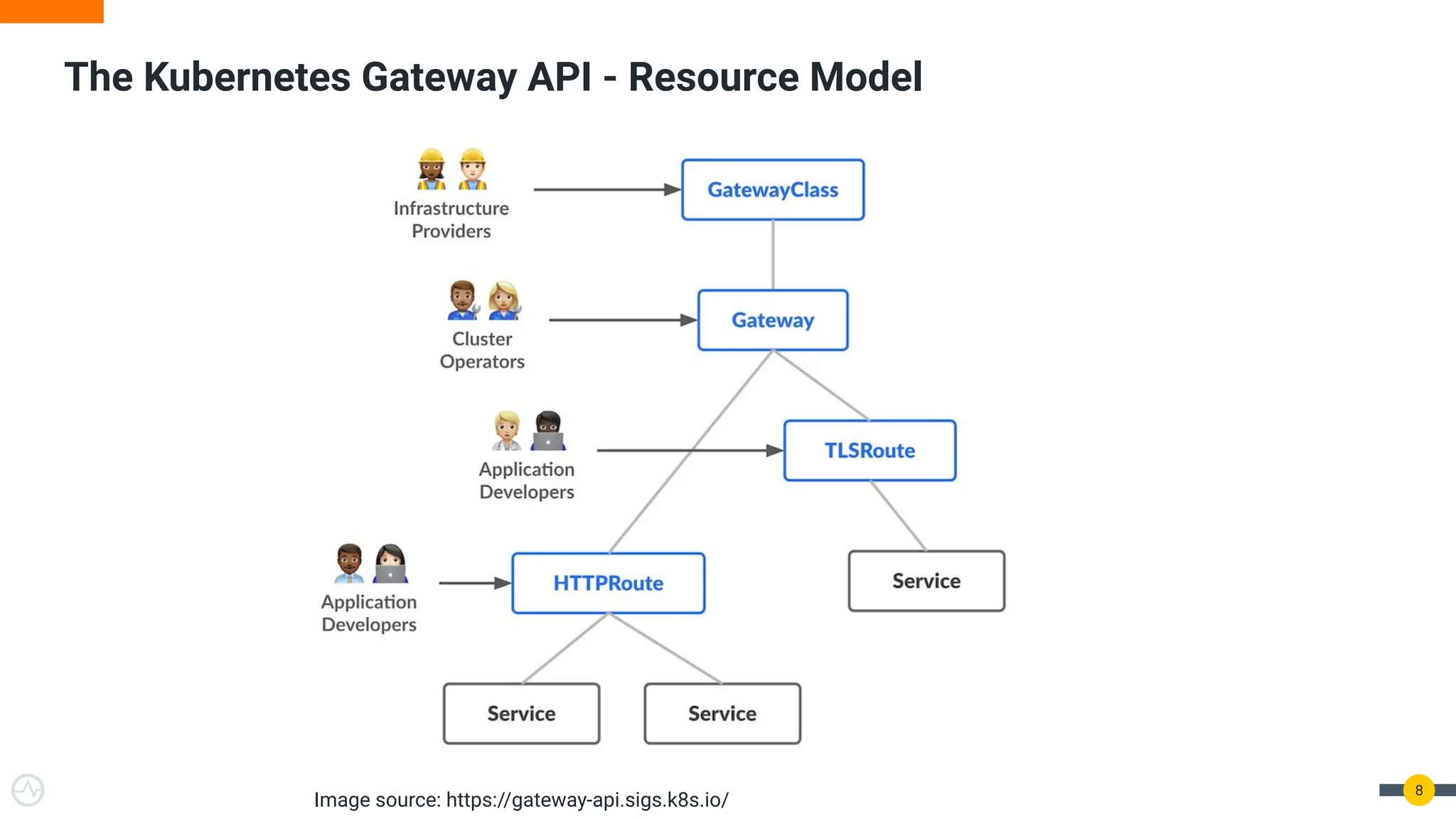
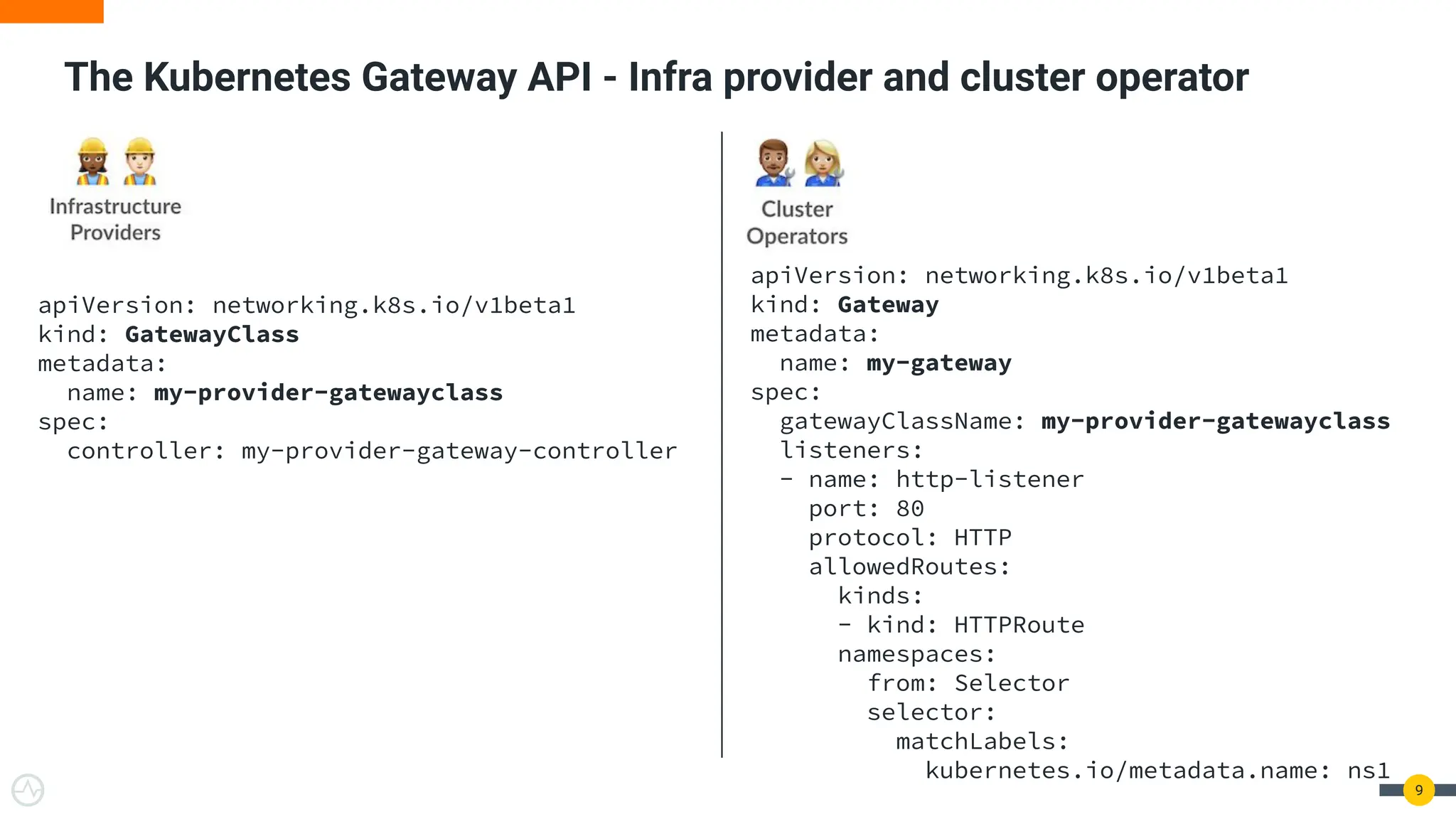
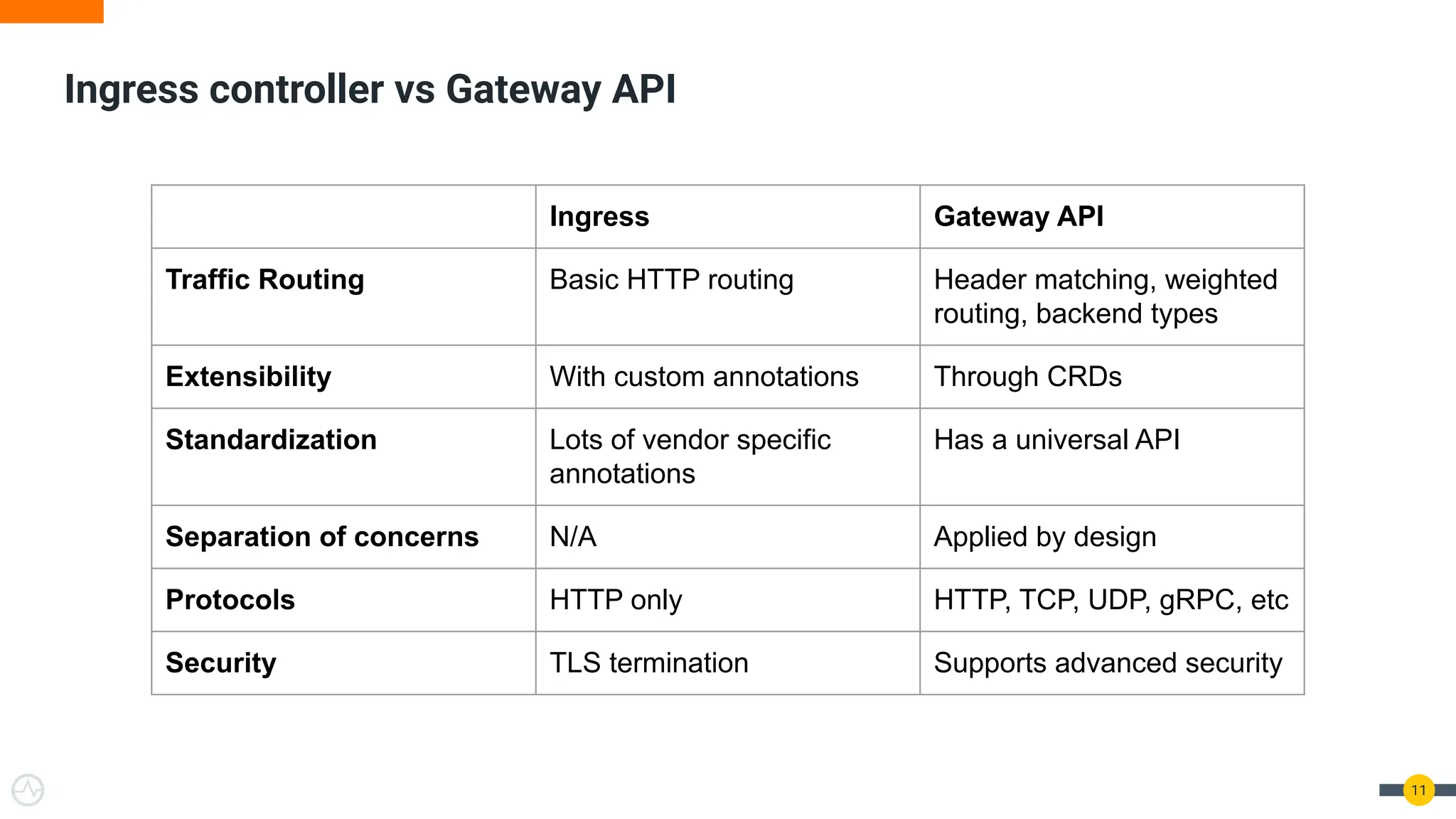
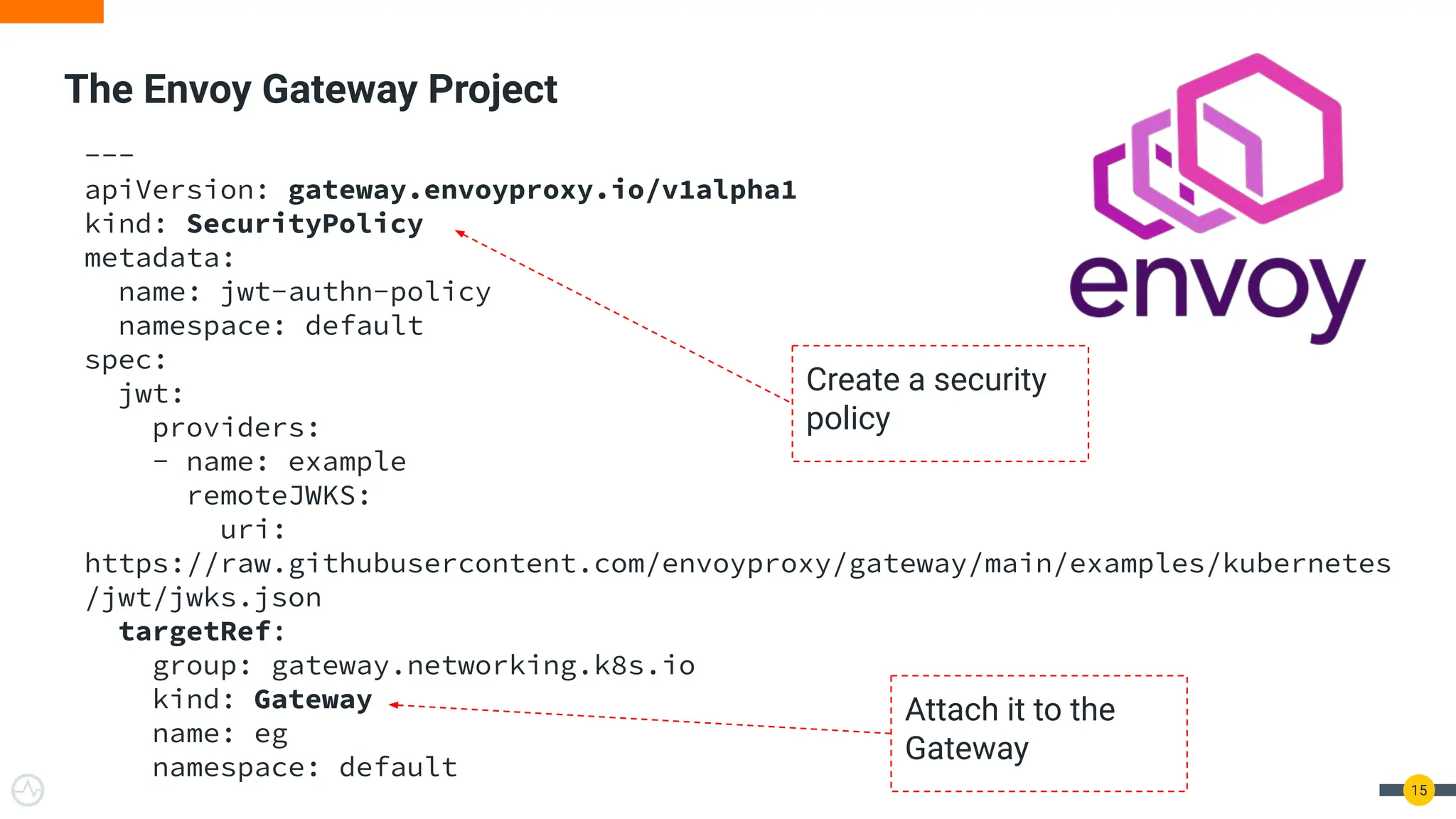
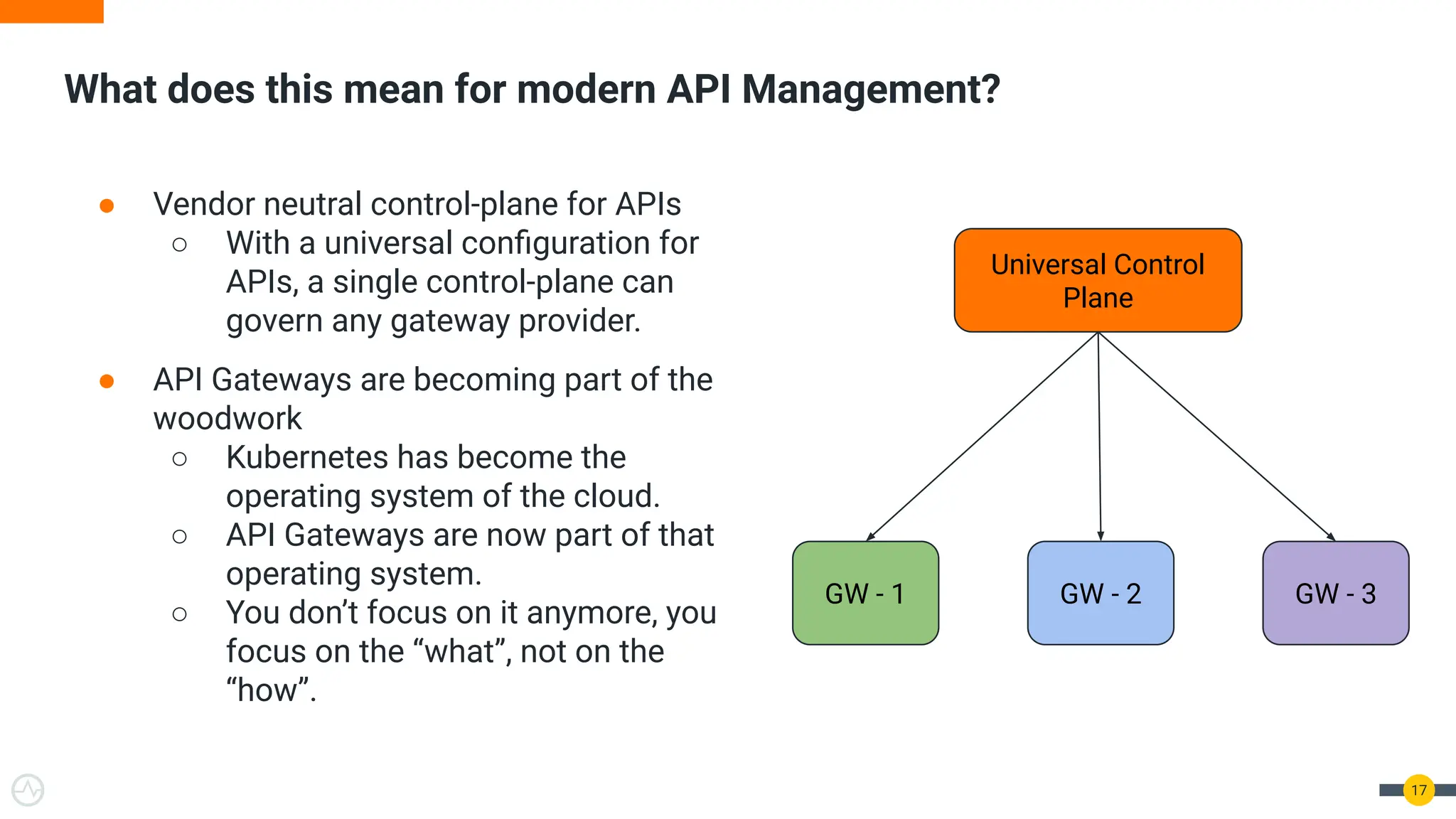
The document discusses the Kubernetes Gateway API, highlighting its advantages over the traditional Ingress API for cloud-native API management. It addresses limitations of the Ingress API and describes how the Gateway API offers improved traffic routing and flexibility with support for multiple protocols. The text emphasizes the importance of shifting towards a standardized Gateway API for better manageability and vendor-neutral control in API management.