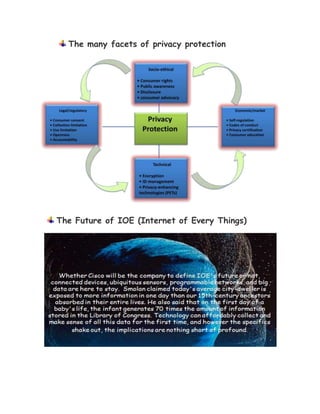
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT), which refers to the network of devices that can sense, collect data, and communicate over the internet, potentially transforming how people and industries operate. While IoT presents exciting future applications, it raises concerns about privacy, energy consumption, and the reliability of the technology. The report emphasizes the need for further research and development to address these challenges and suggests that, despite skepticism, IoT will significantly impact society positively.











![3. Protection Mechanisms
In the classic identity management certain protection methods have
been established over the years to protect an identity from abuse. We
have authentication methods to proof identities, secure channels to
transmit identity attributes and passwords and data are stored
encrypted.
3.1 Security concepts like integrity, availability, authenticity, non-
repudiation are built in classic identity protocols like SAML and Open
ID. In the Internet of Things the situation is different. Here many
communication protocols are not based on internet protocol. Many
sensors or actuators have just restricted resources in terms of energy,
bandwidth, connectivity. Protocols like en Ocean[www.enocean.com] or
KNX[www.knx.org] use only few bytes to send commands or receive
values. There is no room for encryption, challenge response procedure or
other security mechanisms
3.2 Authentication The classic authentication mechanisms
(ex.: login /password) may not directly work in the IoT.
Objects have to provide some sort of lightweight token or
certificate for an authentication where no user (providing a
password) is involved. For stronger authentication means of
individuals we usually combine two or multiple factors. These
factors are based on following proofs:
“Something that you have"
“Something that you know”
“Something that you are” (e.g. biometry)
In the IOT the last two proofs are not applicable to objects
anymore](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theinternetofthingsuop-150311111229-conversion-gate01/85/The-Internet-Of-Things-UOP-15-320.jpg)