Embed presentation
Download to read offline
![fold
λ
Haskell> foldl (+) 0 [1,2,3,4]
10
Haskell> take 4 (iterate (+ 1) 1)
[1,2,3,4]
Haskell> scanl (+) 0 [1,2,3,4]
[0,1,3,6,10]
Haskell>
scala> List(1,2,3,4).foldLeft(0)(_+_)
val res0: Int = 10
scala> Stream.iterate(1)(_ + 1).take(4).toList
val res1: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3, 4)
scala> List(1,2,3,4).scanLeft(0)(_+_)
val res2: List[Int] = List(0, 1, 3, 6, 10)
scala>
Implementing mathematical induction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functional-programming-triad-fold-scan-iterate-with-minor-correction-201010074225/75/The-Functional-Programming-Triad-of-fold-scan-and-iterate-2-2048.jpg)

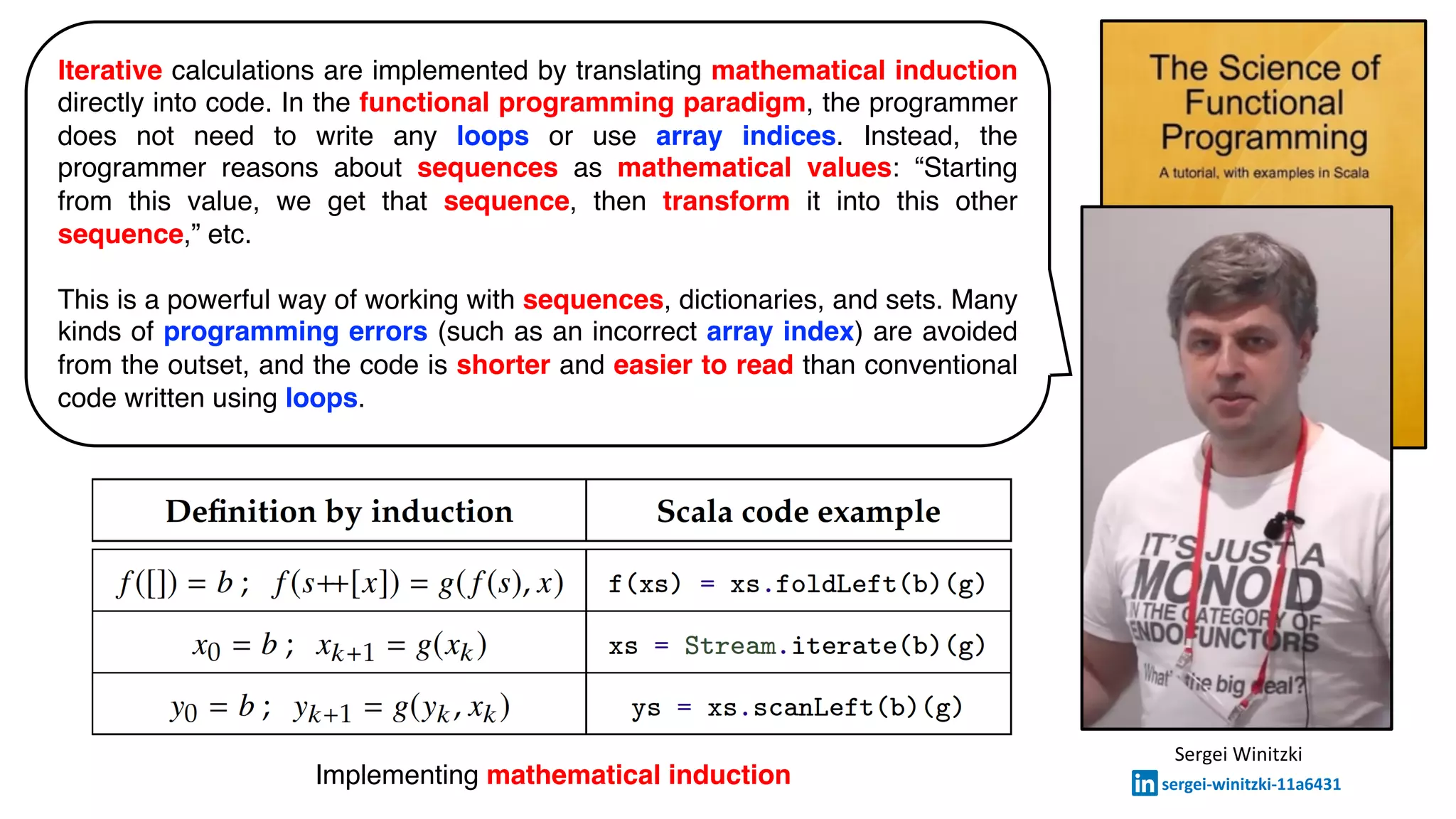
The document discusses the implementation of iterative calculations through mathematical induction in functional programming, highlighting that loops and array indices are unnecessary. It emphasizes reasoning about sequences as mathematical values, resulting in shorter and more readable code while avoiding common programming errors. Examples in Haskell and Scala are provided to illustrate these concepts.

![fold
λ
Haskell> foldl (+) 0 [1,2,3,4]
10
Haskell> take 4 (iterate (+ 1) 1)
[1,2,3,4]
Haskell> scanl (+) 0 [1,2,3,4]
[0,1,3,6,10]
Haskell>
scala> List(1,2,3,4).foldLeft(0)(_+_)
val res0: Int = 10
scala> Stream.iterate(1)(_ + 1).take(4).toList
val res1: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3, 4)
scala> List(1,2,3,4).scanLeft(0)(_+_)
val res2: List[Int] = List(0, 1, 3, 6, 10)
scala>
Implementing mathematical induction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functional-programming-triad-fold-scan-iterate-with-minor-correction-201010074225/75/The-Functional-Programming-Triad-of-fold-scan-and-iterate-2-2048.jpg)