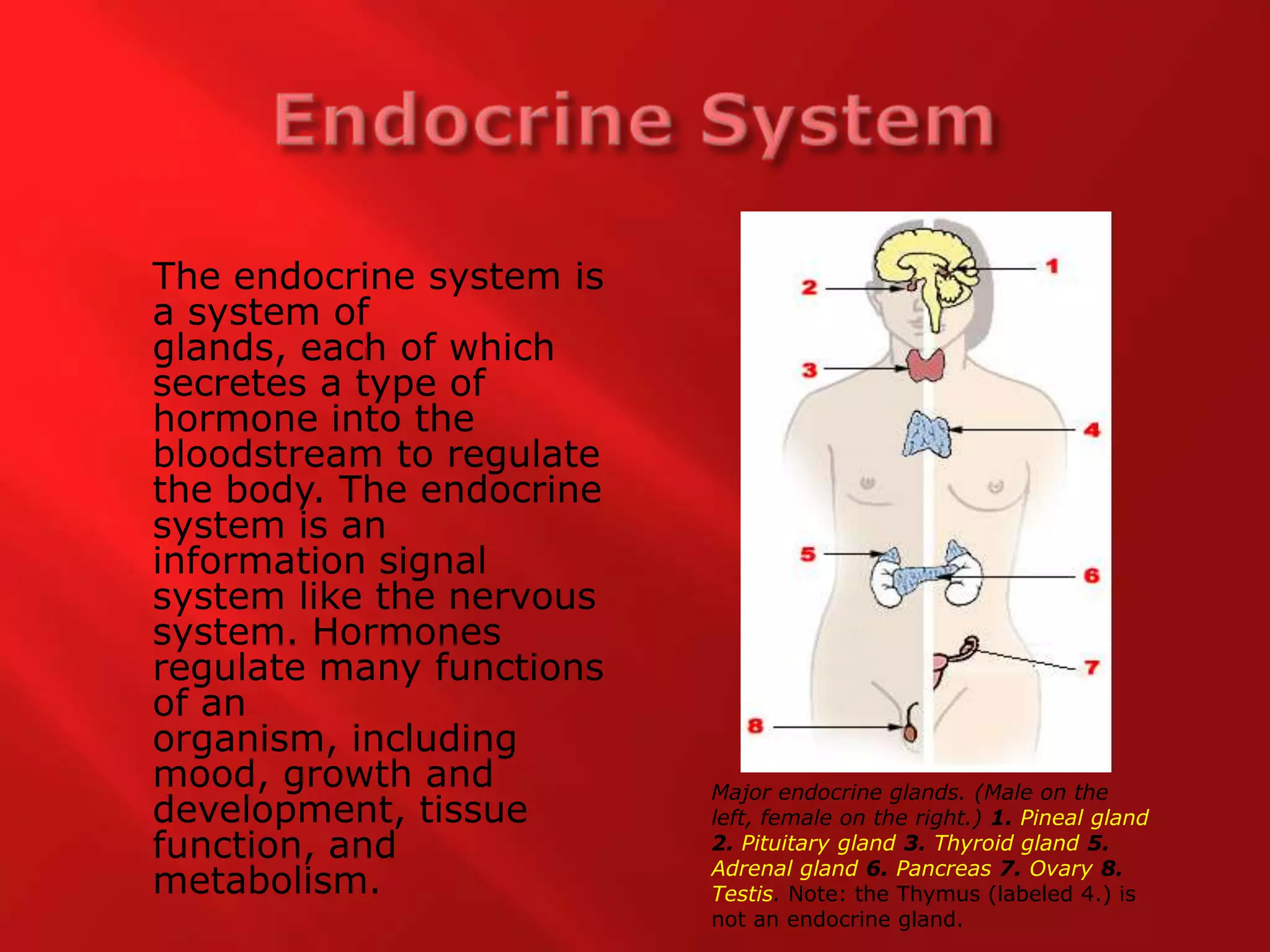
The endocrine system is made up of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream to regulate various body functions including mood, growth, metabolism and tissue function. The major endocrine glands are the pineal gland, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland and pancreas in both males and females as well as the ovaries in females and testes in males. The suffixes -emia and -tropin are used in medical terminology where -emia means "in the blood" and is used to describe conditions involving elevated or abnormal levels of substances in the blood, while -tropin means "to stimulate" and is used in names of hormones like ACTH and somatropin that stimulate the function of other