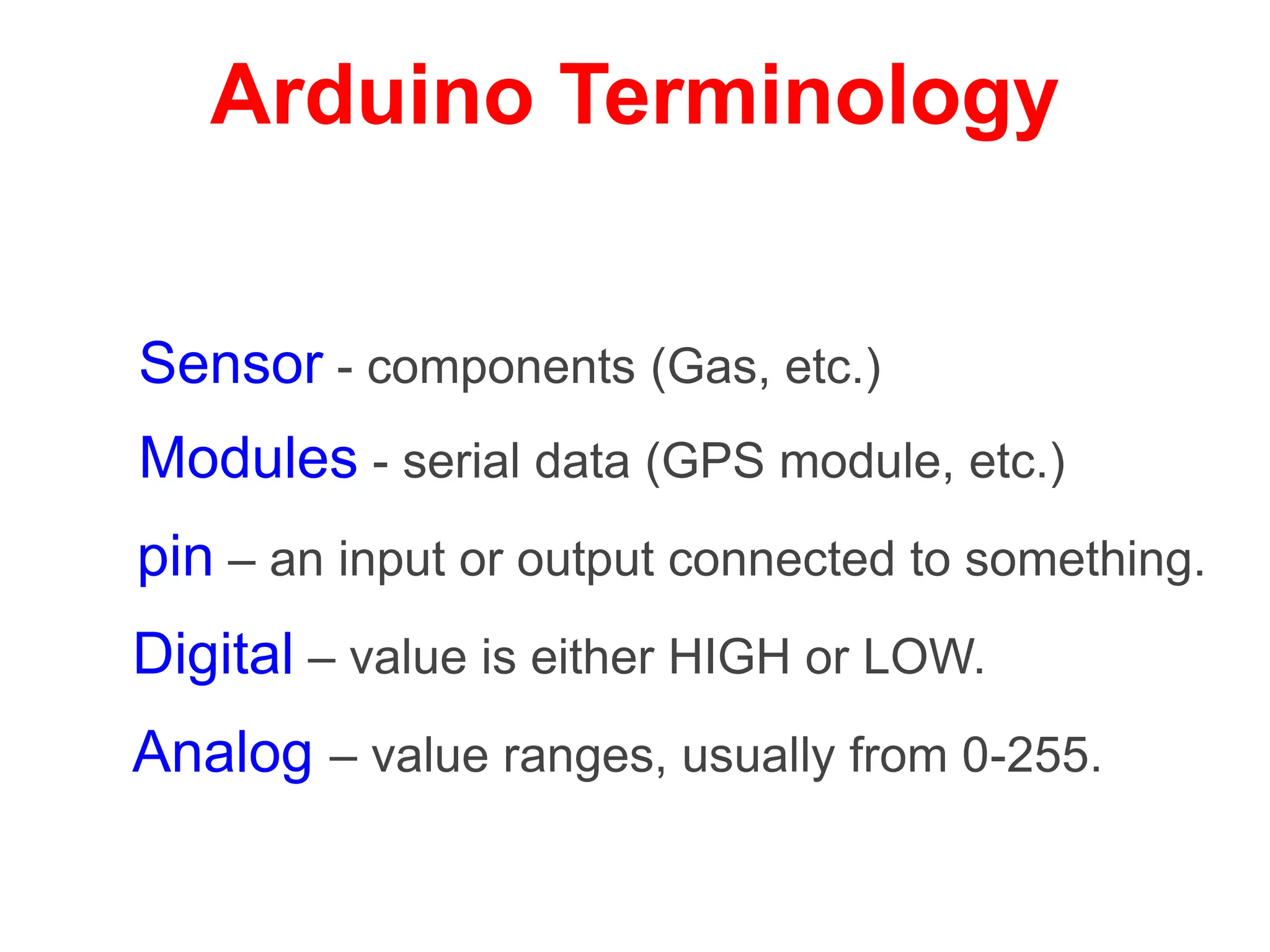
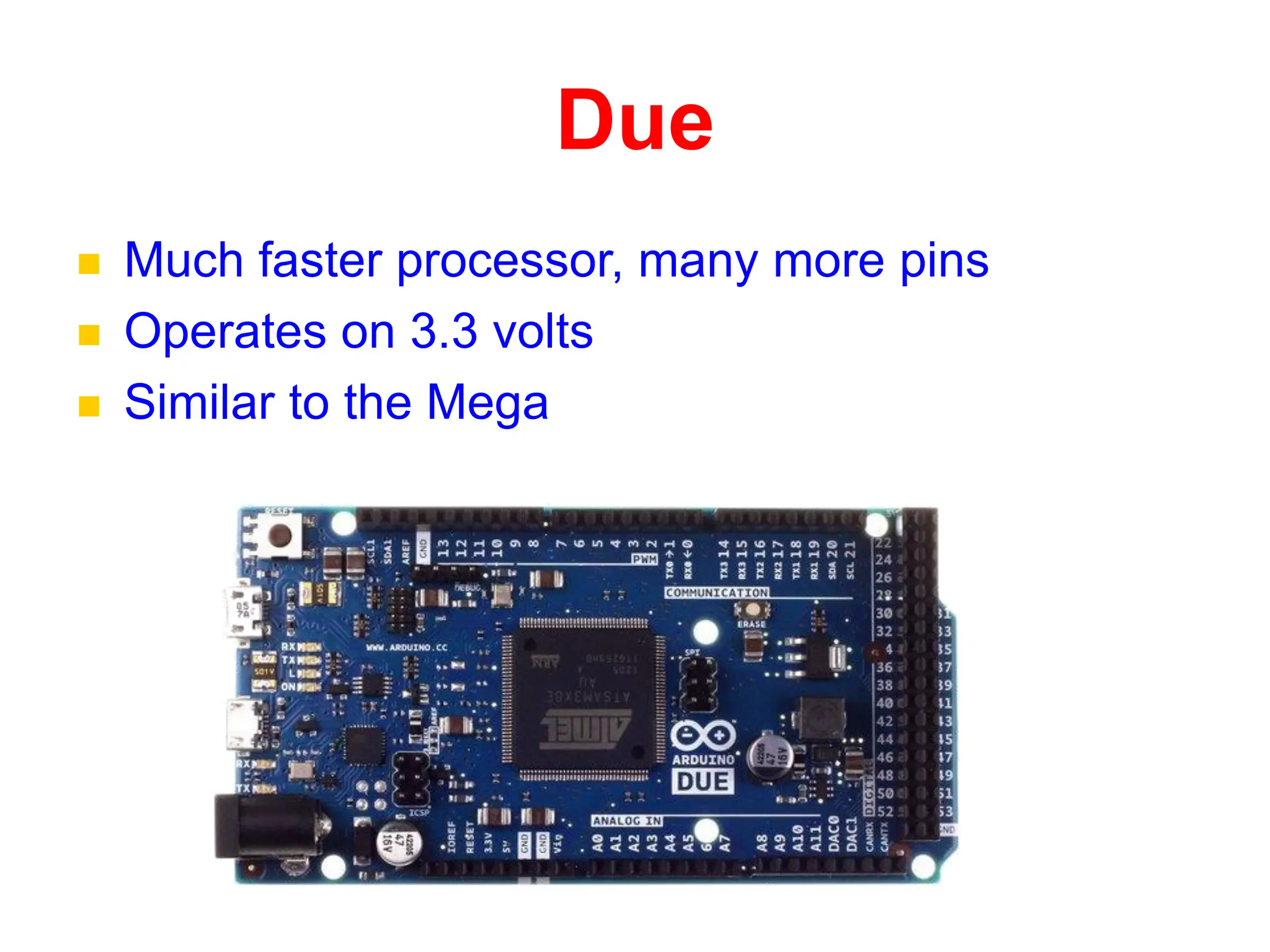
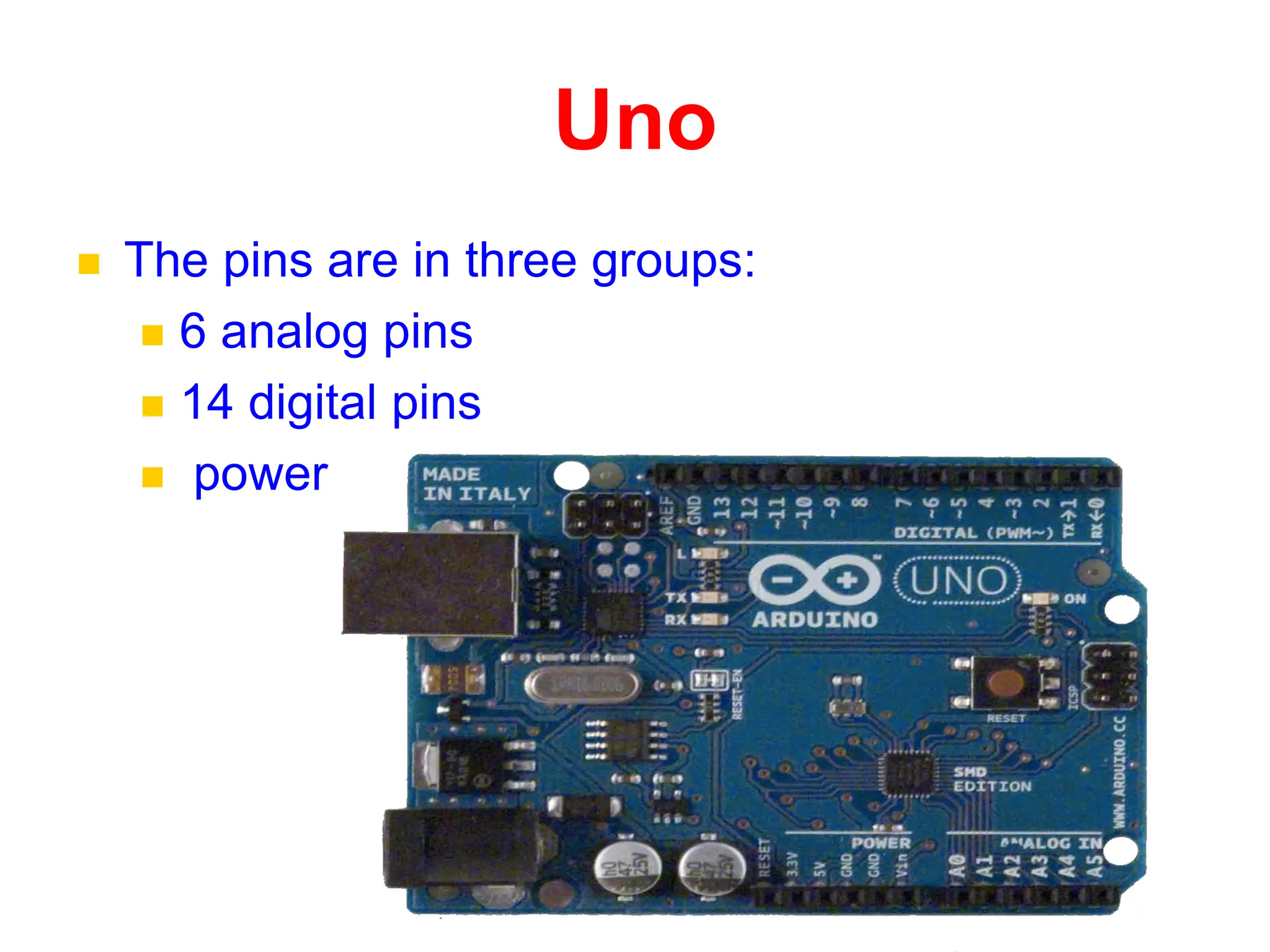
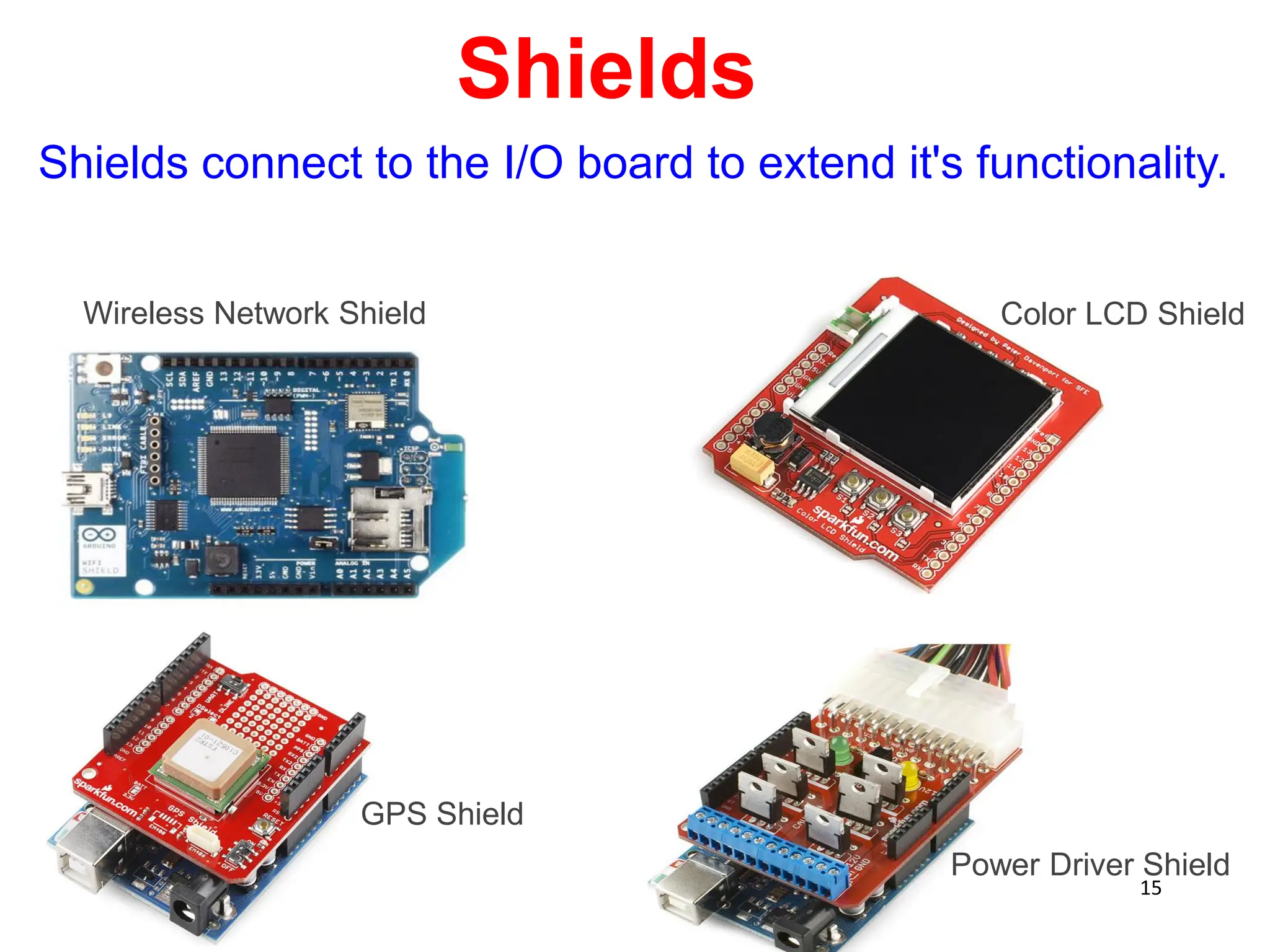
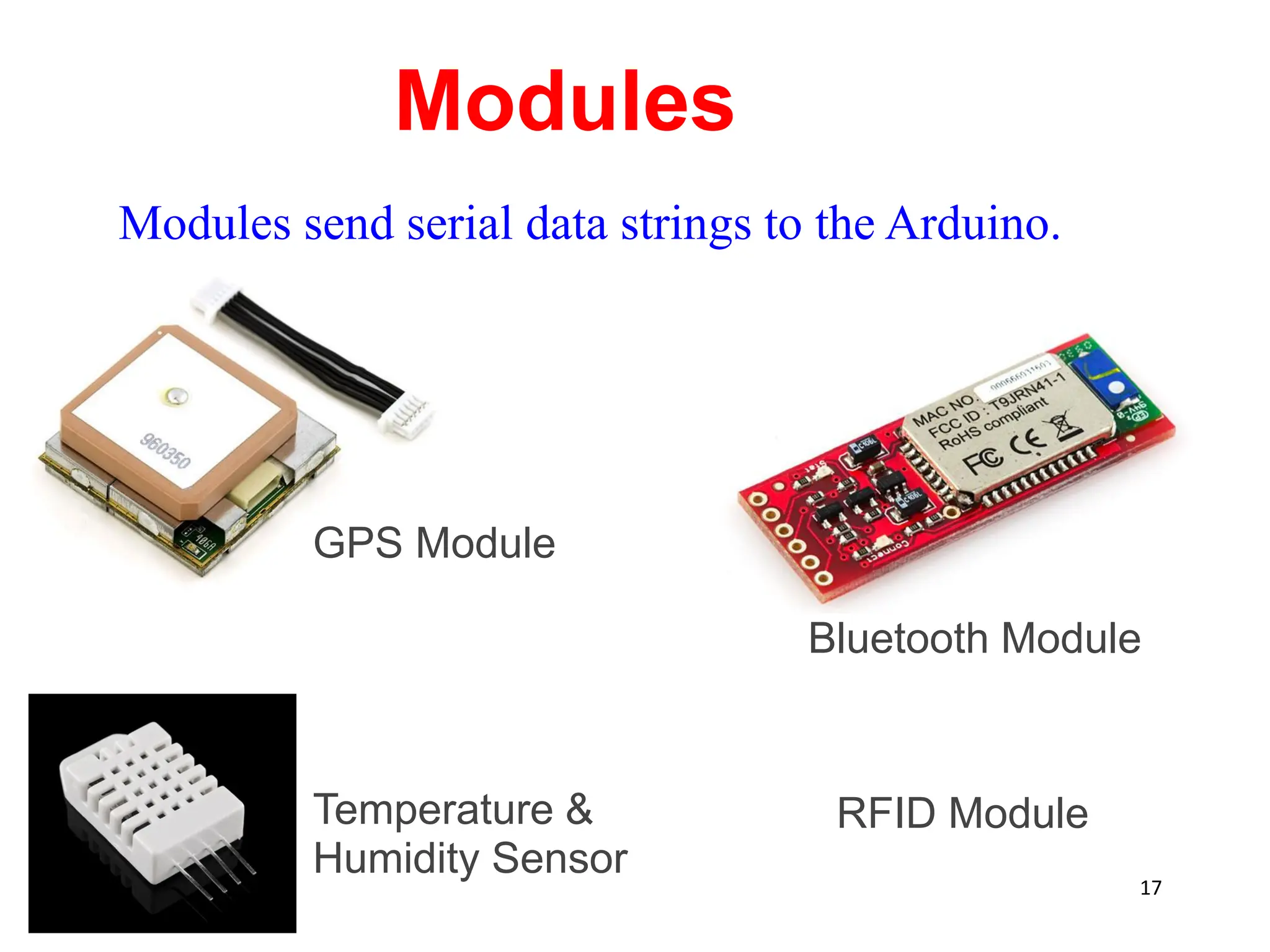
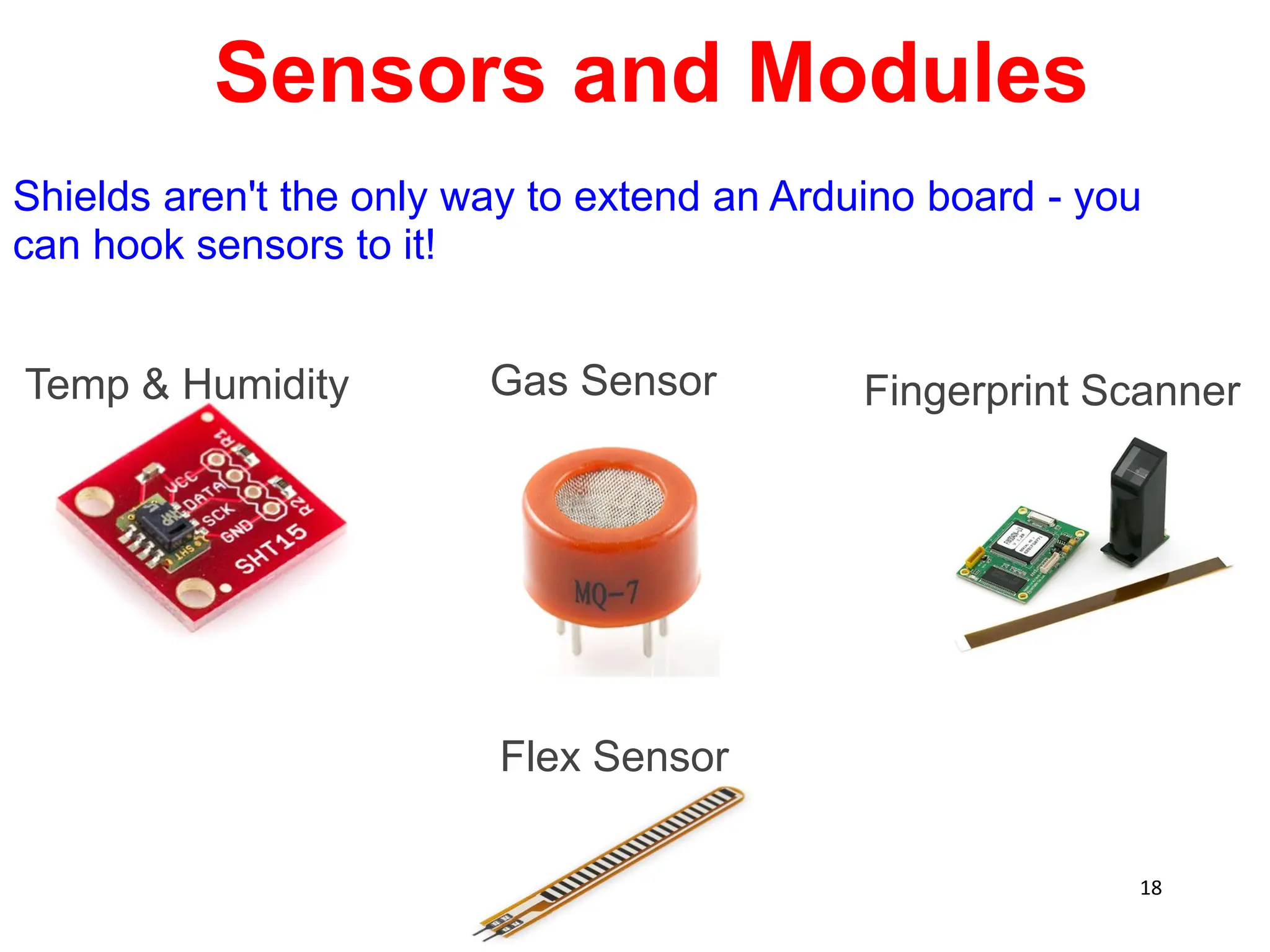
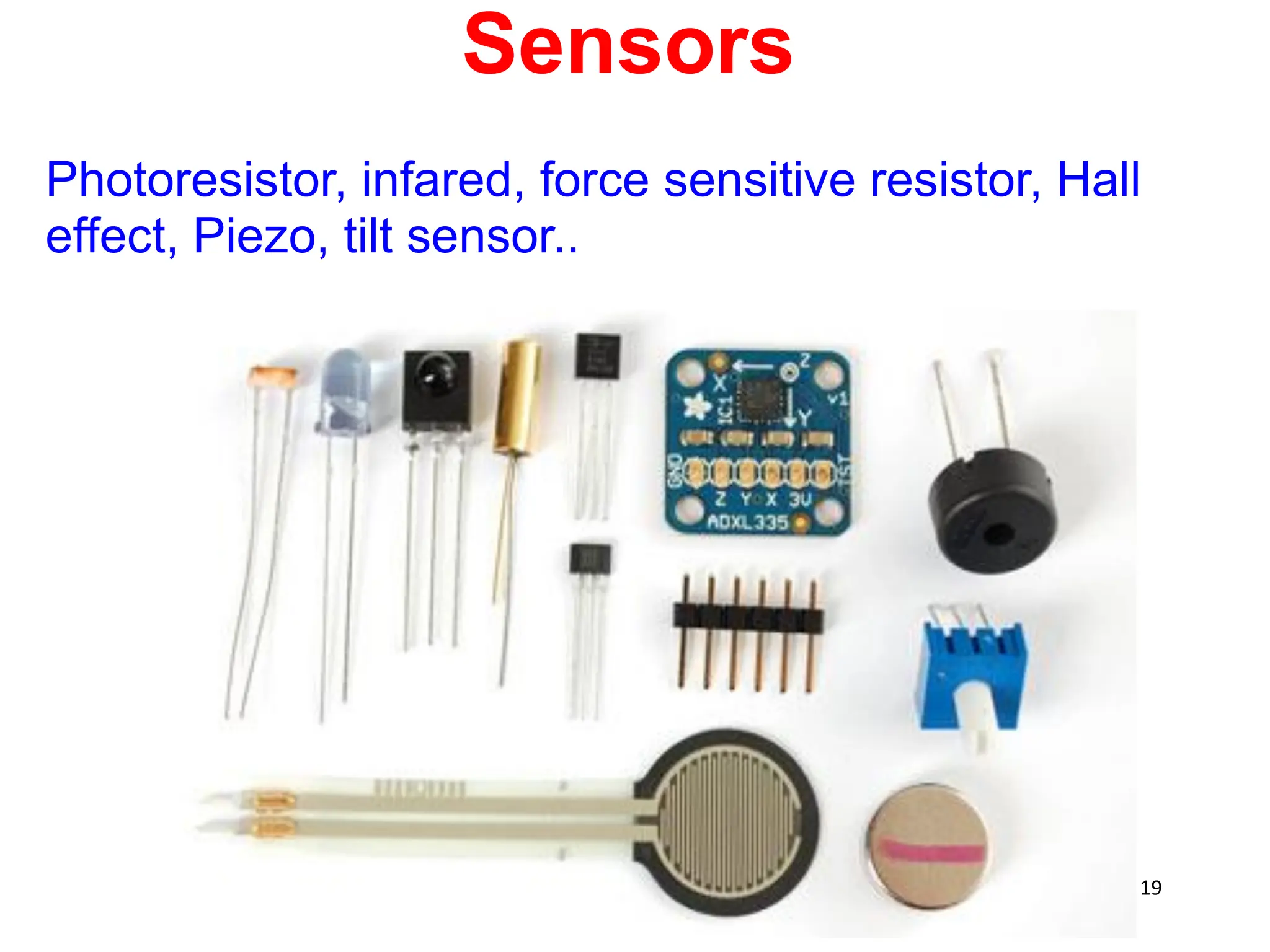
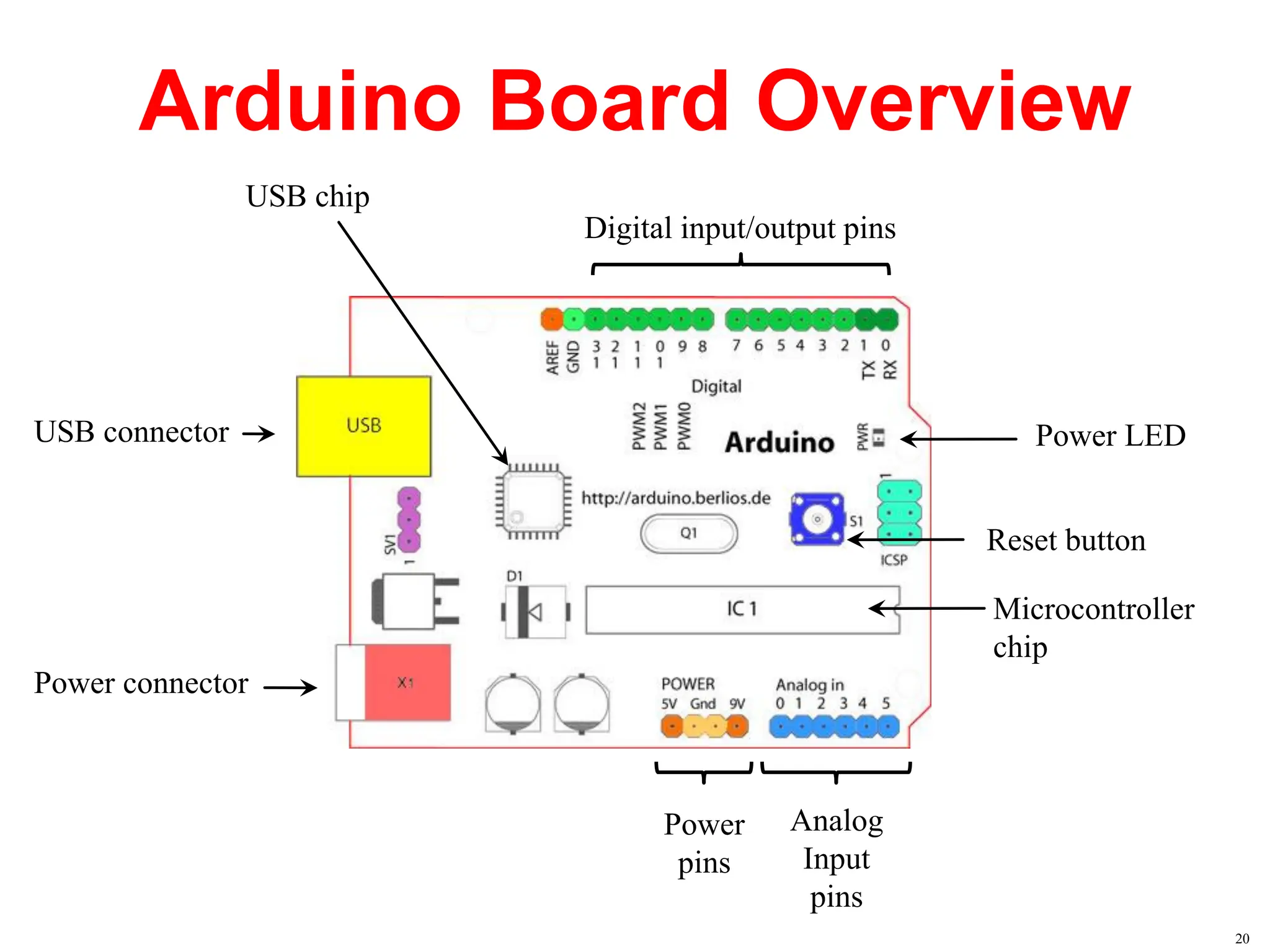
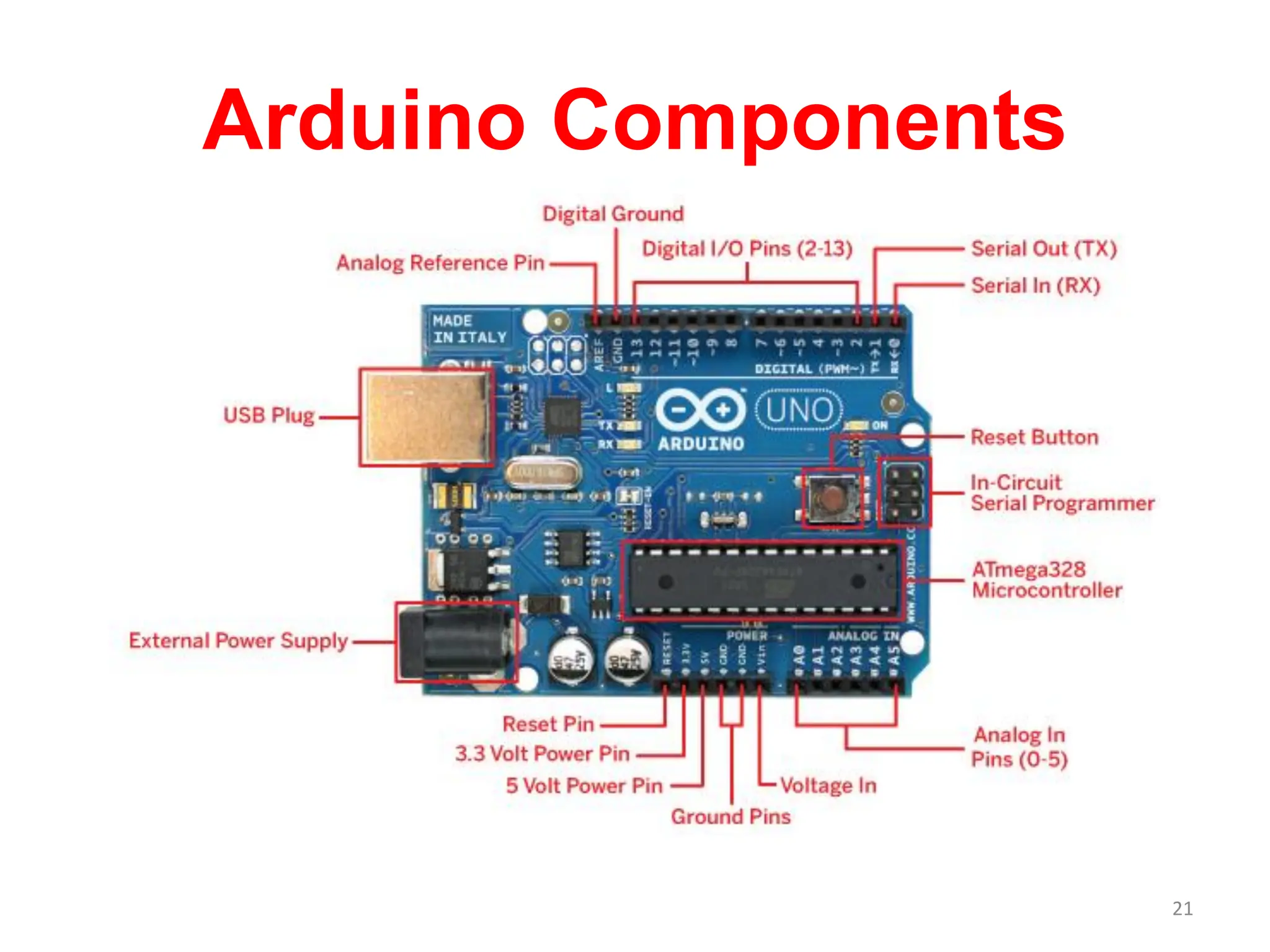
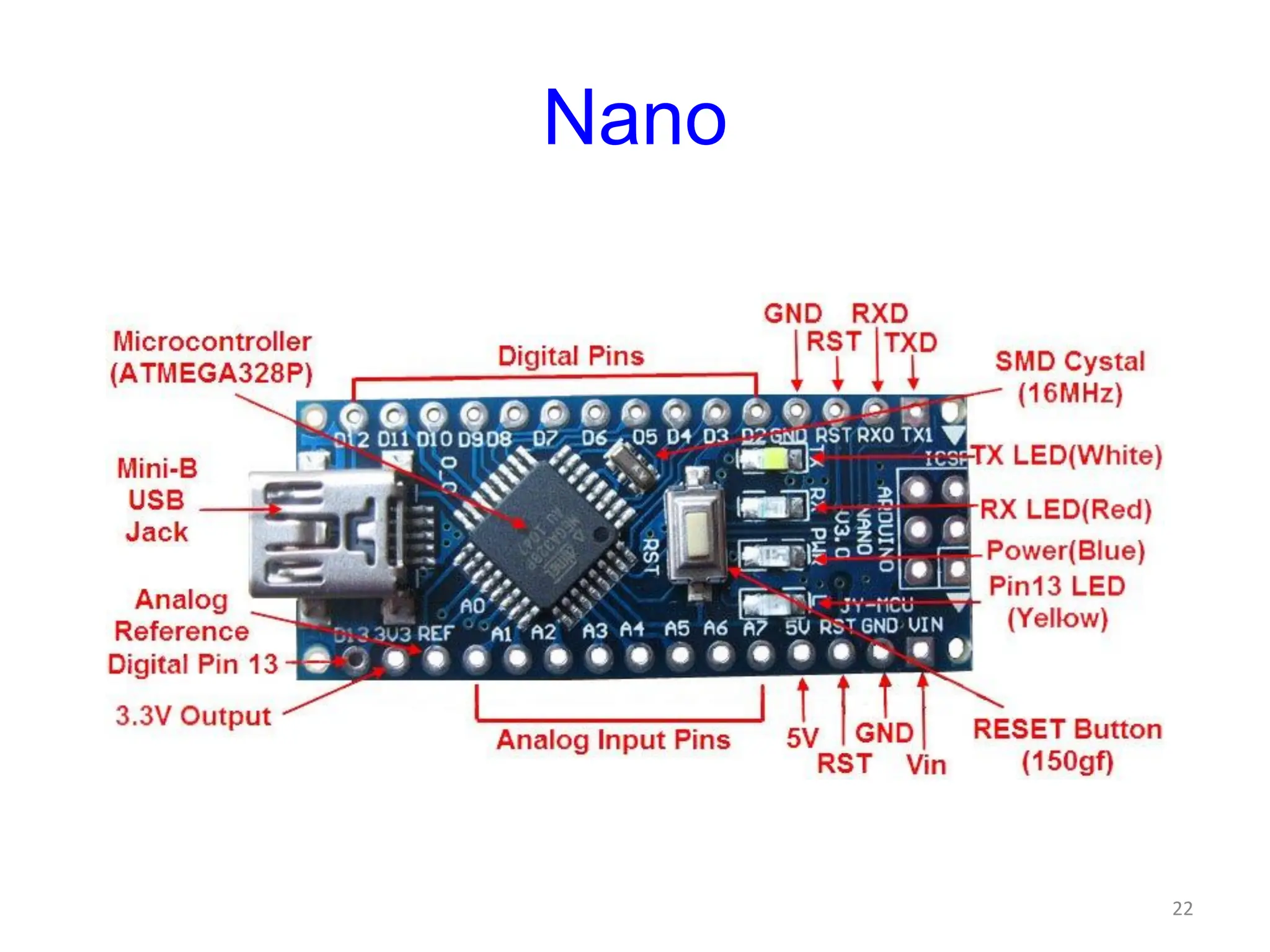
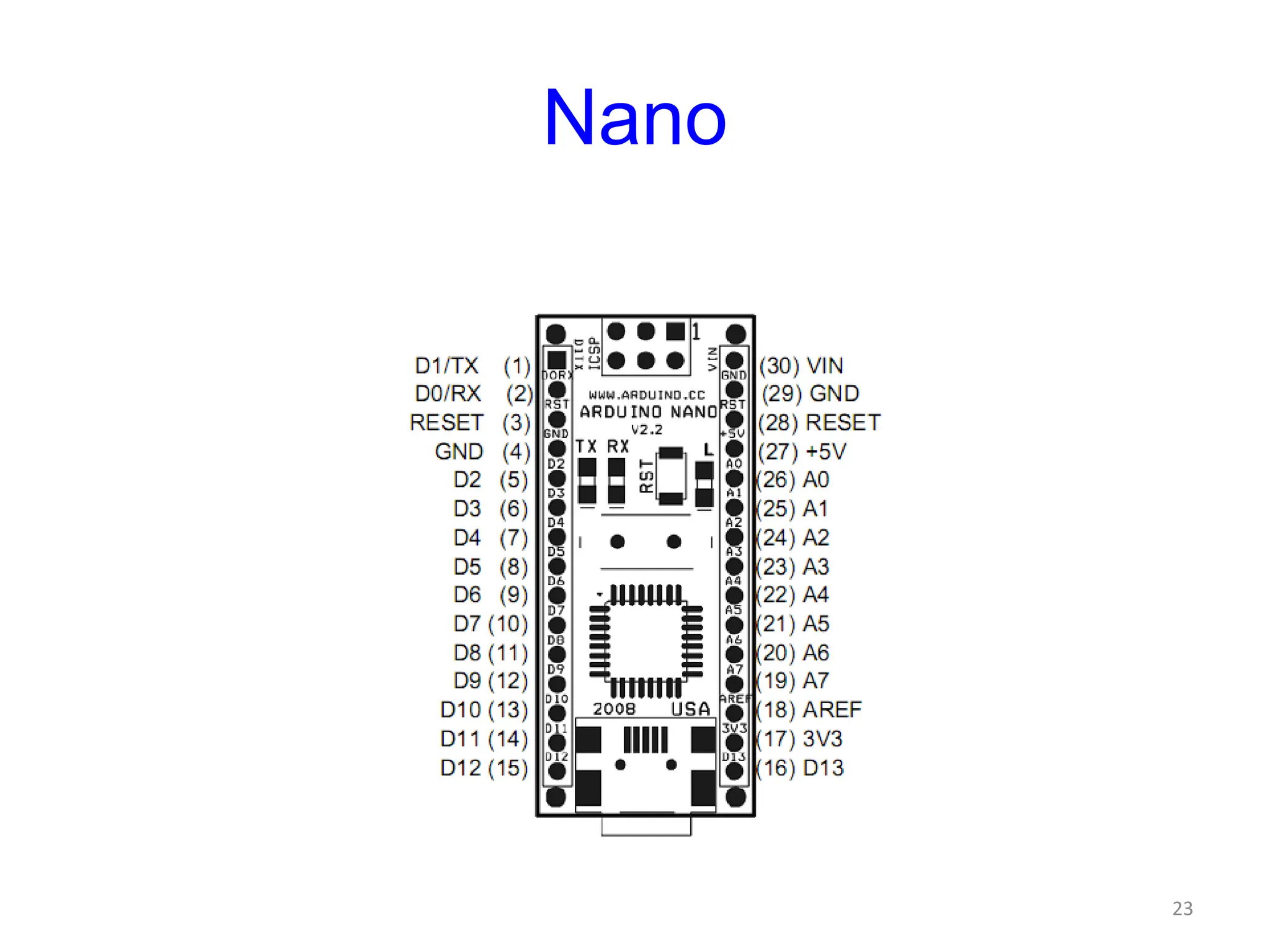
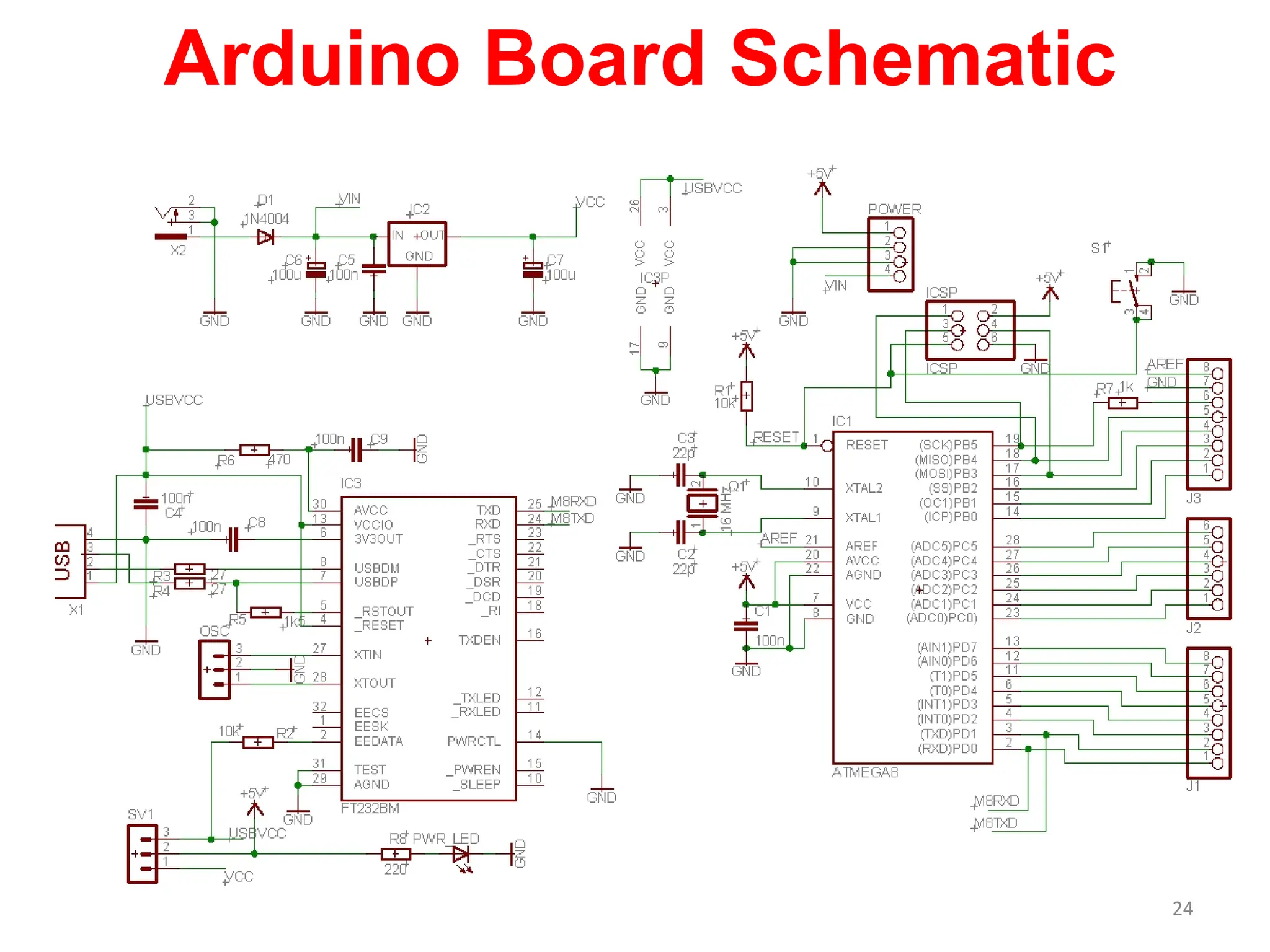
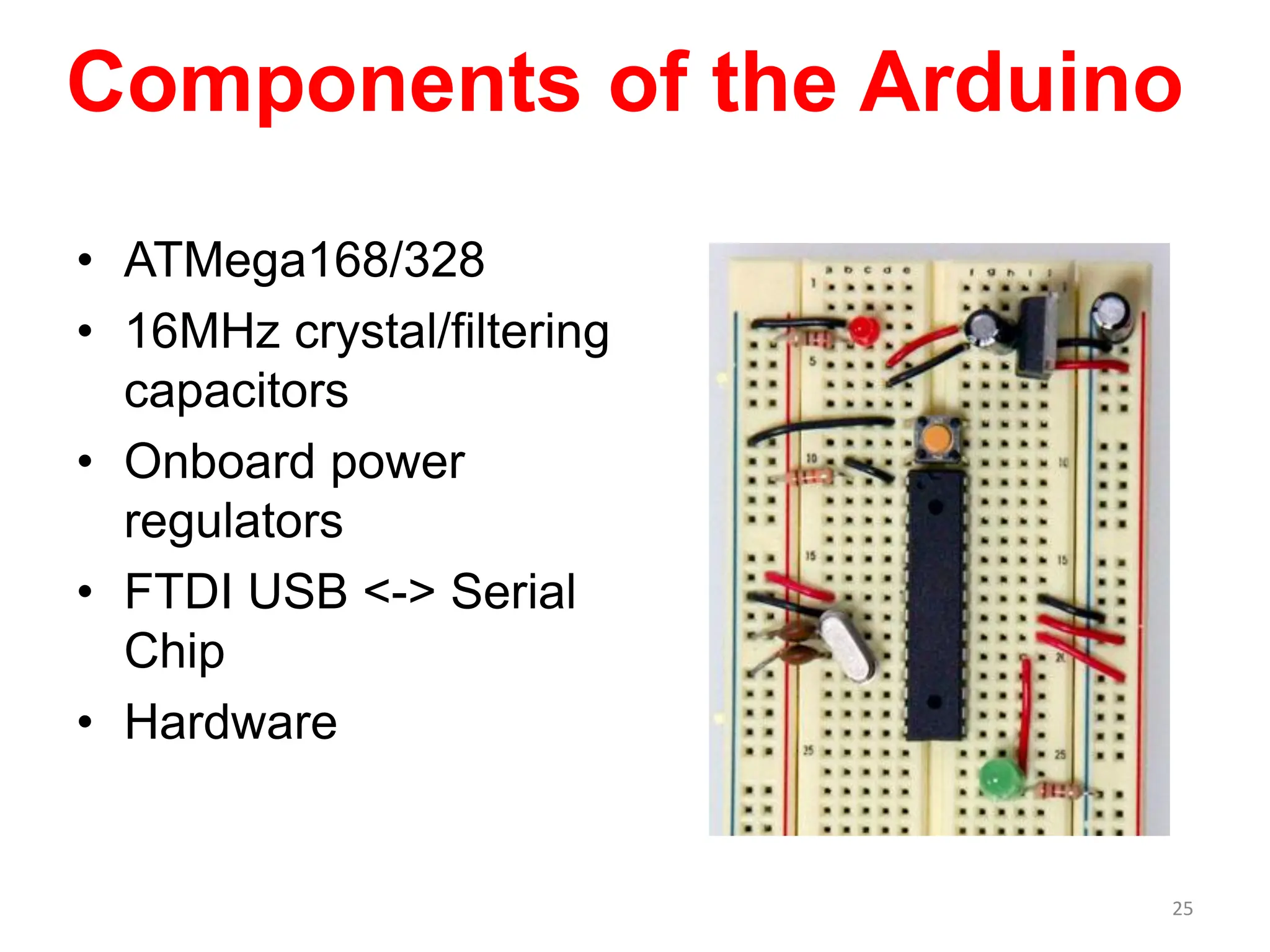
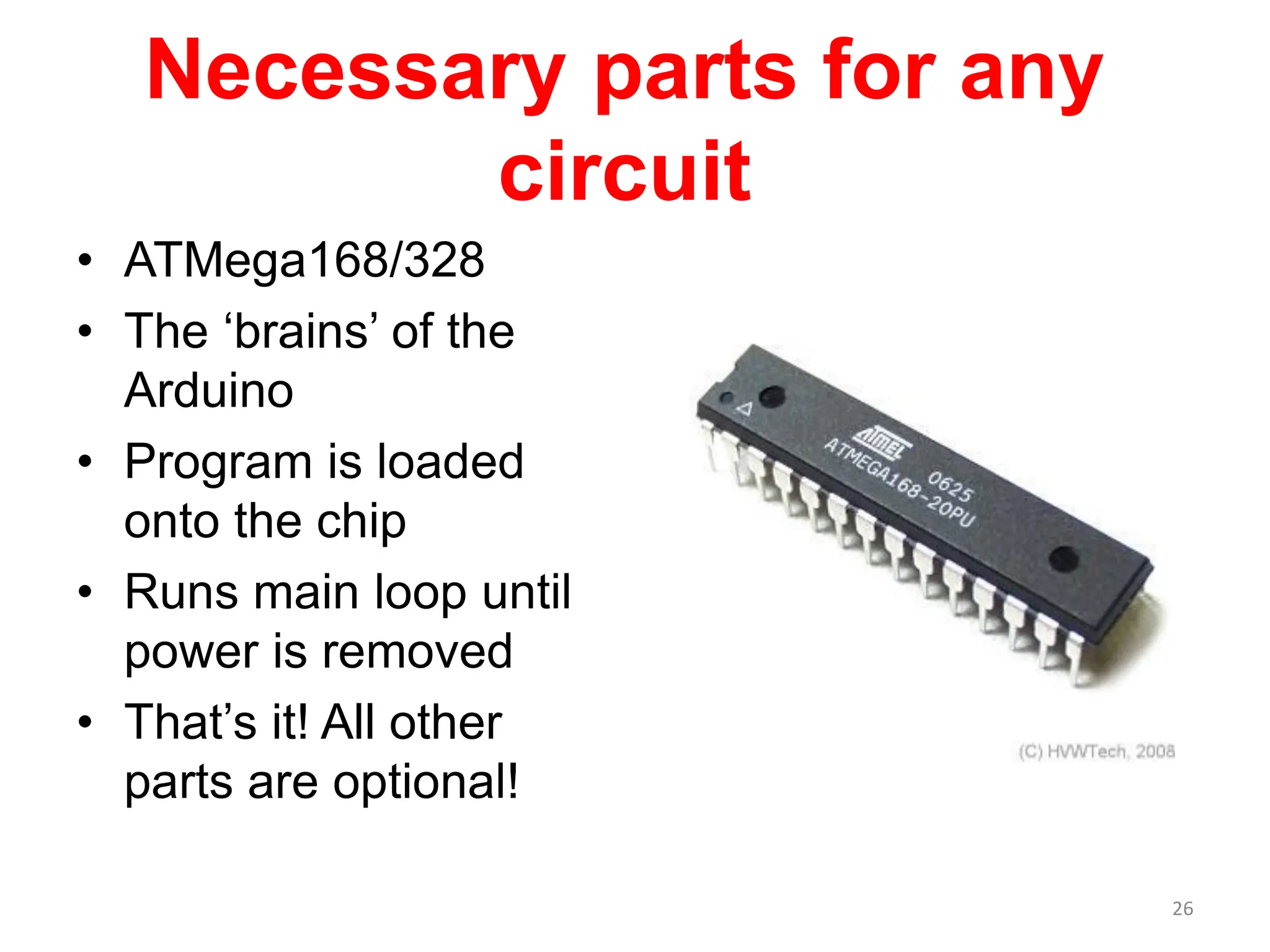
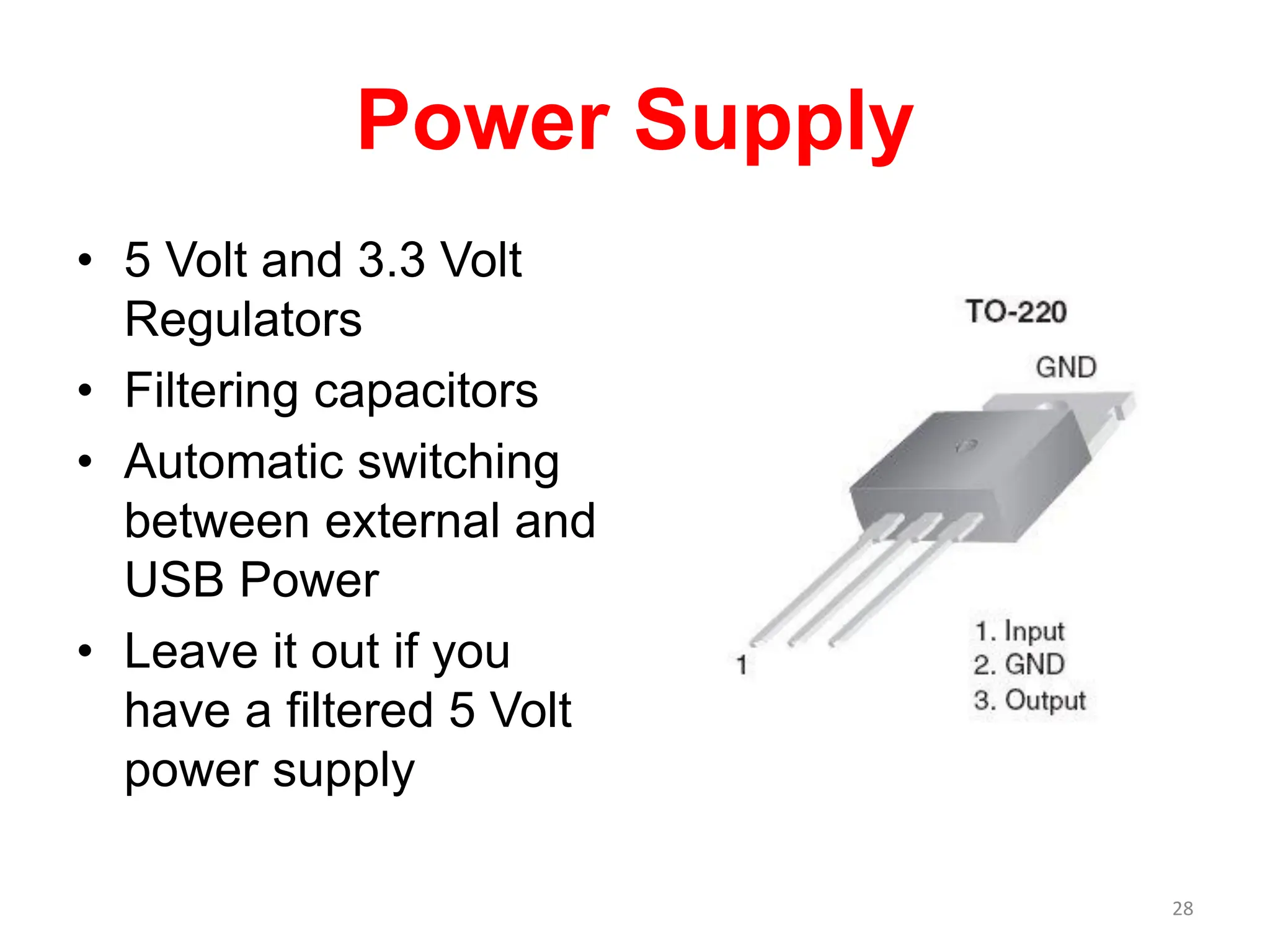
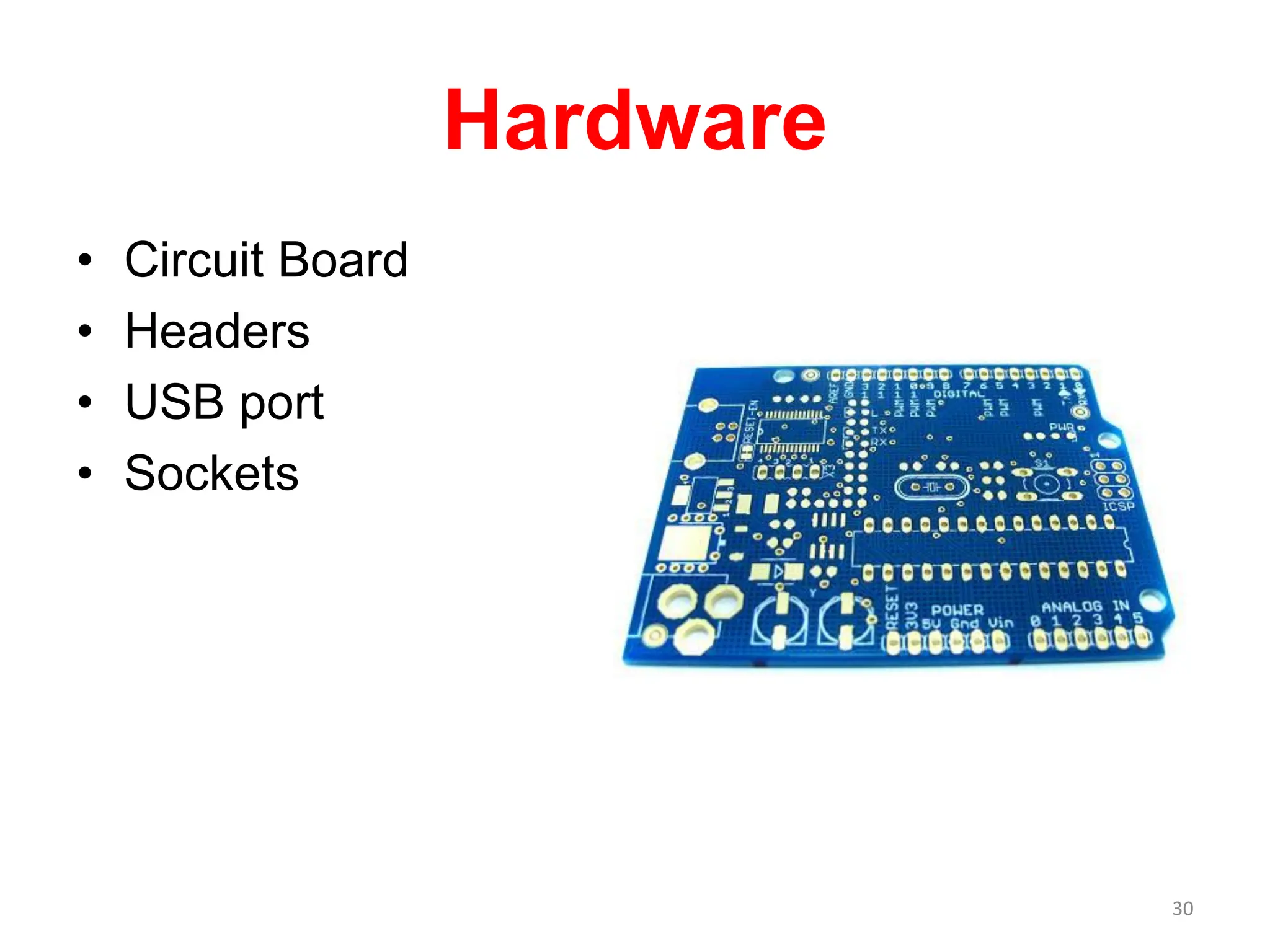
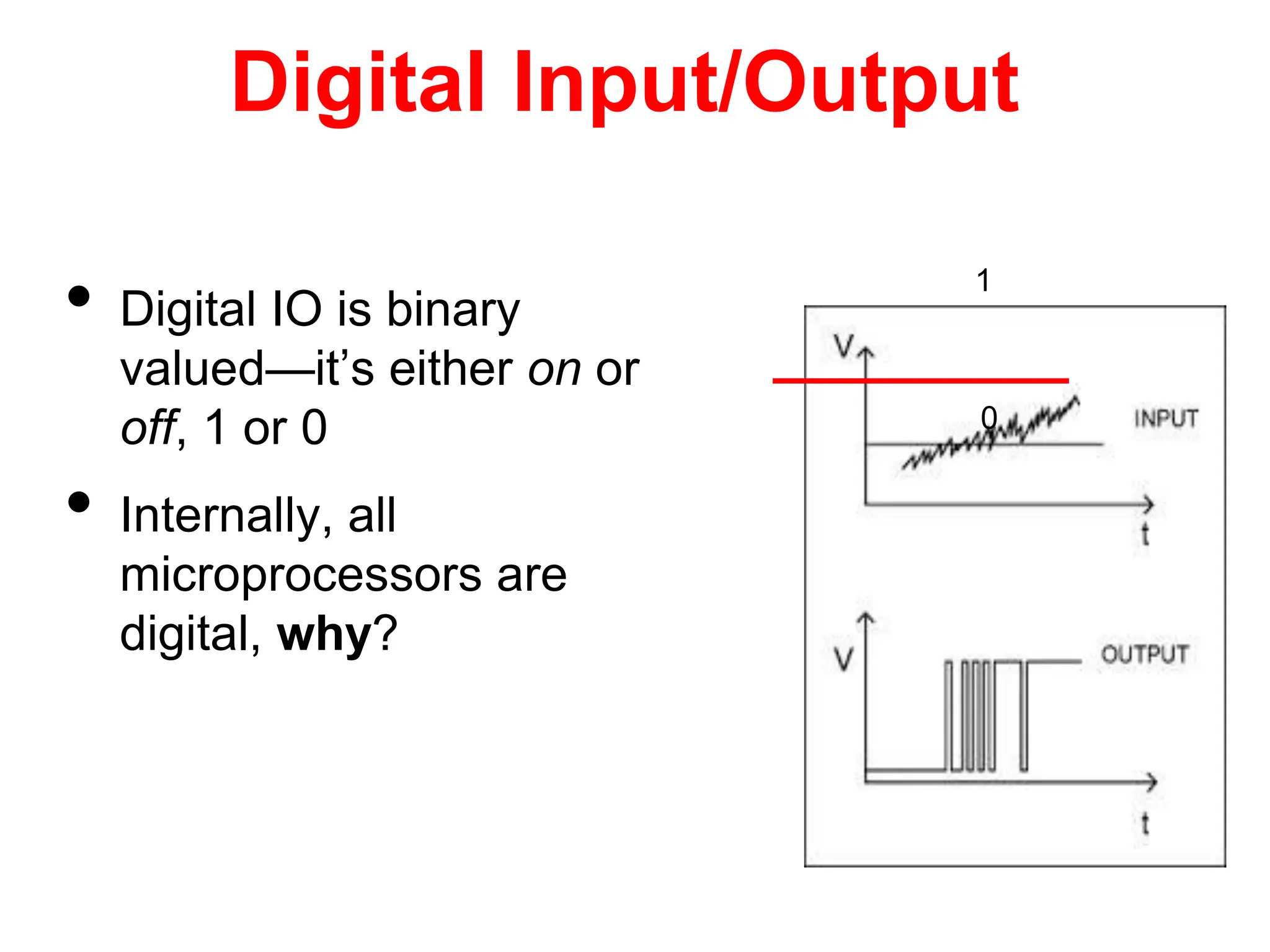
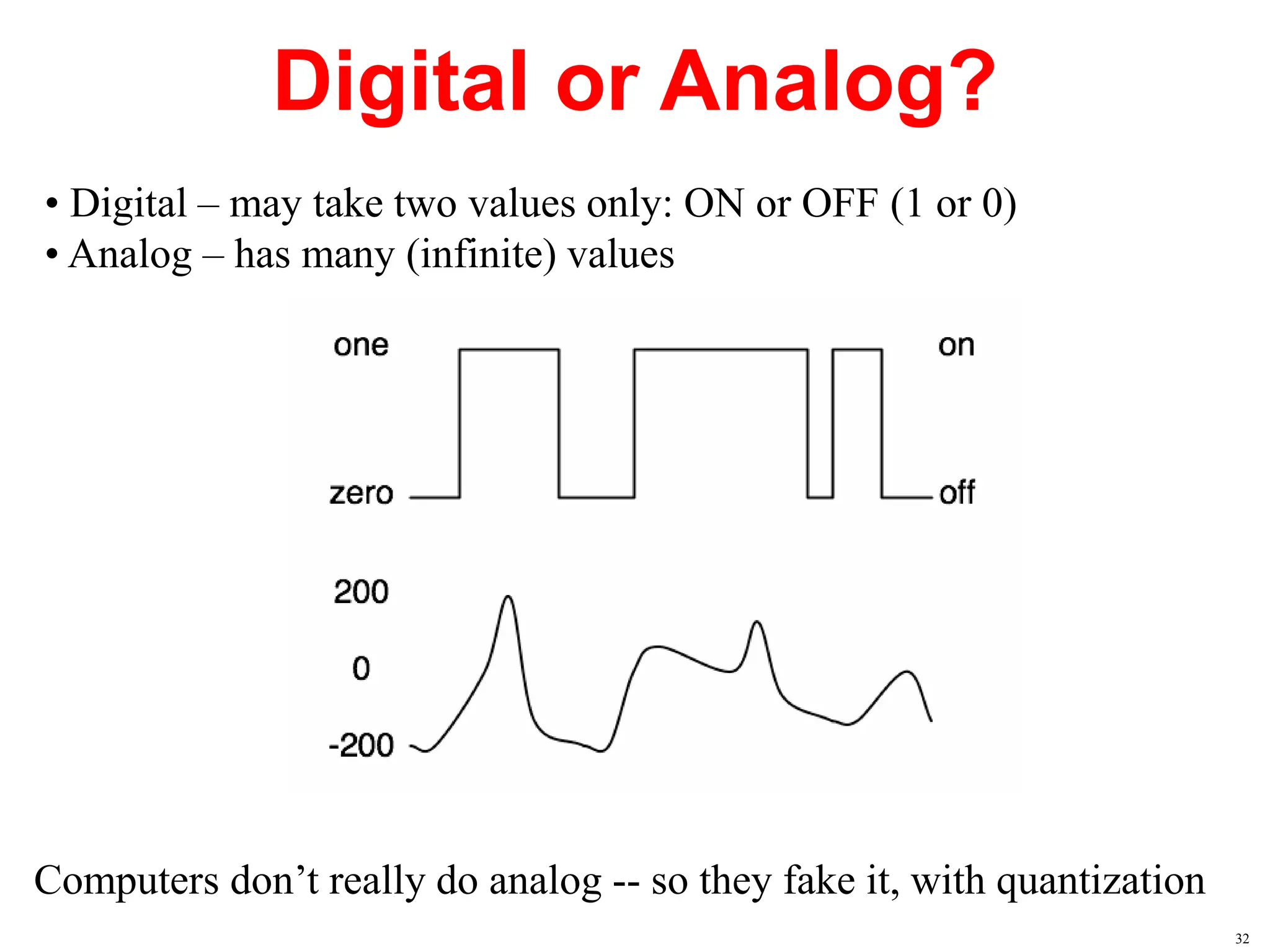
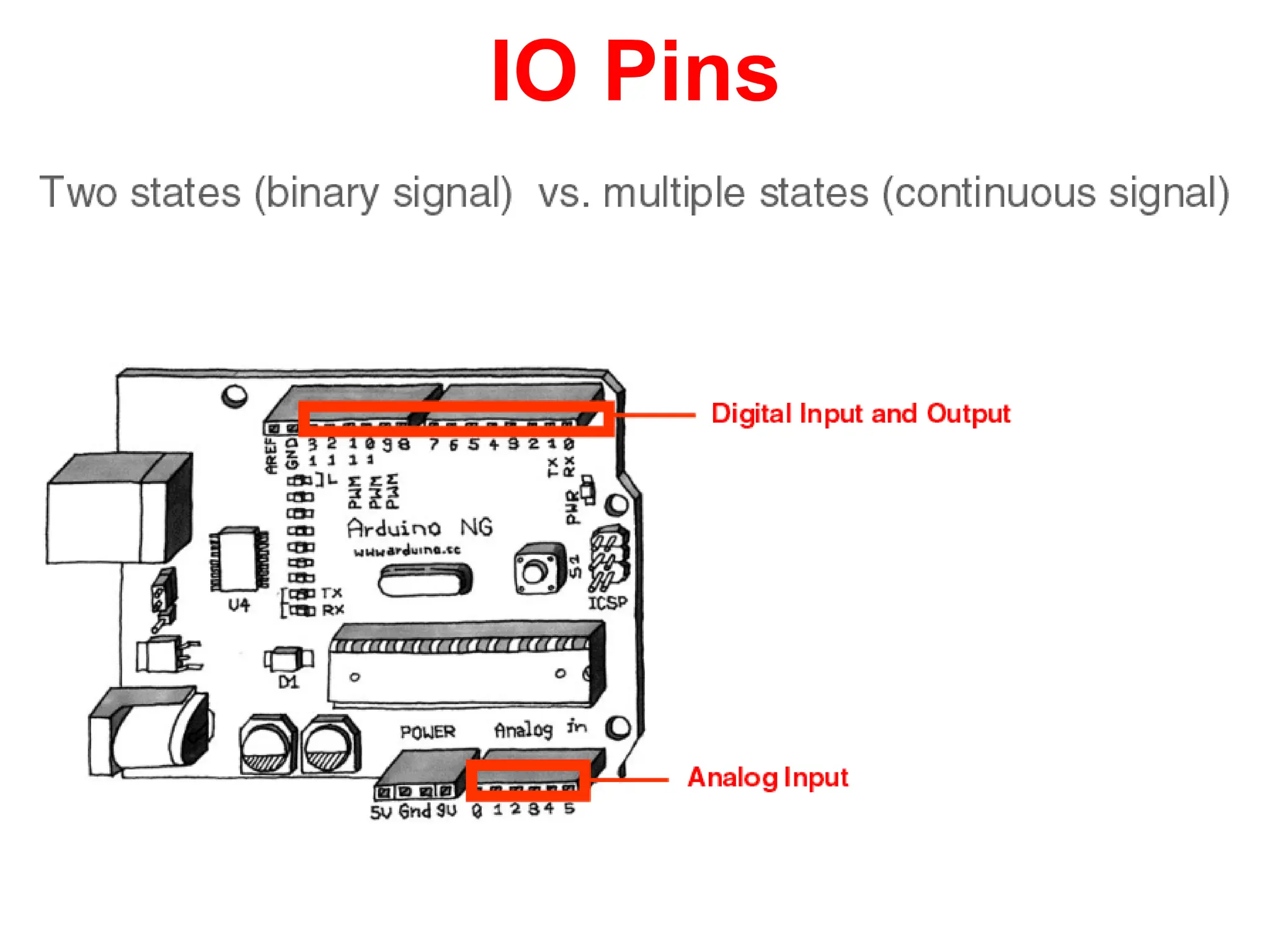
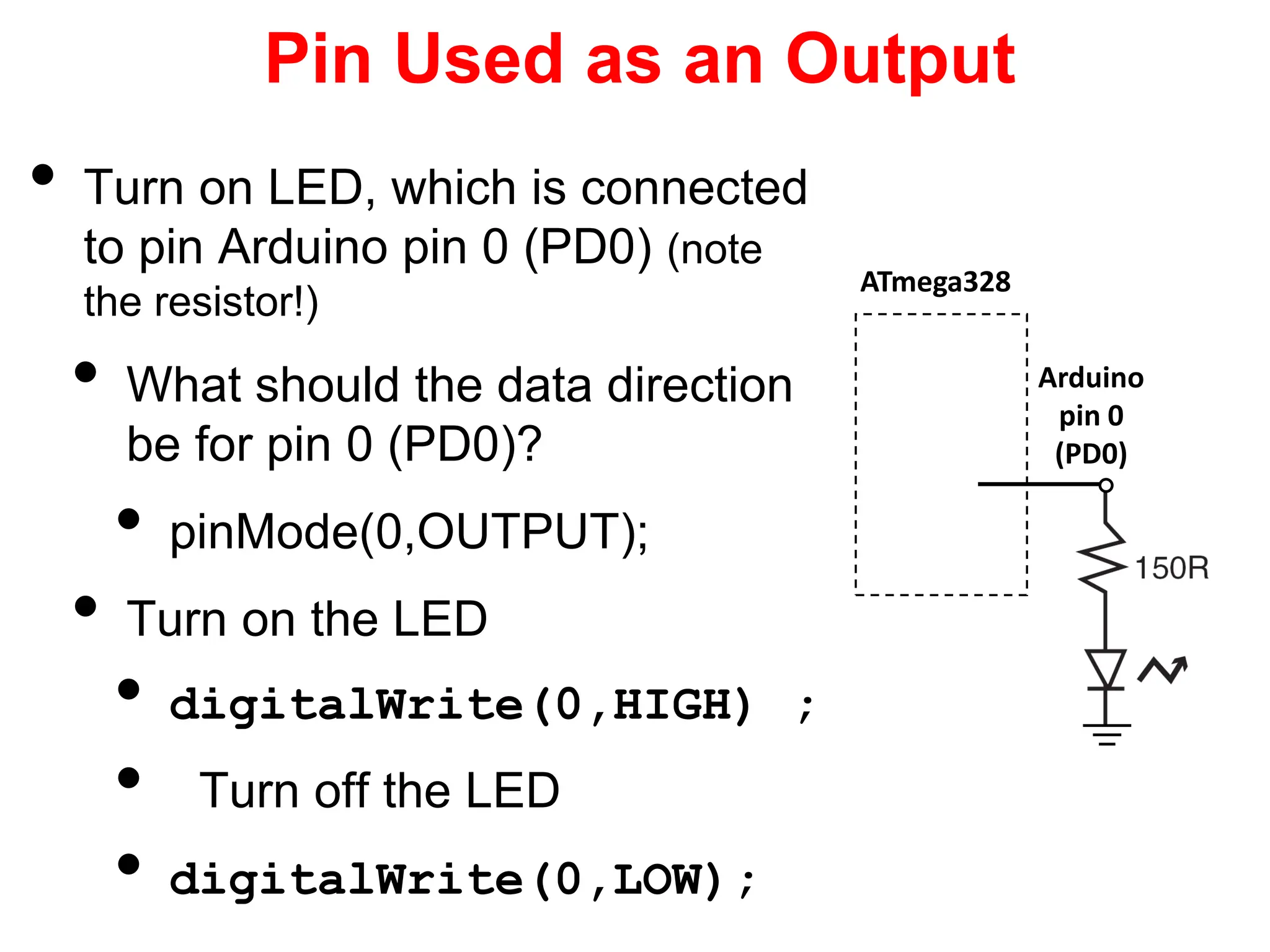
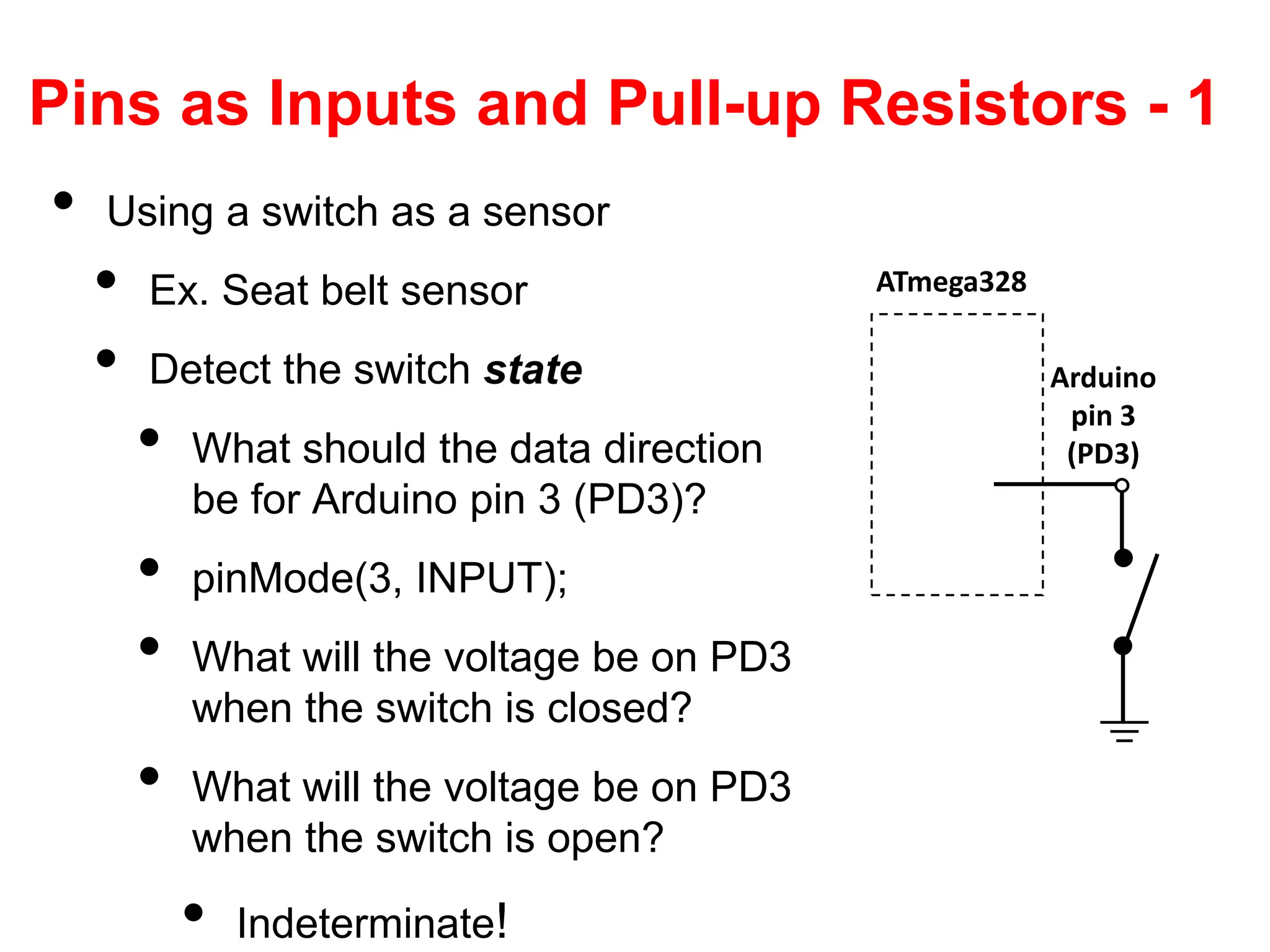
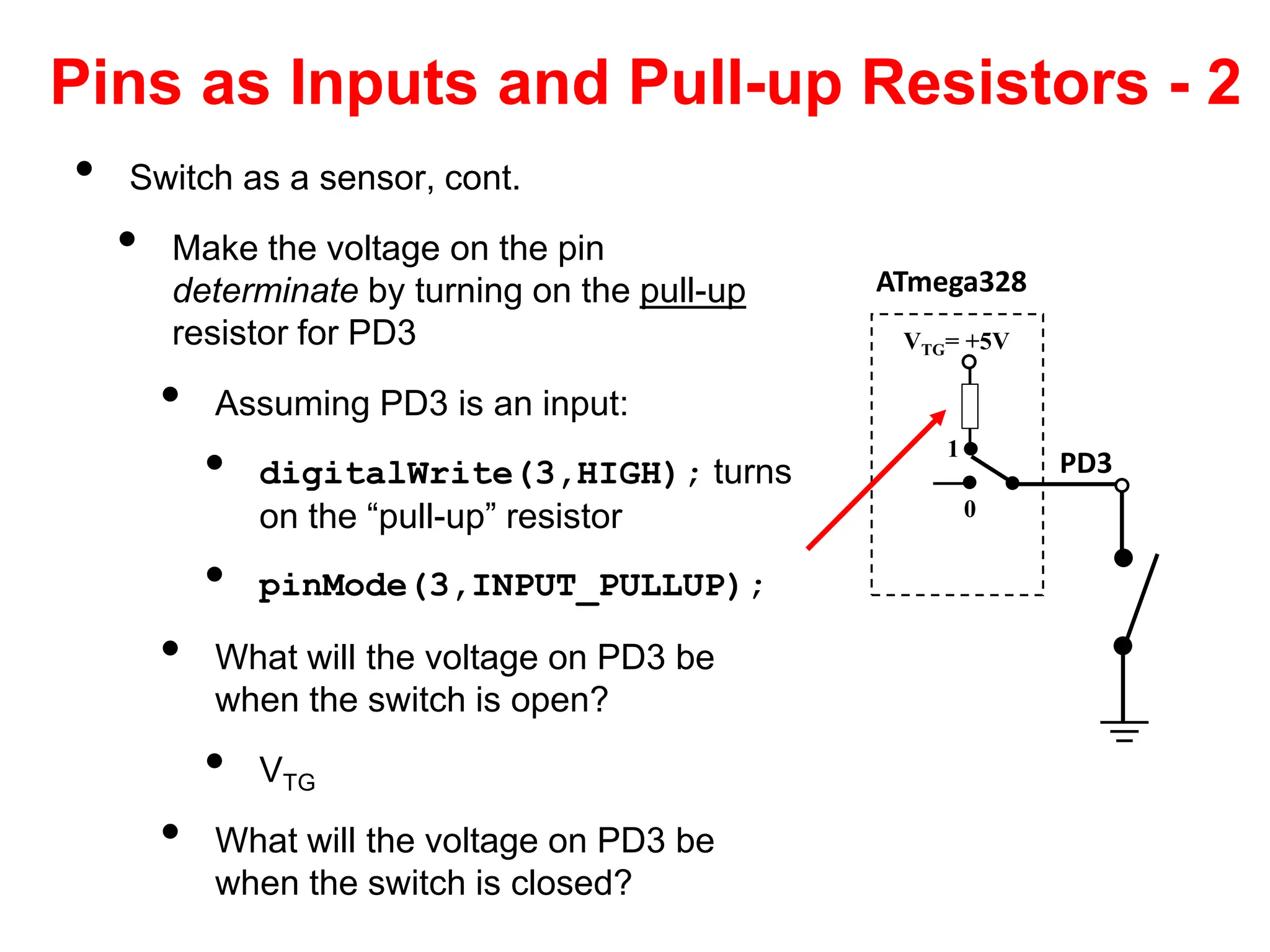
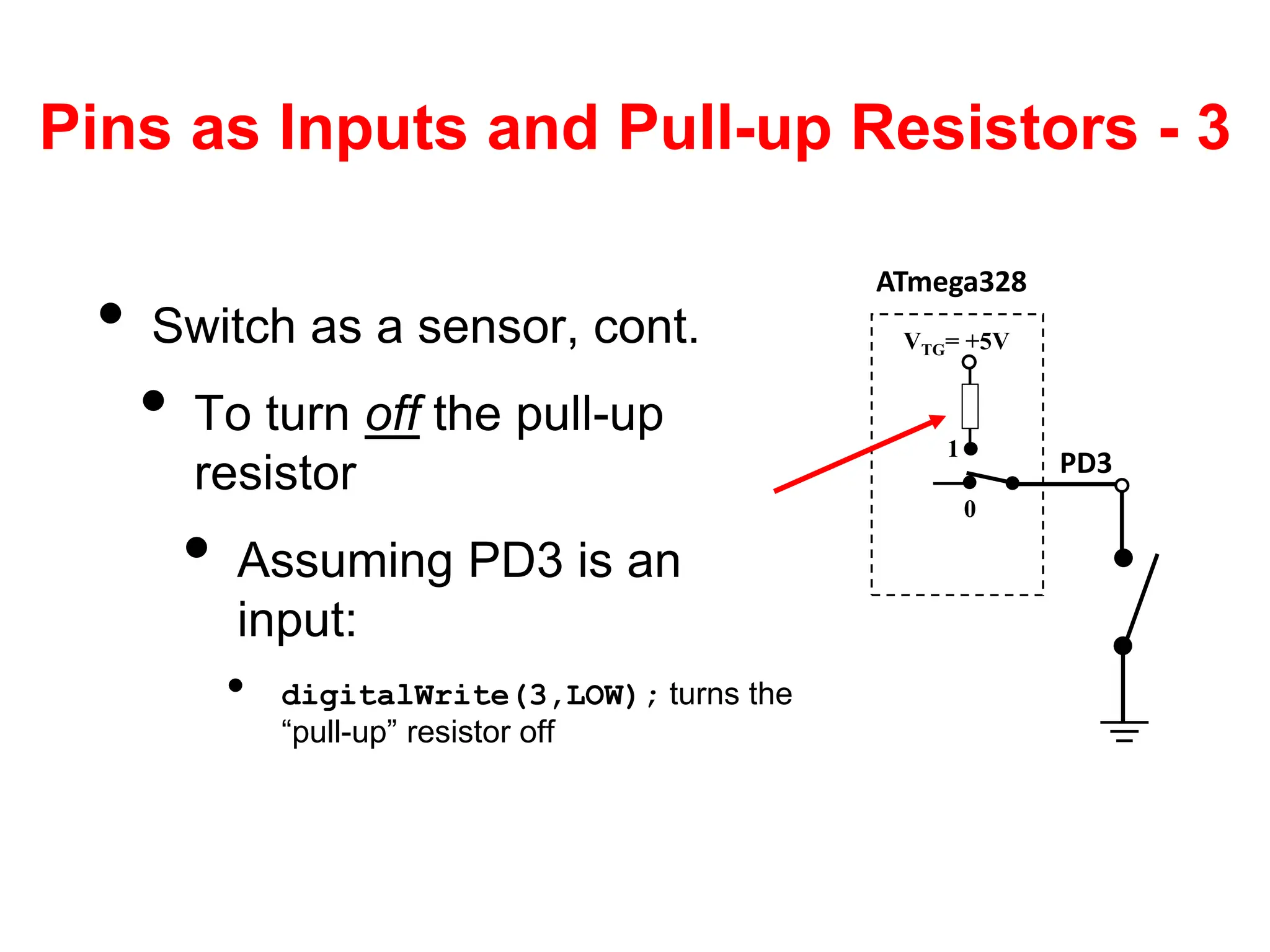
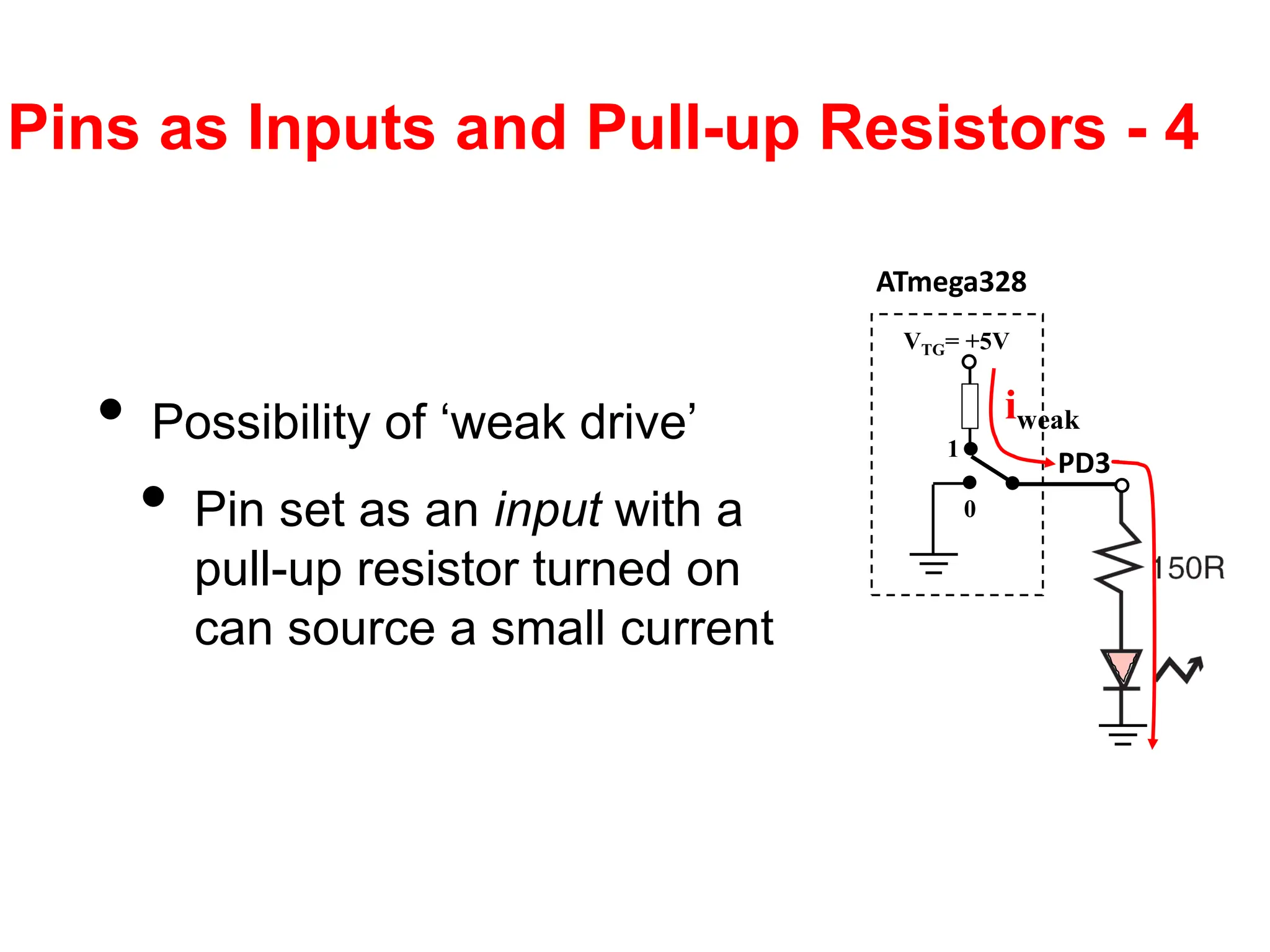
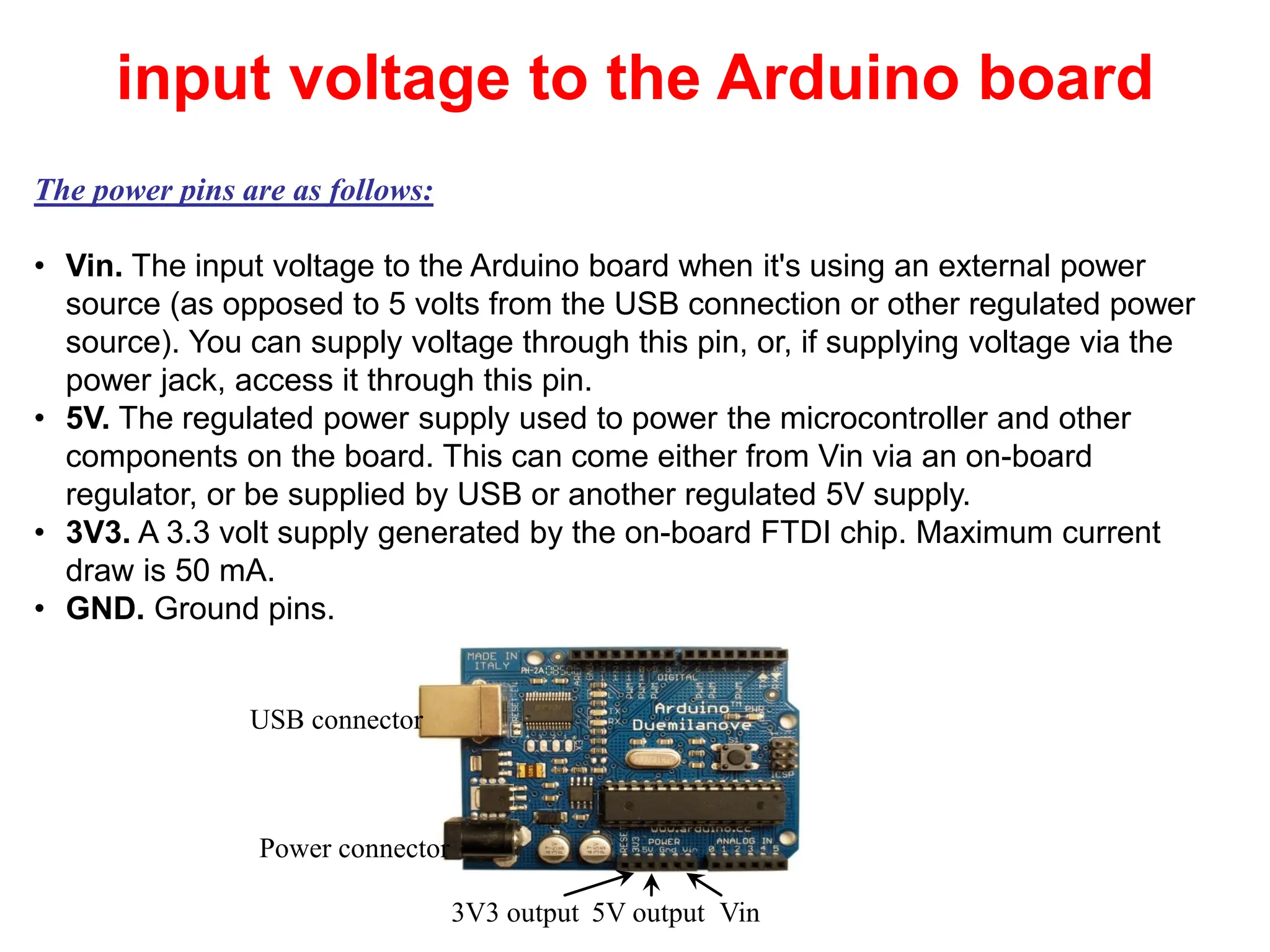
The document provides an overview of the Arduino development board, including necessary components like USB cables and software, as well as its functionalities like digital and analog input/output pins. It details various Arduino types, terminology, and optional hardware components, highlighting the open-source nature of its design. Key technical specifications and coding examples illustrate how to interact with the board's components and manage inputs and outputs.