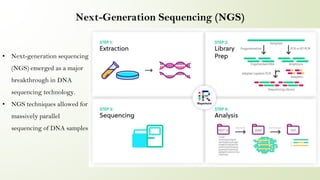
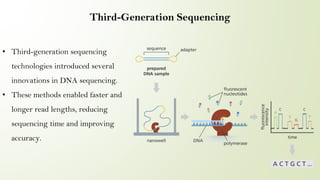
This presentation discusses the development of DNA sequencing technology from early techniques to current and future innovations. It covers early methods like Maxam-Gilbert and Sanger sequencing that involved chemical modifications and gel electrophoresis. Next-generation sequencing allowed for massively parallel sequencing and fueled projects like the Human Genome Project. Third-generation techniques enabled faster, longer reads. Advancements have increased accuracy and speed while expanding applications in medicine, agriculture, and more. The future holds potential for sequencing that is faster, cheaper and more accessible to further genomic research.