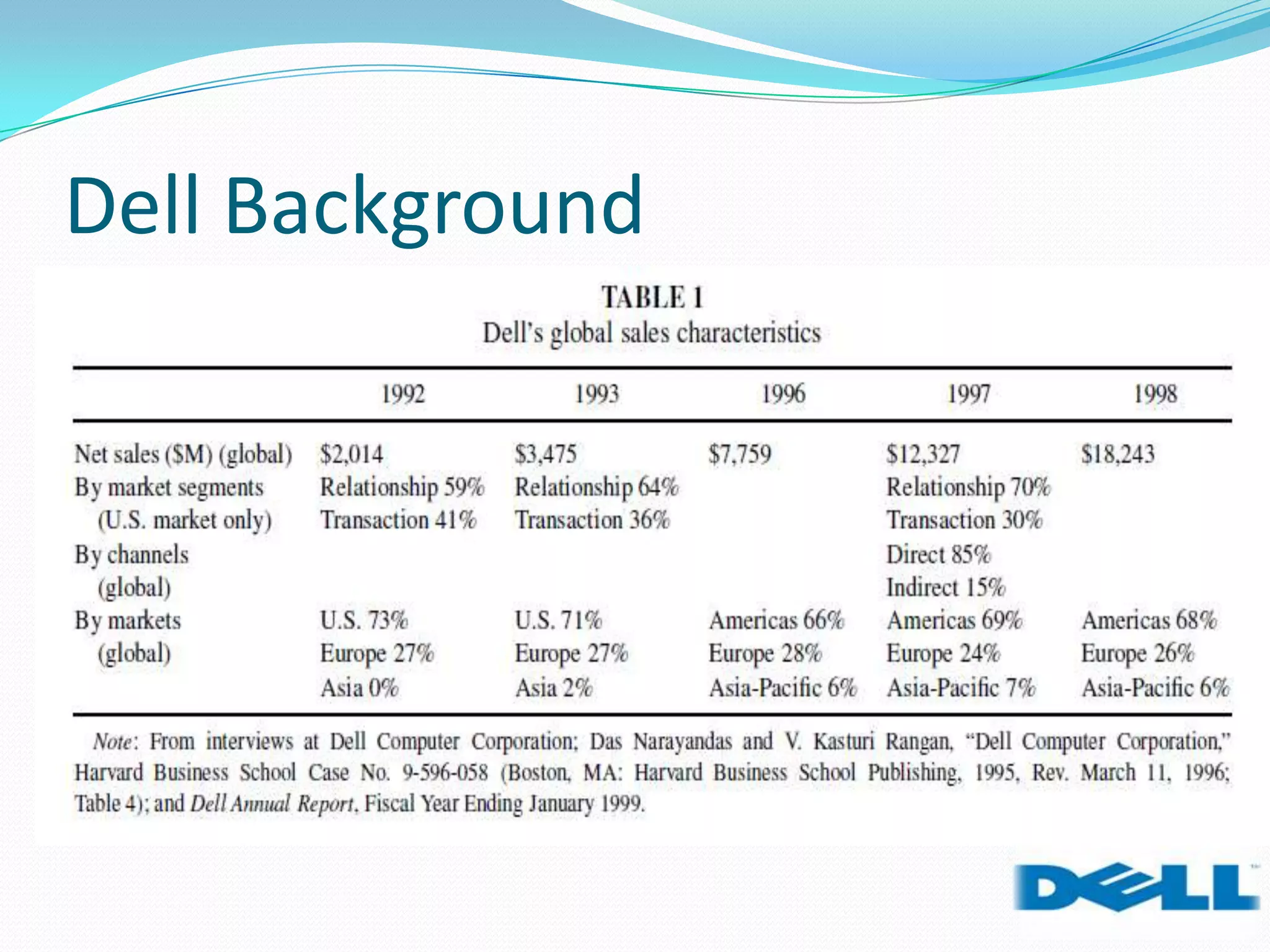
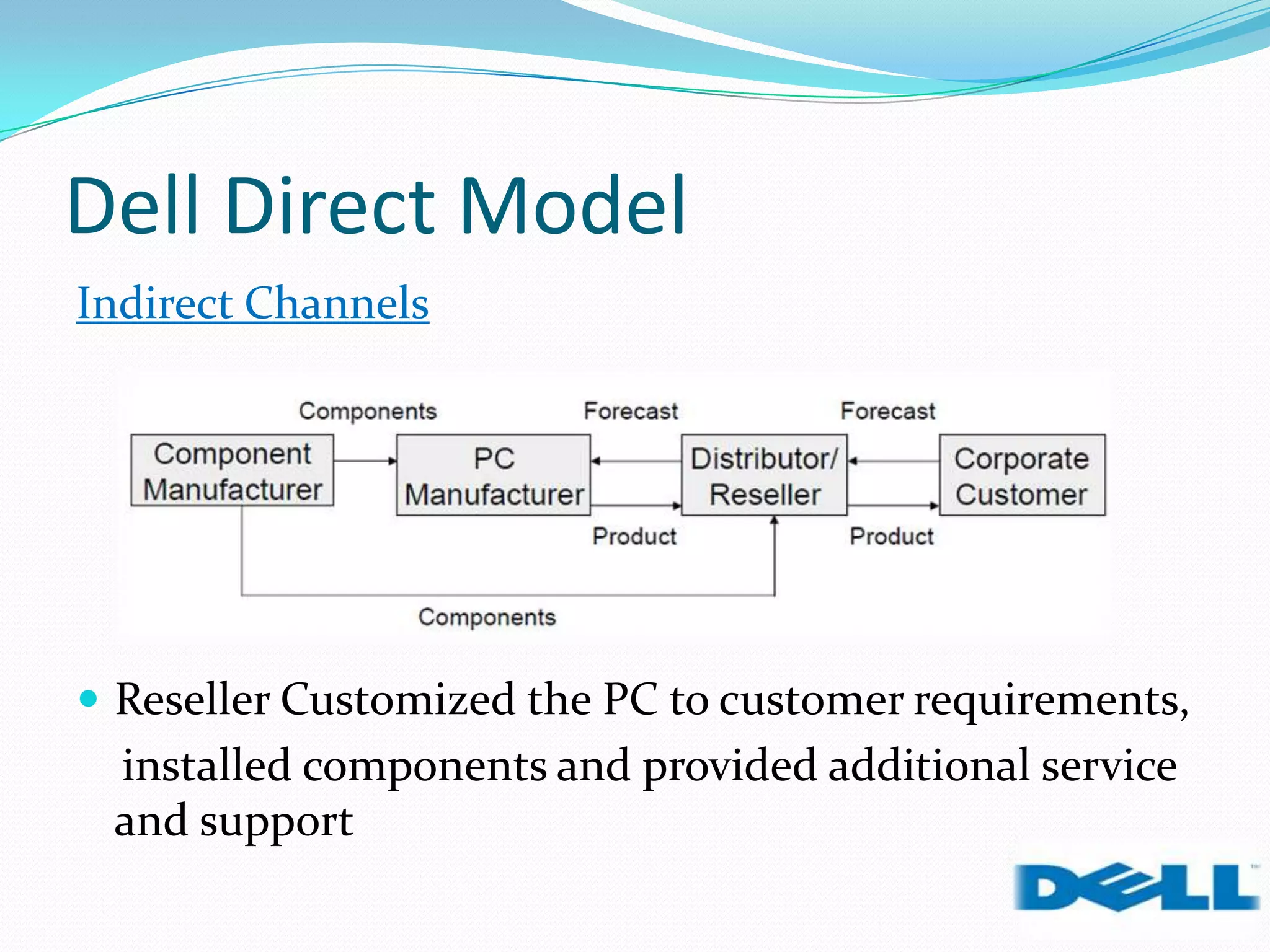
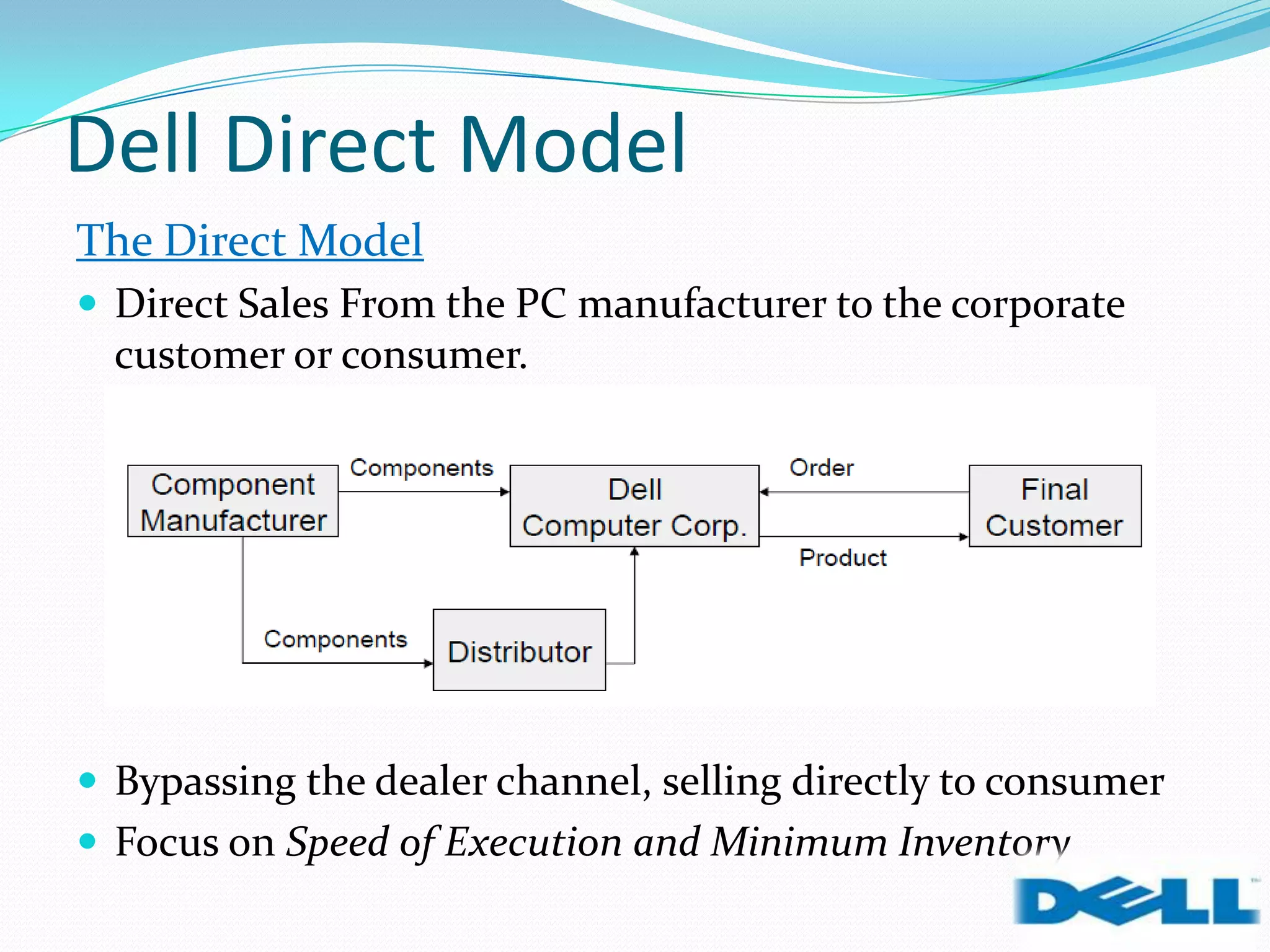
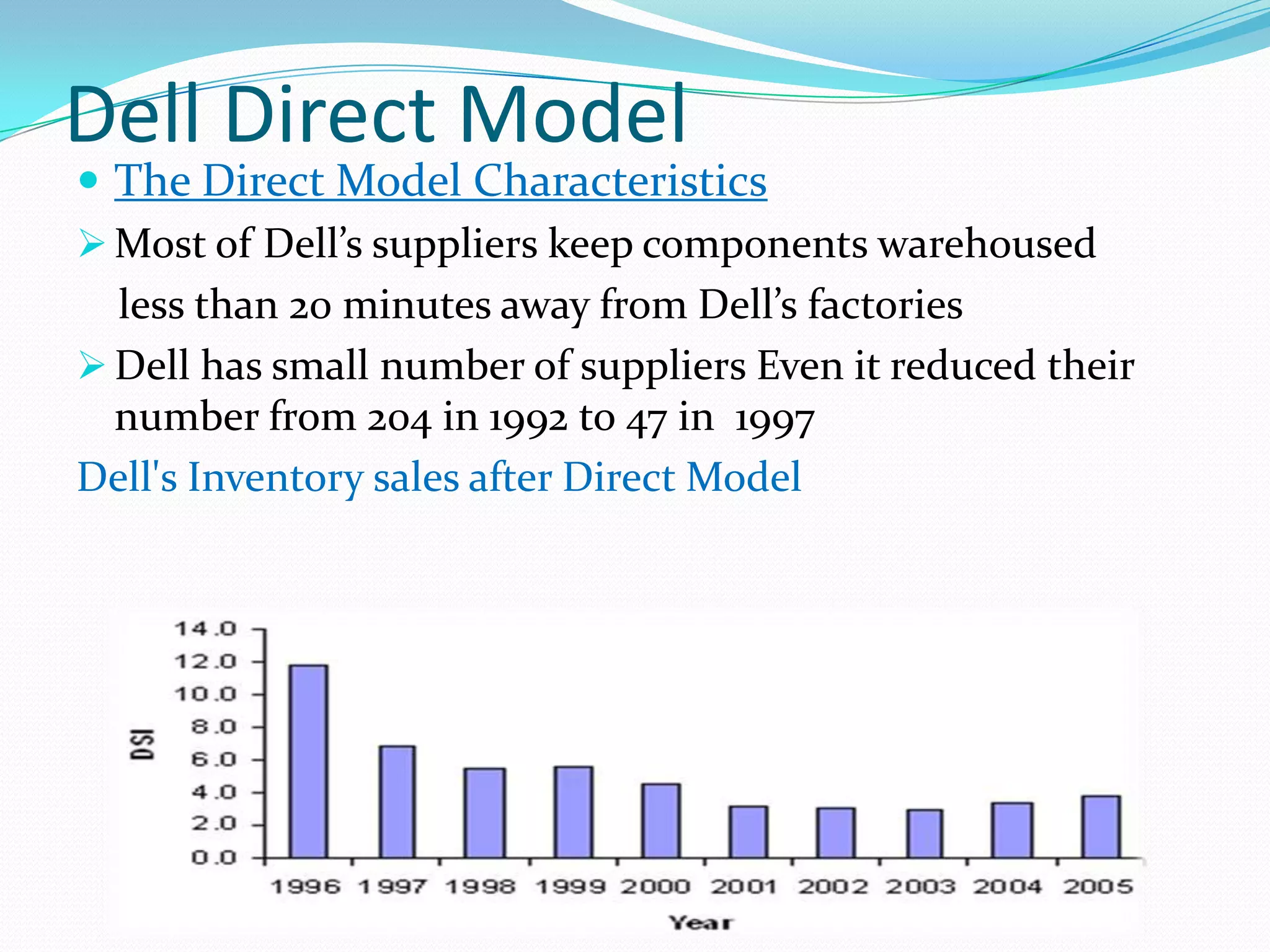
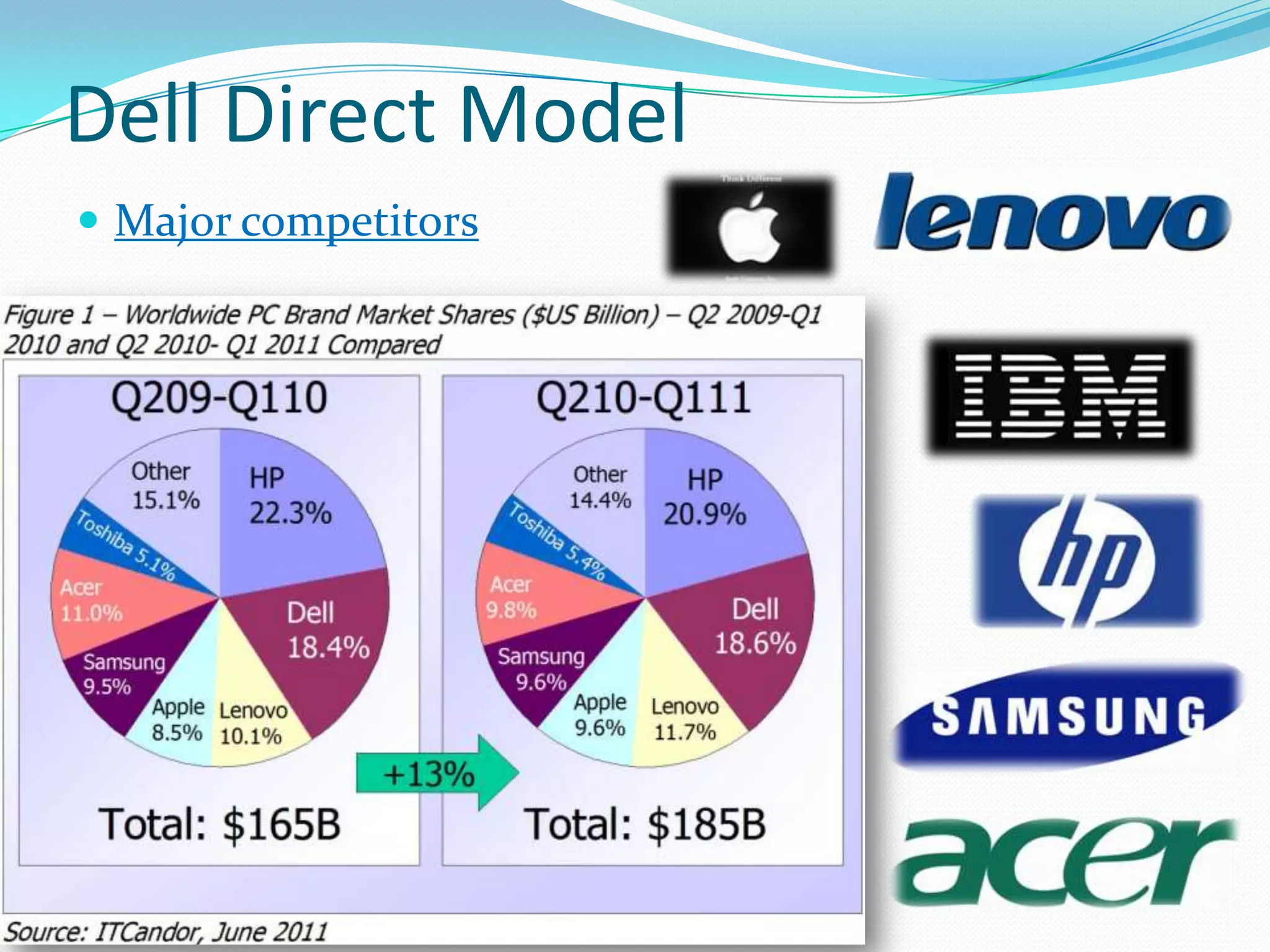
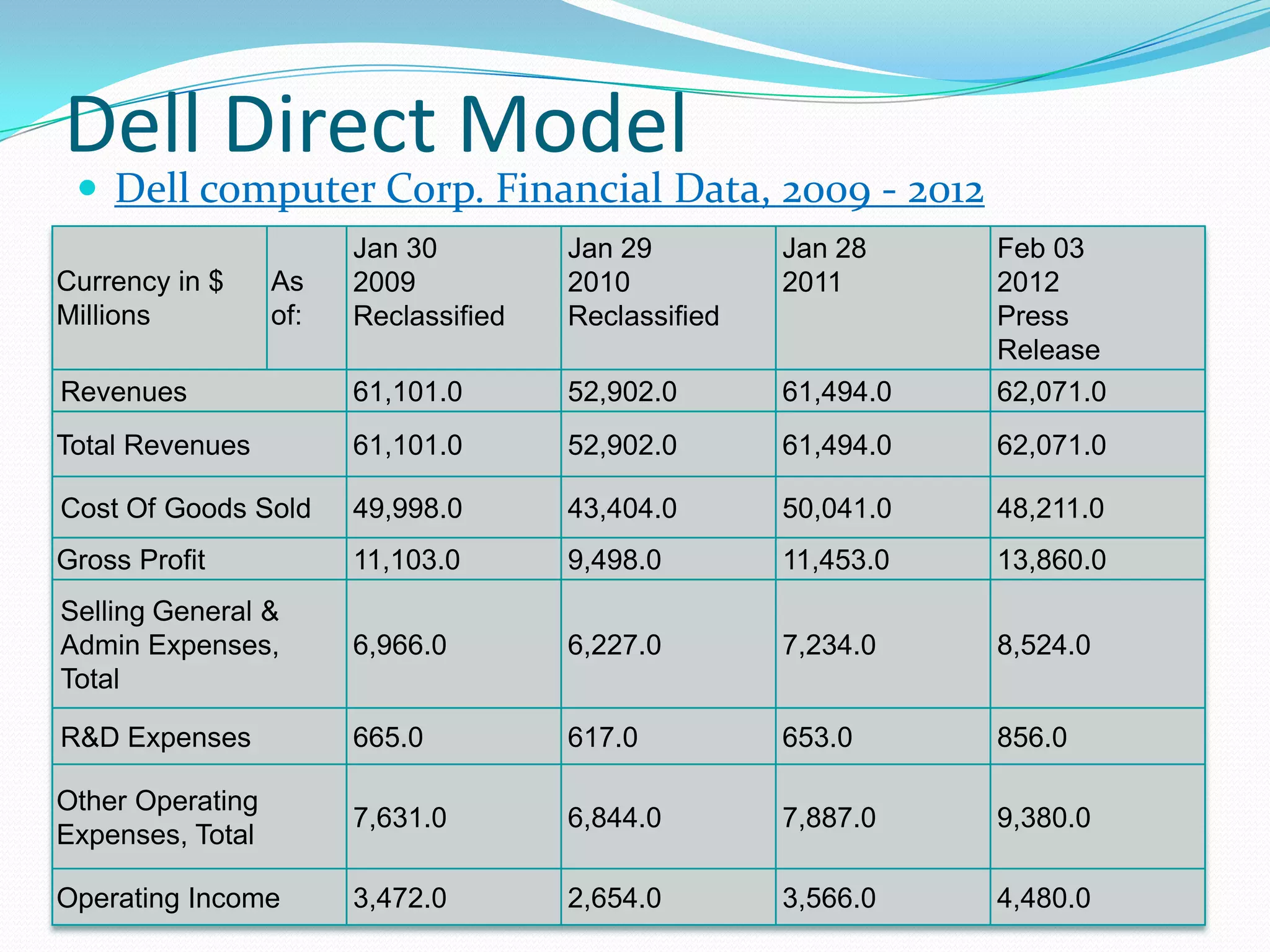
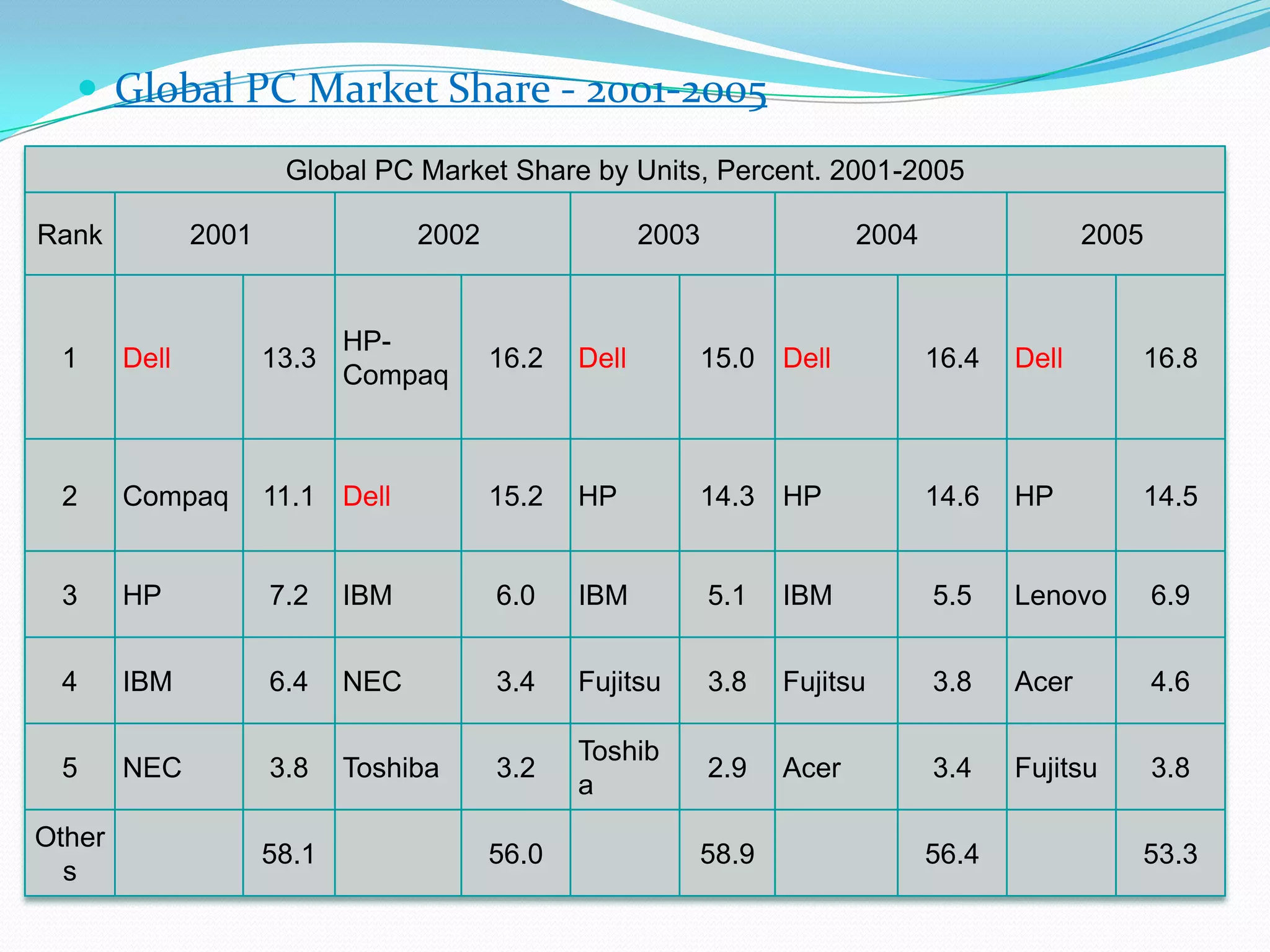
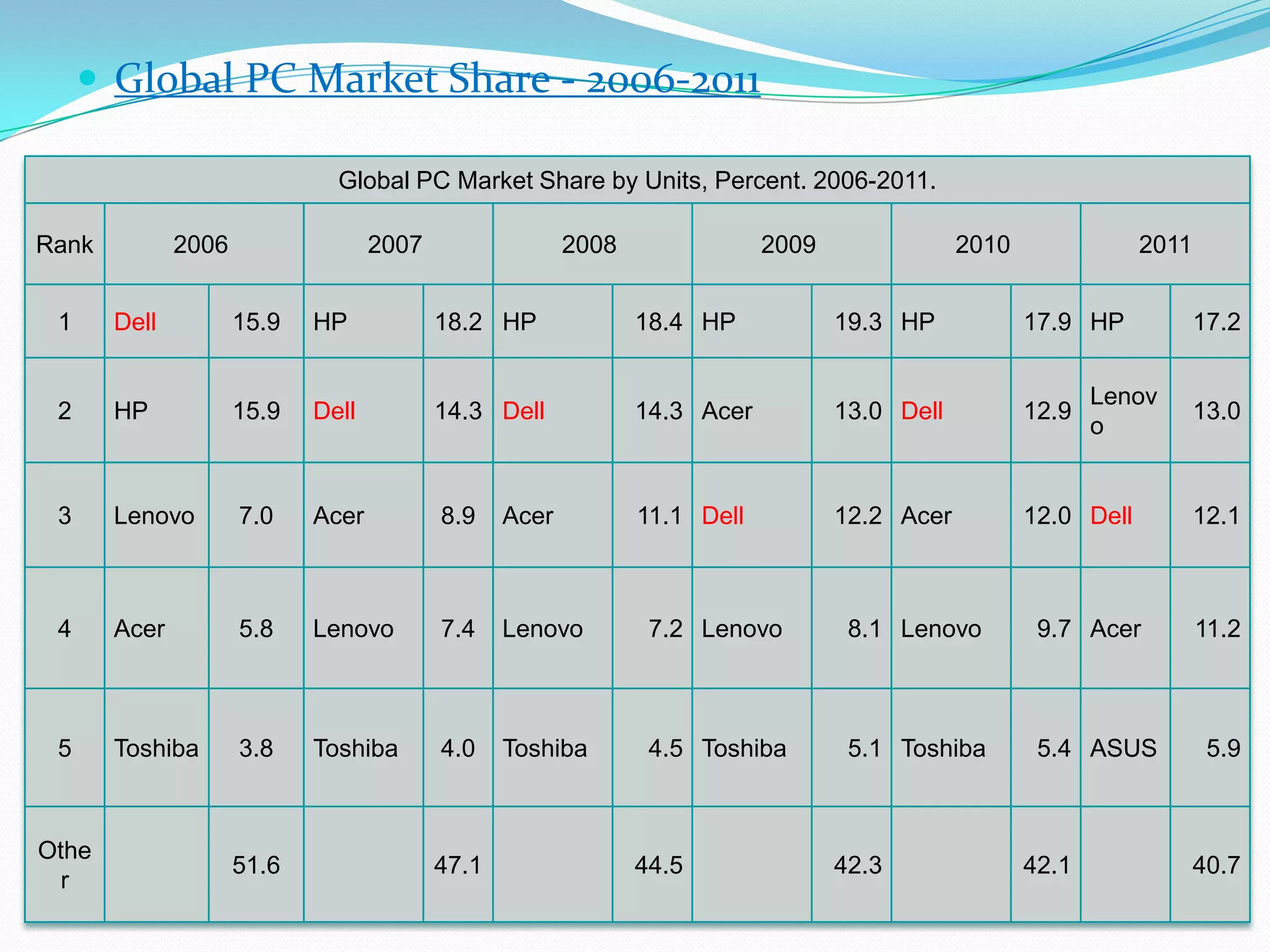
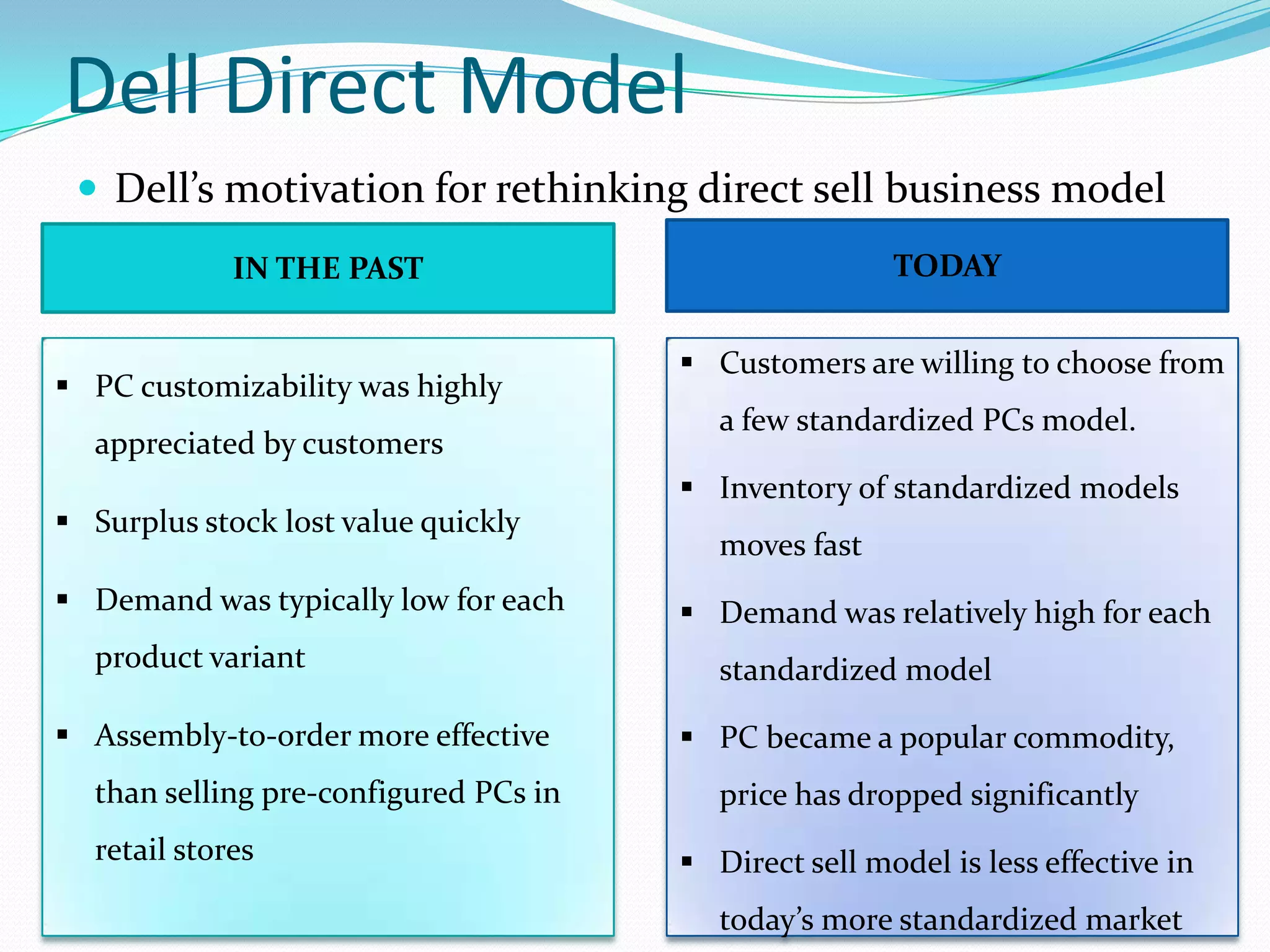
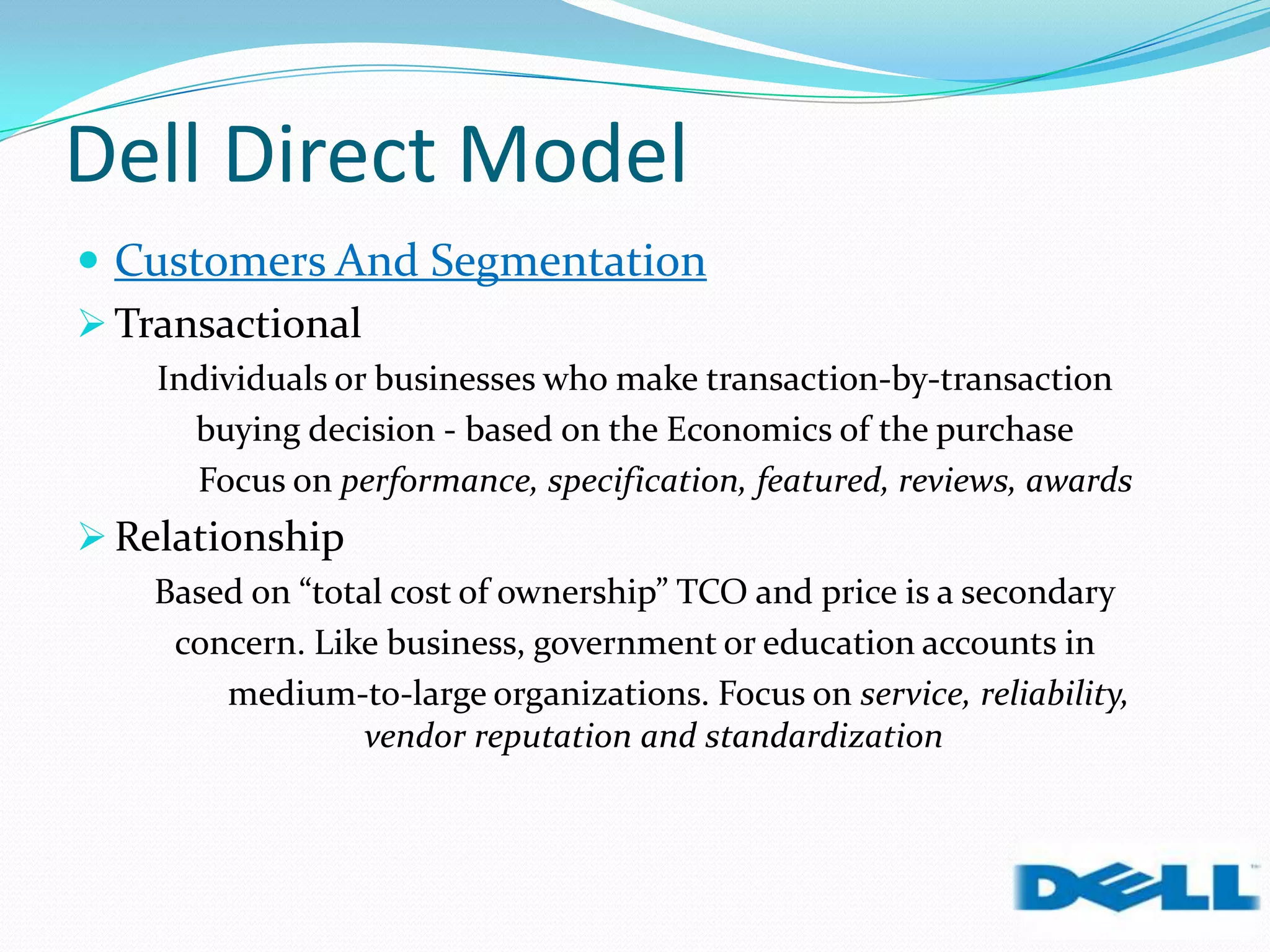
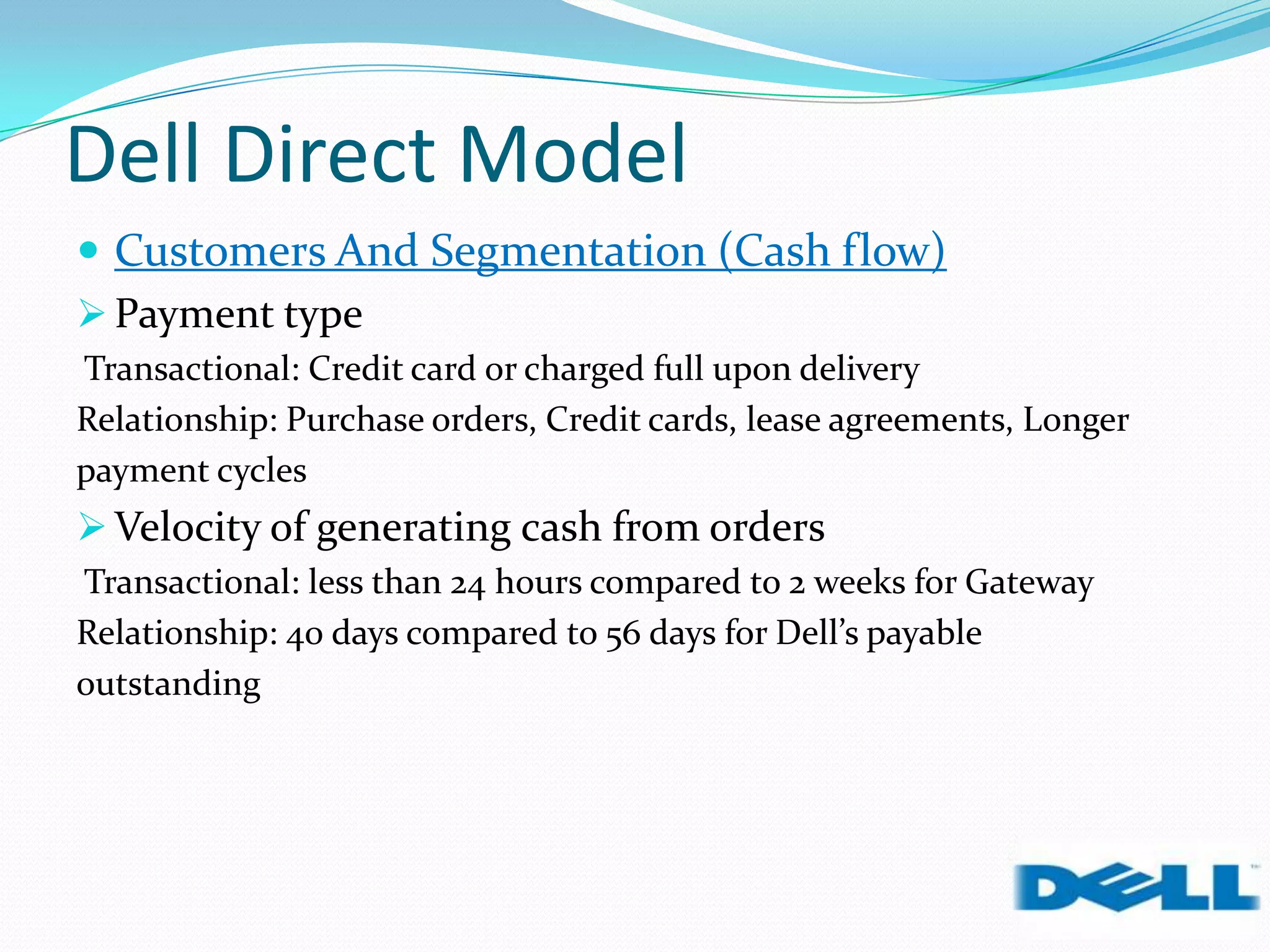
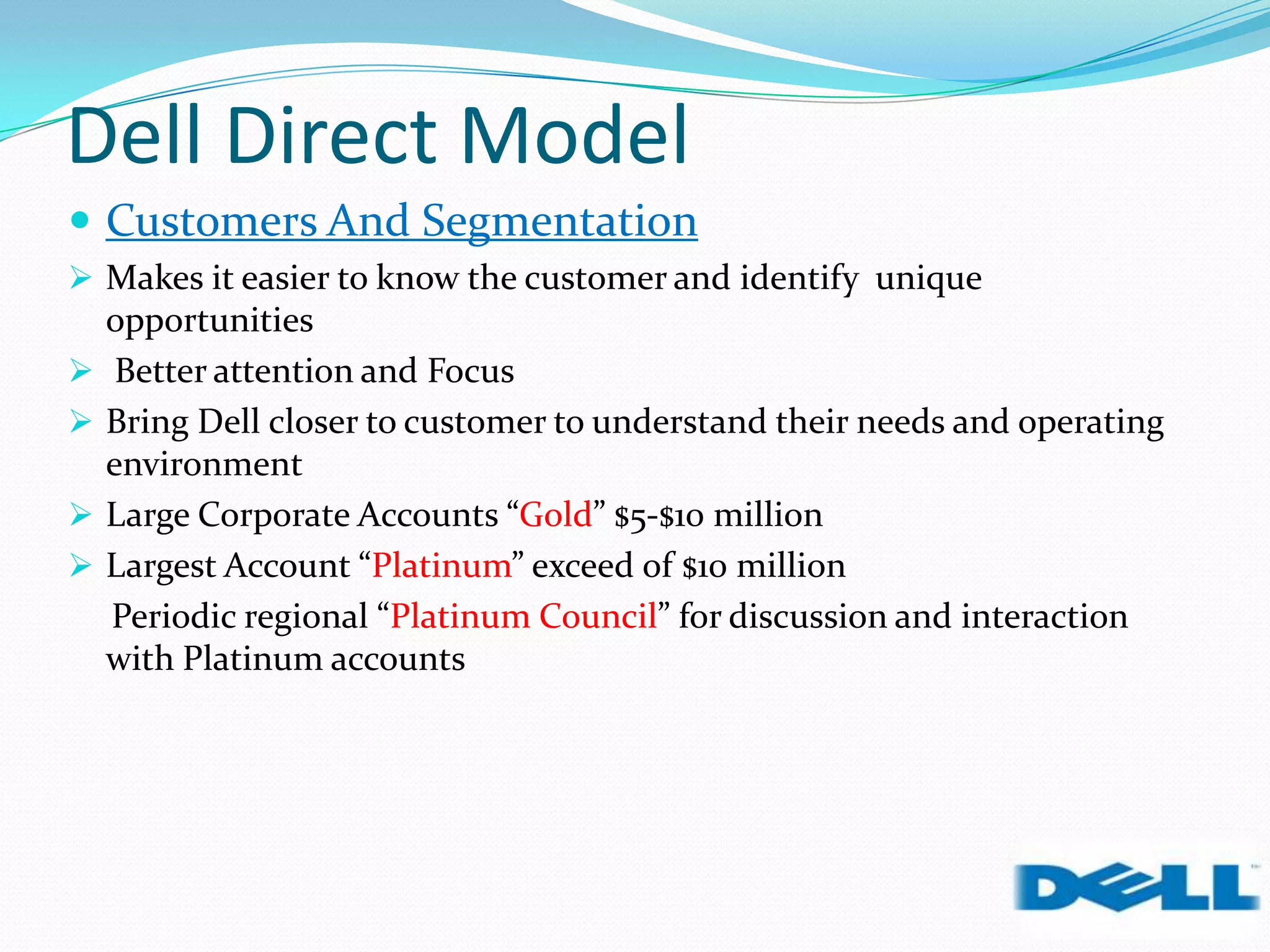
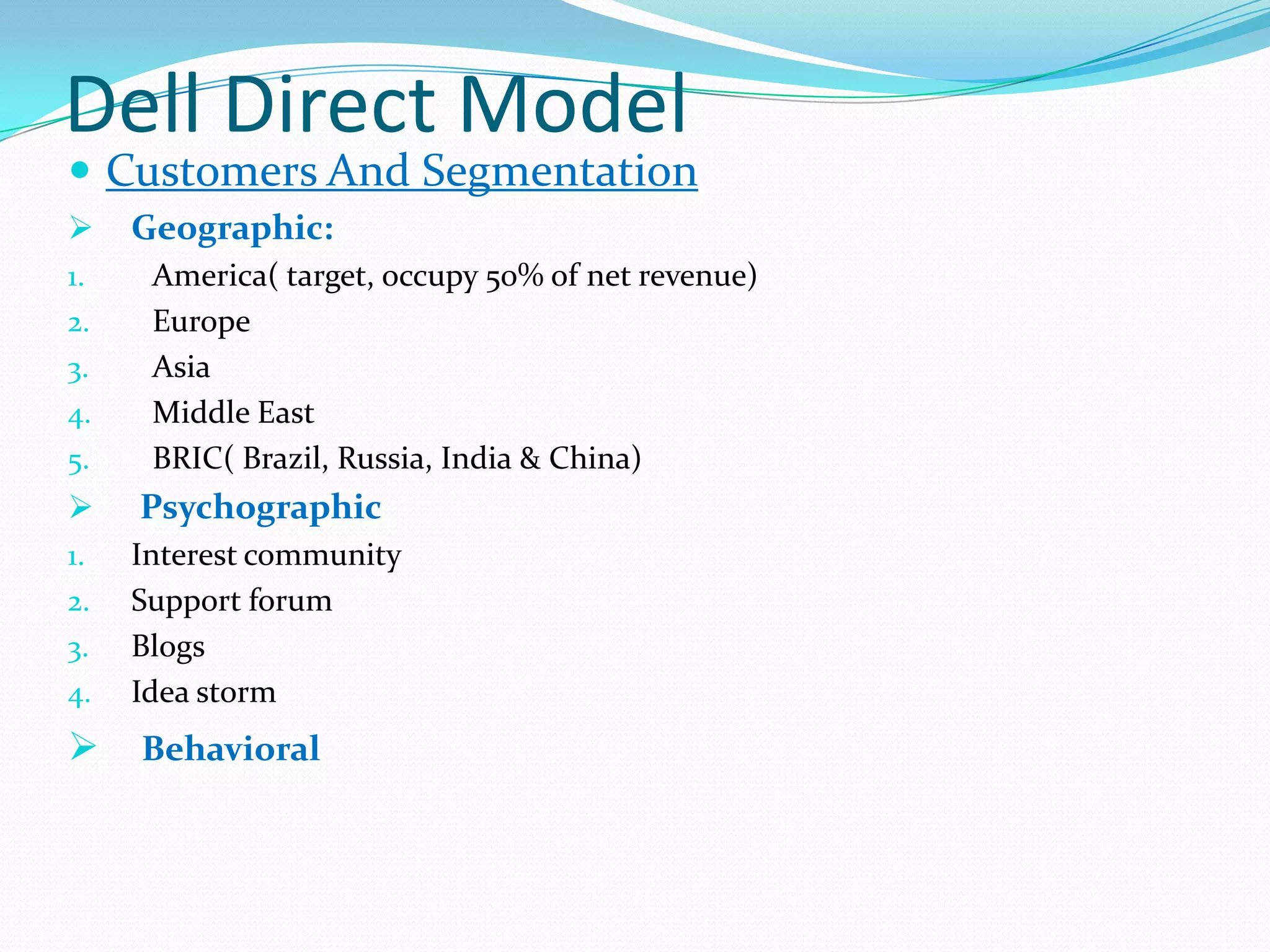
Dell grew rapidly from its founding in 1984 by directly selling custom-built PCs to customers. Dell's direct sales model eliminated inventory costs and reseller margins, allowing it to produce PCs in a matter of hours. Dell used IT to closely coordinate its operations and supply chain. This efficient build-to-order process and high-quality customer service supported Dell's rise to become the largest PC maker in the world in the late 1990s and early 2000s.