This document discusses Indonesia's railway transport policy environment and plans for reform. It covers:
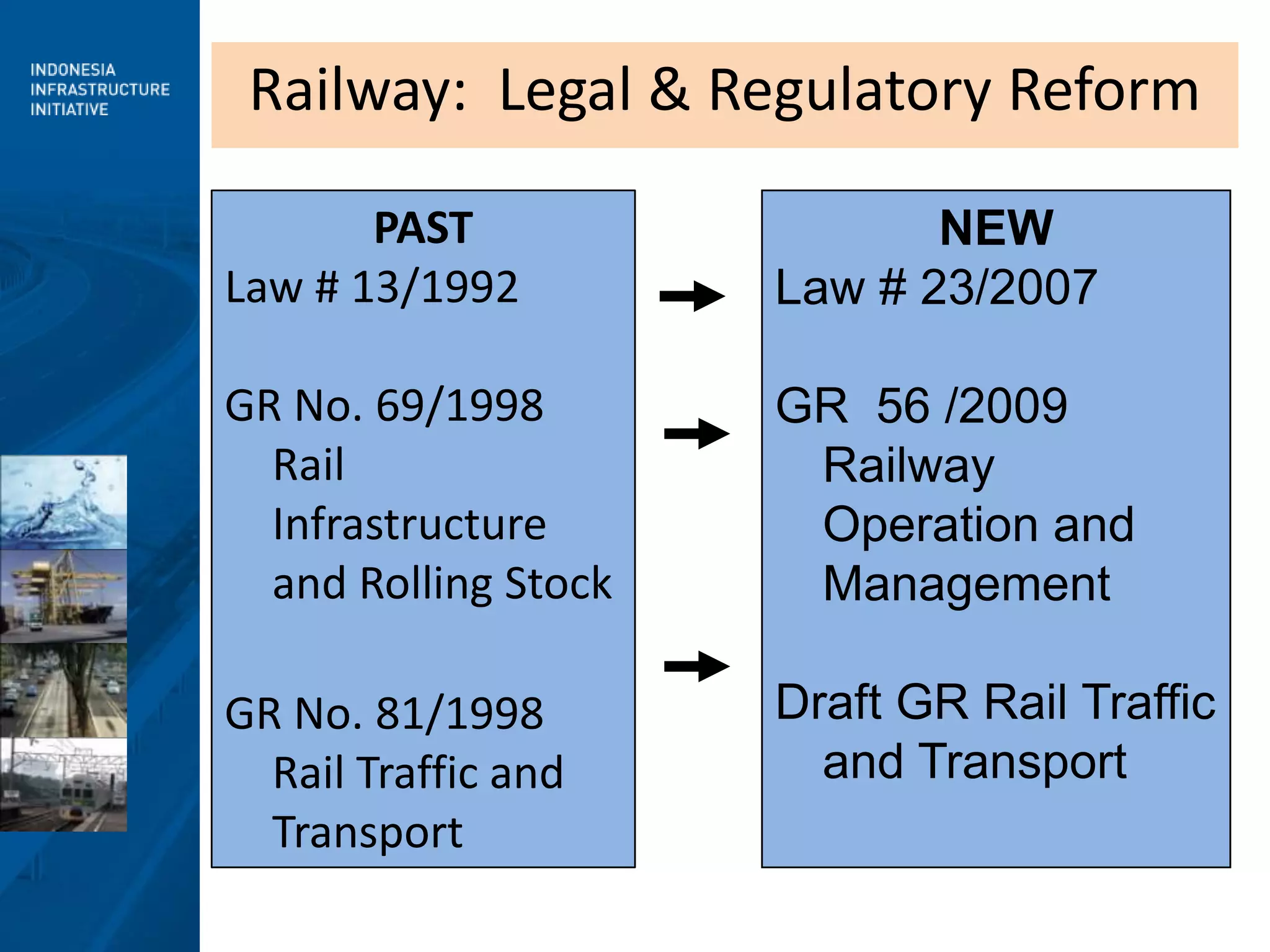
1) Law 23/2007, which aims to reform the railway sector by opening it to greater private sector participation and competition, and establishing clearer regulations.
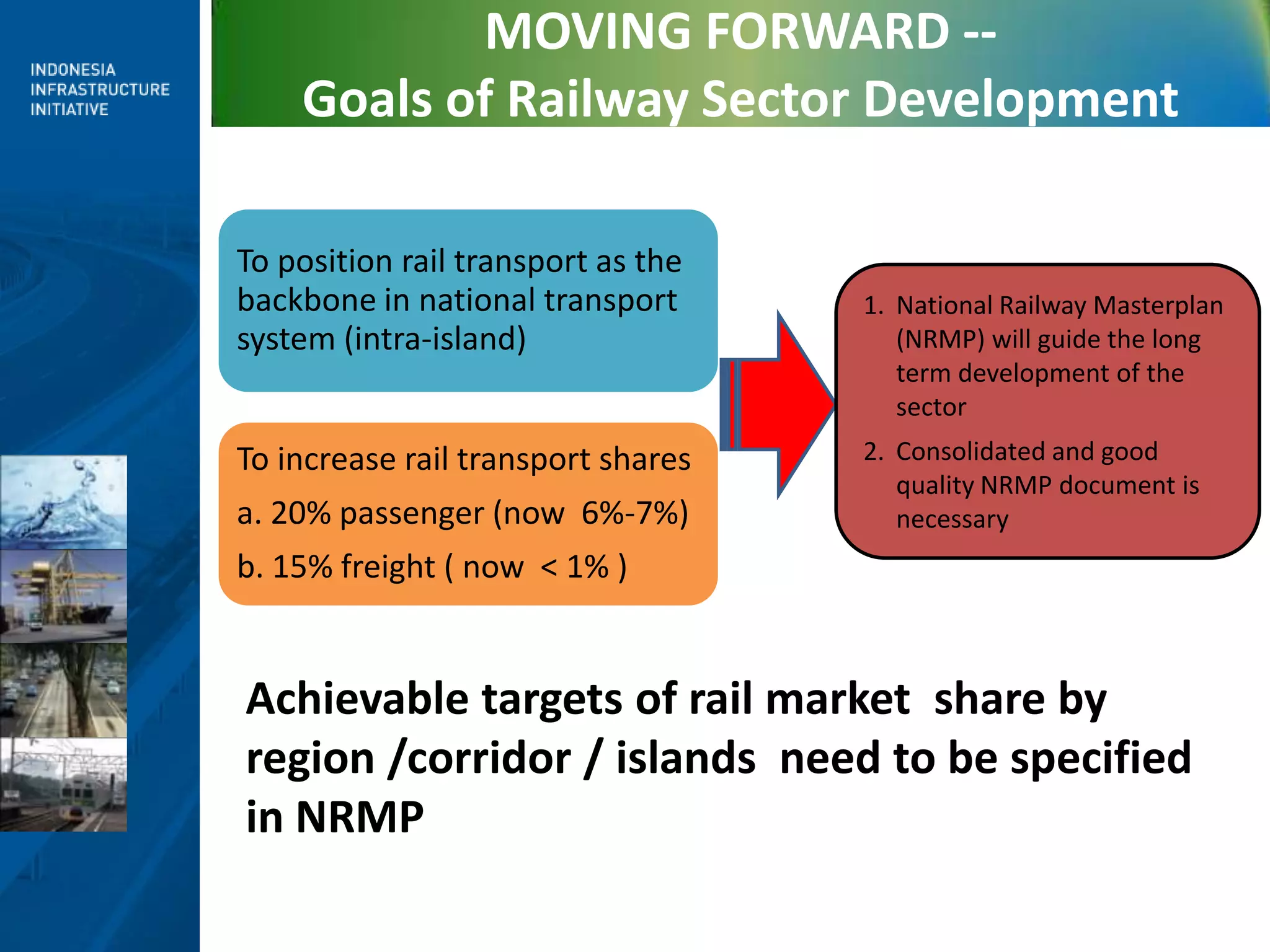
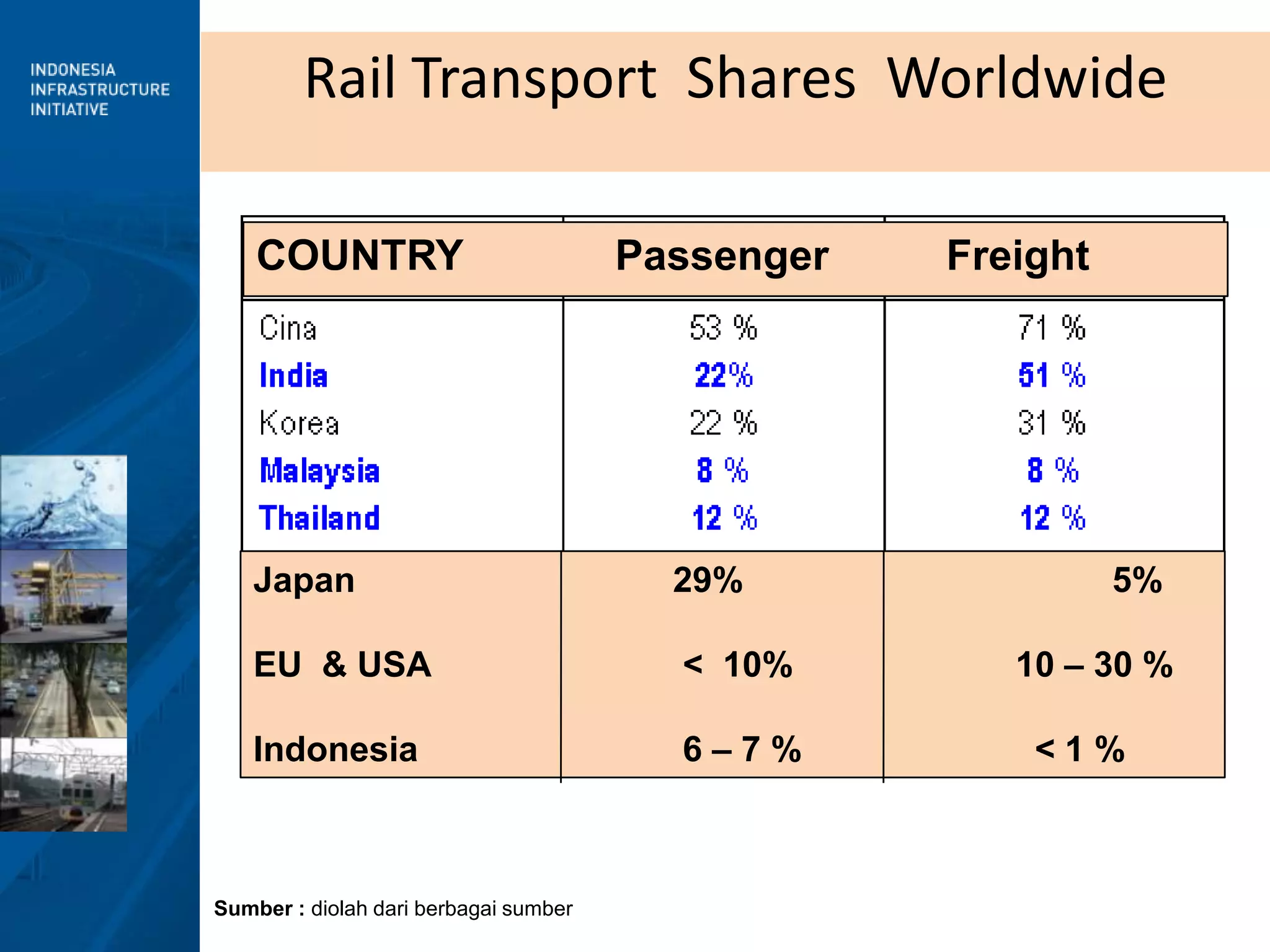
2) The goals of reform include improving efficiency, promoting investment, and increasing rail's mode share for both passenger and freight transport.
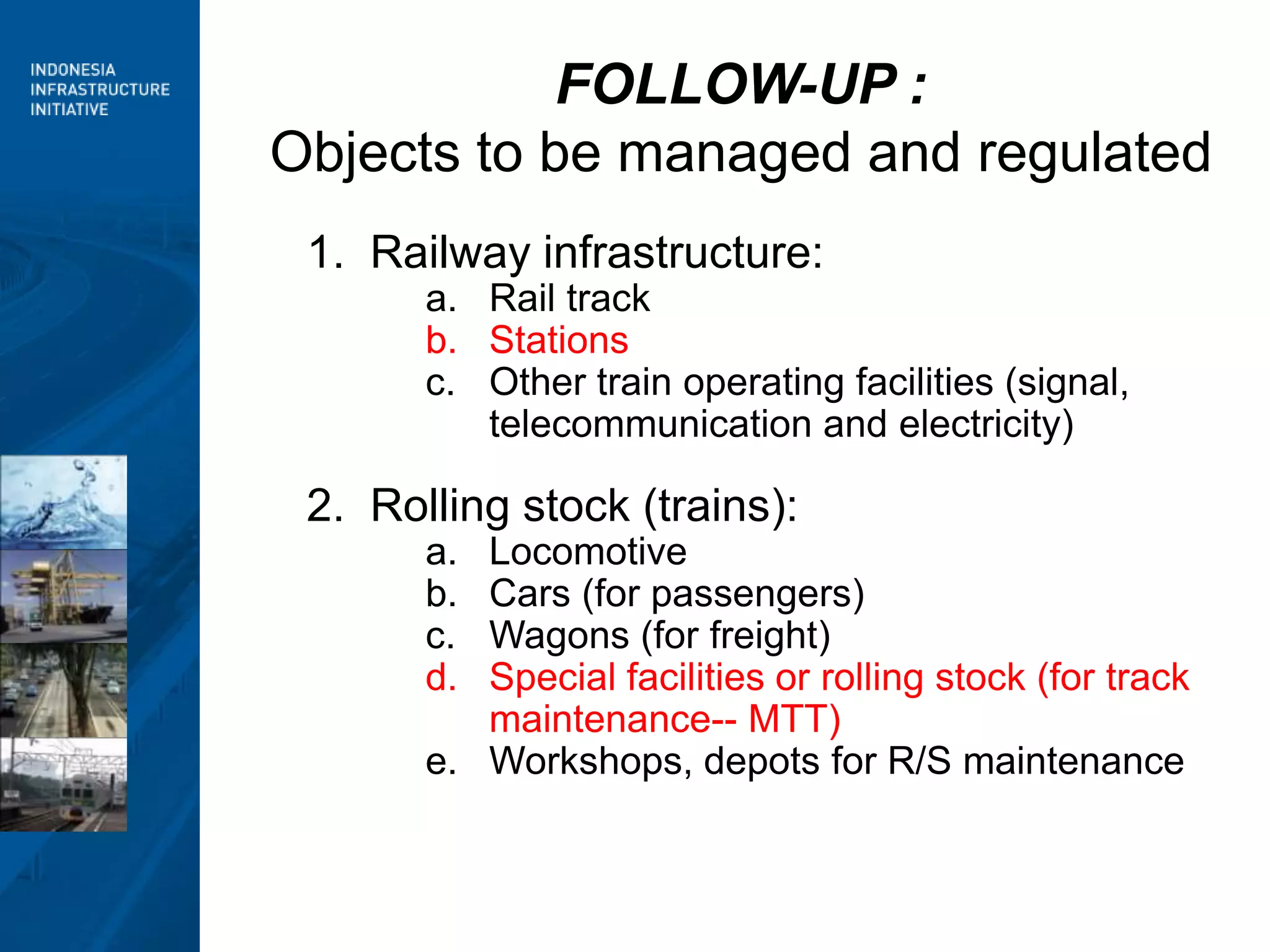
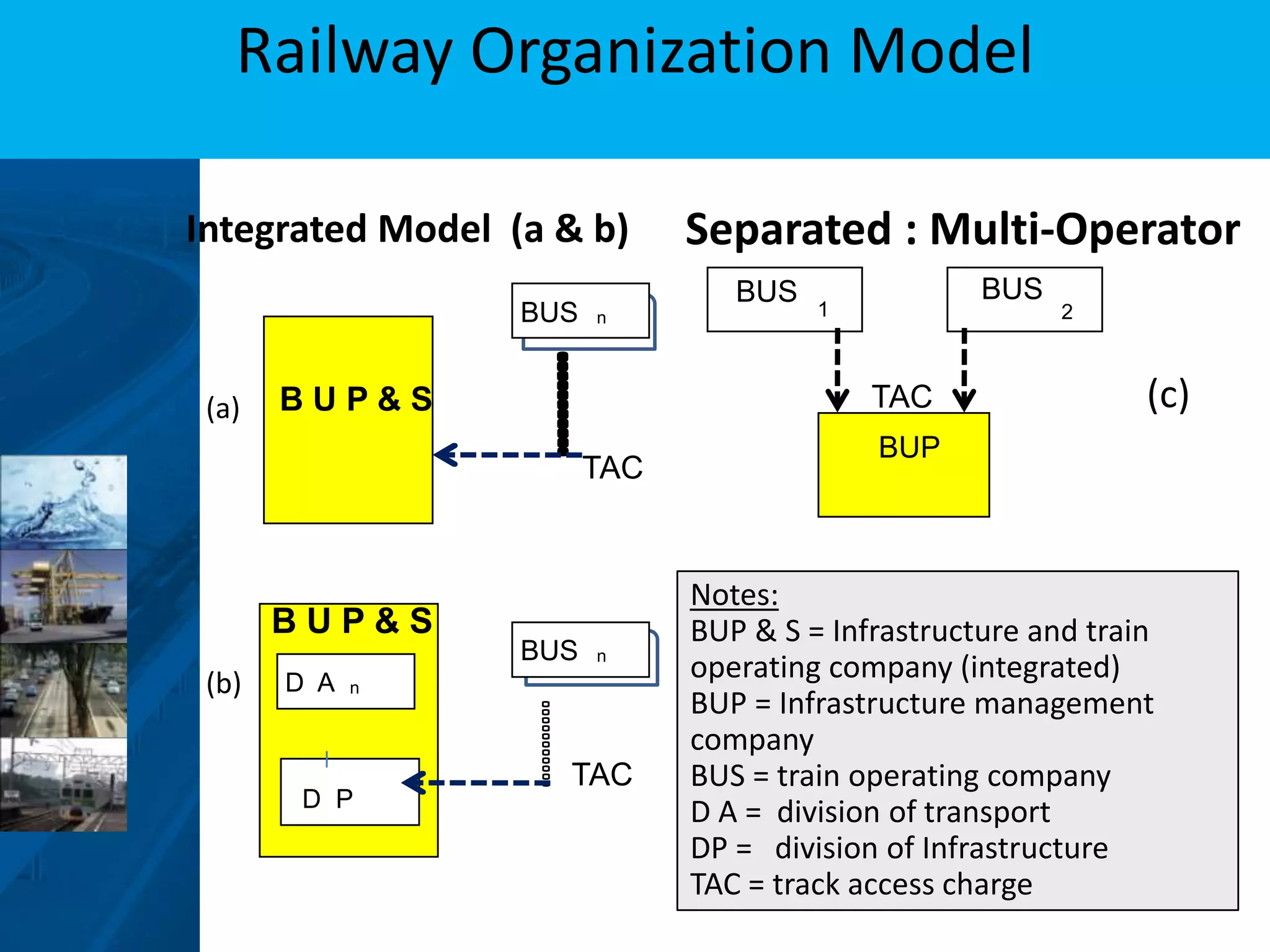
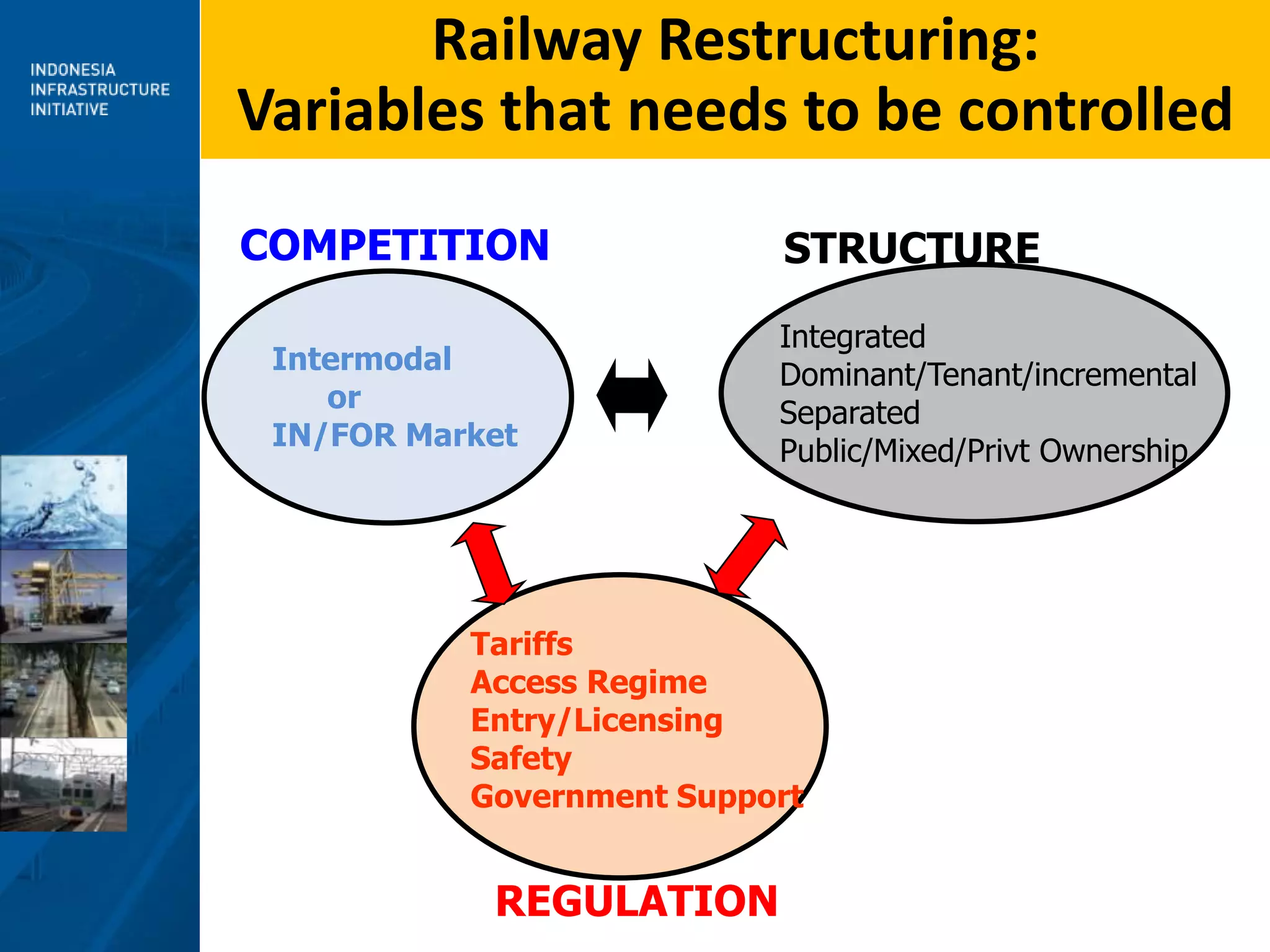
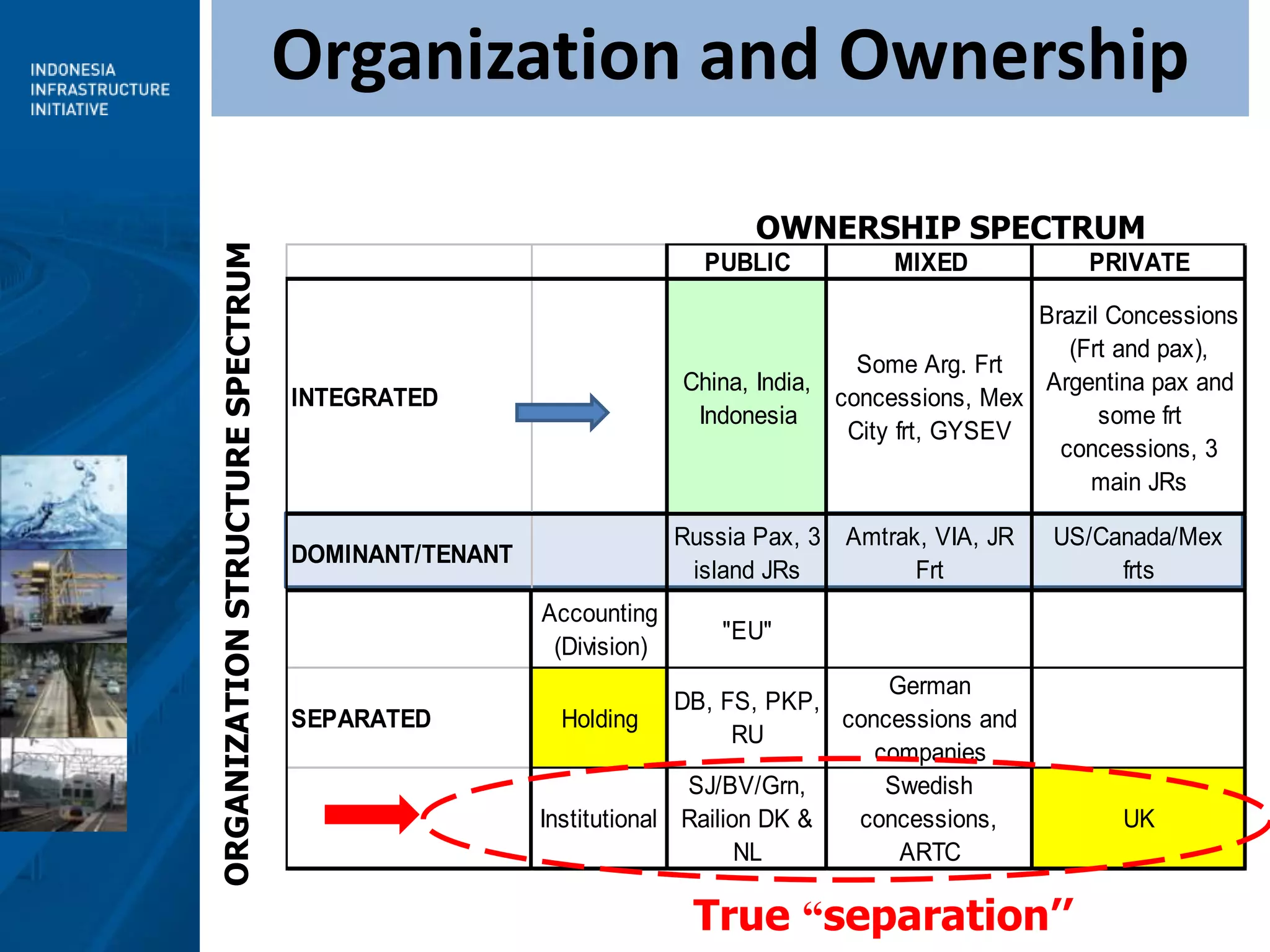
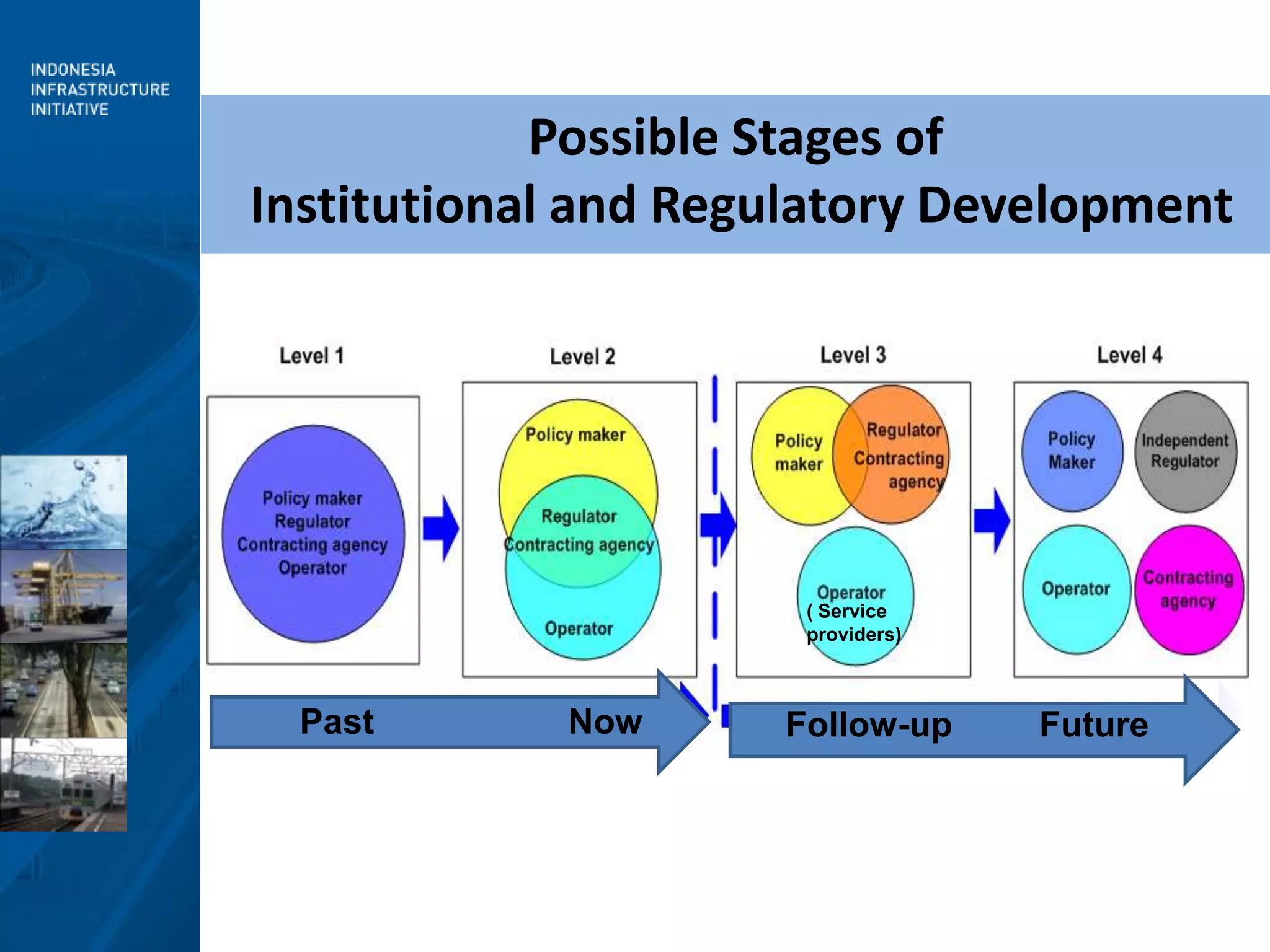
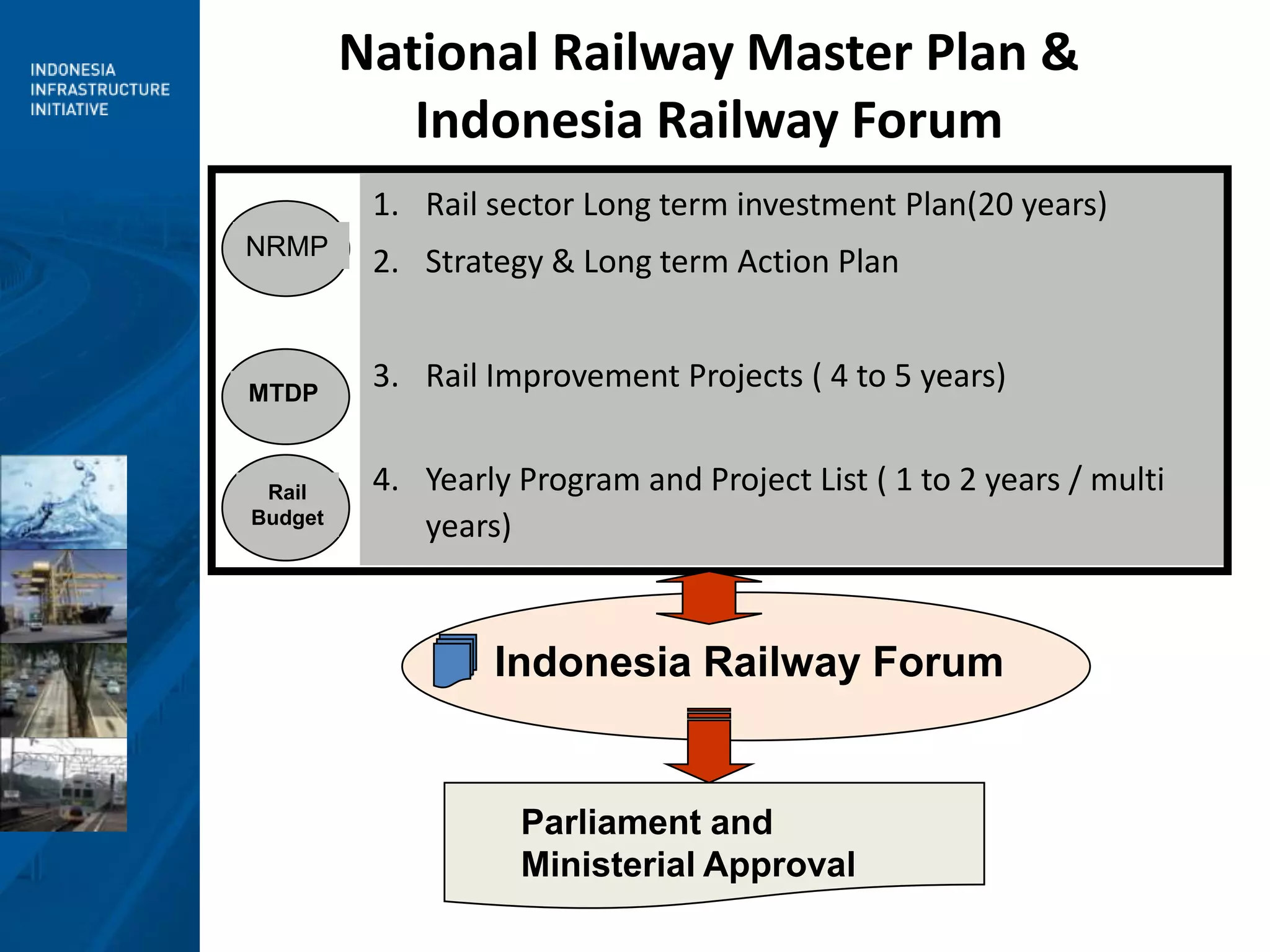
3) Moving forward, a National Railway Masterplan will guide long-term development, including setting achievable targets for rail market share. Institutional restructuring options are also discussed to separate regulatory and operating functions.