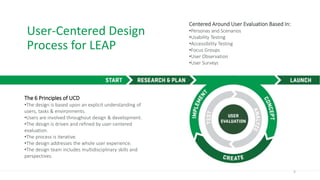
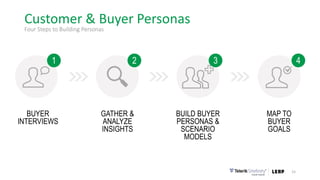
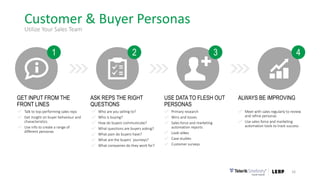
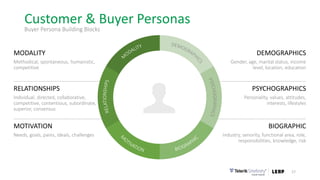
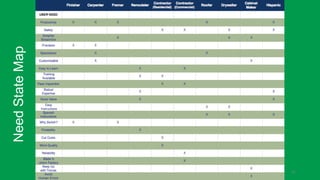
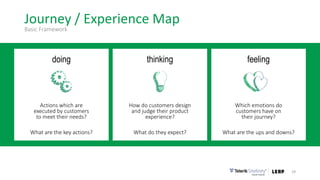
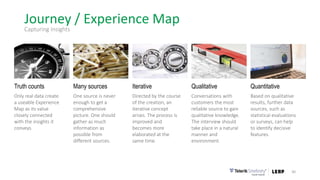
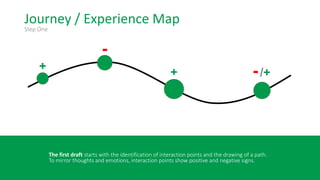
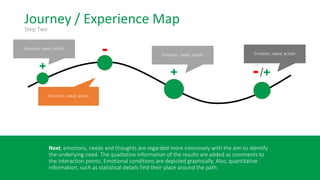
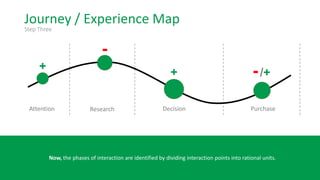
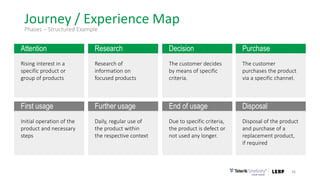
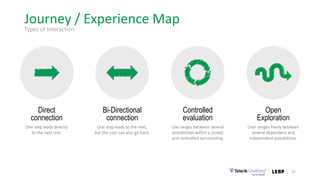
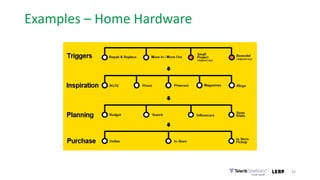
This document discusses the consumer journey and how understanding it through personas and journey mapping can improve marketing outcomes. It provides an overview of user-centered design principles and outlines the benefits of creating buyer personas to understand different customer types. The key aspects of building personas like gathering insights and utilizing sales teams are described. Examples of personas are also presented. Finally, the document discusses how to create journey maps by mapping the customer path and identifying touchpoints, emotions, and opportunities for improvement.