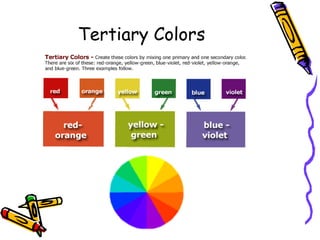
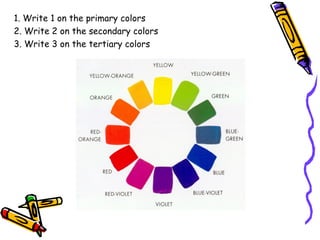
The document provides an overview of the history and theory of the color wheel. It discusses how Sir Isaac Newton first developed the color wheel by splitting white light into a visible spectrum using a prism. Johannes Itten later modified Newton's color wheel, basing it on red, yellow, and blue primary colors with twelve total hues. The document also outlines some cultural, political, and religious associations that different colors can have.